Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-050415-1
- Publication
- Uemura et al., 2005 - Comparative functional genomics revealed conservation and diversification of three enhancers of the isl1 gene for motor and sensory neuron-specific expression
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
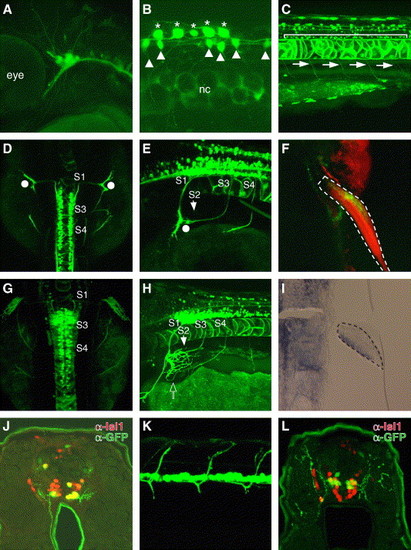
Sensory and motor neuron-specific GFP expression driven by zCREST2 in stable transgenic zebrafish. zCREST2 drives GFP expression both in the primary sensory neurons and in subsets of motor neurons innervating the ventral trunk muscles and the abductor pectoral fin muscle in transgenic zebrafish embryos. (A?E, G, and H) Lateral (A?C, E, and H) and dorsal (D and G) views of Tg(zCREST2-hsp70:GFP)rw011 embryos. At 36 hpf, GFP expression was observed in the trigeminal ganglion neurons (A) and in Rohon-Beard neurons (asterisks in B). GFP expression was detected in other tissues, such as the notochord and some commissural interneurons in the spinal cord (arrowheads). nc, notochord. (C) GFP was expressed in the spinal motor neurons (bracket) that project their axons ventrally (arrows) by 72 hpf. (D, E, G, and H) The GFP-positive fin motor neurons were distributed from the spinal segment 1 (S1) through 4 (S4), as described for Medaka fish embryos (Okamoto and Kuwada, 1991). (D and E) At 54 hpf, the GFP-positive fin motor nerves from S1 to S3 had reached the base of the fin bud without entering (white dots). Meanwhile, the nerve from S4 was still extending toward the fin bud. (G and H) By 72 hpf, the GFP-positive nerves from S1 to S3 had completely converged and entered the pectoral fin at the dorsal end of its base, while the nerve from S4 had entered at the opposite end (open arrow). (F) Ventral view of the 120-hpf Tg(zCREST2-hsp70:GFP)rw011 embryo stained with rhodamine phalloidin. The GFP-positive fin motor nerves terminated in the abductor pectoral fin muscle. The pectoral fin is enclosed in a broken line. (I) Expression of the lmx1b gene in the adductor pectoral fin muscle of the wild-type 50-hpf embryo. The developing fin bud is enclosed with a broken line. (J) GFP-positive spinal motor neurons in 72-hpf Tg(zCREST2-hsp70:GFP)rw011 embryo were the ventral subgroup of the Isl1-positive spinal motor neurons. (K and L) In 72-hpf Isl1-GFP-transgenic zebrafish, GFP-positive spinal motor neurons projected their axons dorsally (K, lateral view). (L) GFP-positive spinal motor neurons in the 72-hpf Isl1-GFP-transgenic zebrafish embryo were the dorsal subgroup of Isl1-positive spinal motor neurons. |
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage: | Long-pec |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 278(2), Uemura, O., Okada, Y., Ando, H., Guedj, M., Higashijima, S., Shimazaki, T., Chino, N., Okano, H., and Okamoto, H., Comparative functional genomics revealed conservation and diversification of three enhancers of the isl1 gene for motor and sensory neuron-specific expression, 587-606, Copyright (2005) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.