- Title
-
In vivo analysis using variants of zebrafish BMPR-IA: range of action and involvement of BMP in ectoderm patterning
- Authors
- Nikaido, M., Tada, M., Takeda, H., Kuroiwa, A., and Ueno, N.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
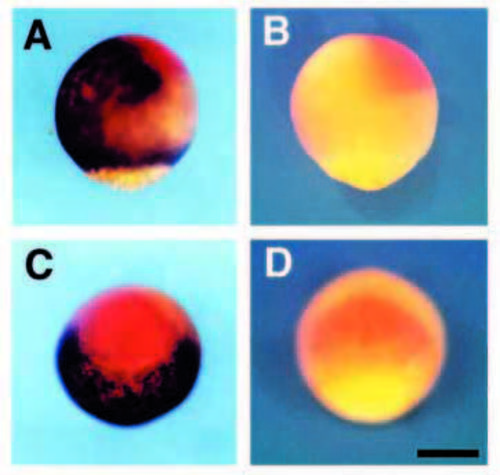
Comparison of the expression domain of zbmp-2 with that of otx-2. (A,C) At 80% epiboly, zbmp-2 (brown) and otx-2 (red) are expressed in contact with each other in the ectodermal region. (B,D) Embryos hybridized with an antisense probe for otx-2 (red) and a sense probe for zbmp-2. (A,B) Lateral views are oriented with the dorsal side to the right. (C,D) Animal pole views show the dorsal side up. Scale bar, 200 7mu;m. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
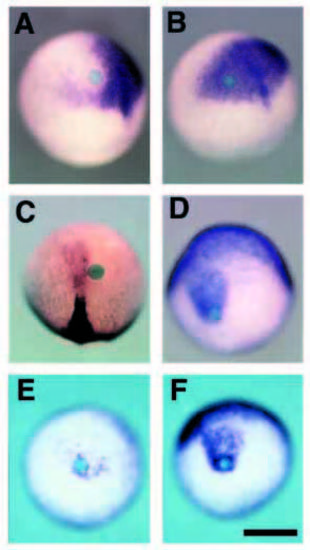
BMP-soaked beads can repress neural differentiation and induce epidermal ectoderm without perturbing normal gastrulation. (A) otx-2 expression was down regulated around the BMP-soaked bead. The effect of the BMP-soaked bead tended to be stronger in the region anterior to the bead than posterior to it. (B) Control BSA-soaked beads did not inhibit otx-2 expression at all. (C) In the same experiment, BMP-soaked beads did not perturb axial mesoderm formation at the morphological and molecular level. Neither gsc nor ntl in chordamesoderm was repressed. The non-neural (epidermal) ectoderm marker, gata-3 (D), was induced by BMP-soaked beads. As shown in Fig. 2A, a stronger effect was observed anterior to the bead. (E) Overexpression of DN-BRIA can repress the induction of gata-3 caused by BMP-soaked beads. In control embryo injected with b- galactosidase mRNA (F), gata-3 is expressed normally. Scale bar, 200 μm. |
|
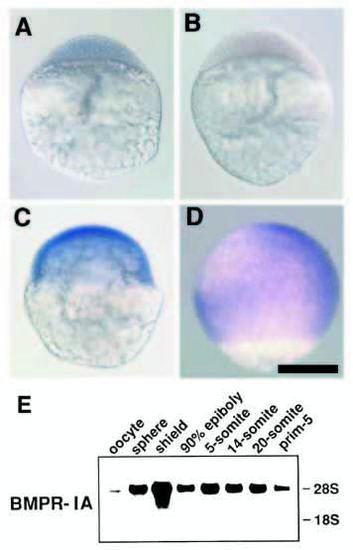
Spatiotemporal expression pattern of BMPR-IA. Wholemount in situ hybridization analysis at different stages; sphere stage (A,B, blastula), shield stage (C, early gastrula) and 80% epiboly (D, late gastrula). As shown in B, in the sphere stage, detectable signals were not obtained using sense probes as a negative control. Note that BMPR-IA was expressed ubiquitously during early embryogenesis. At 80% epiboly stage (D), signals were rarely detected in the ventroanimal region in whole embryos, but in sagittal sections faint signals were observed in this region (data not shown). Lateral views are oriented with their dorsal side to the right except for (A). Scale bar; 200 μm. (E) Northern blot analysis demonstrated that BMPR-IA transcripts were present at low levels maternally. Zygotically, strong signals persist during early embryogenesis with a peak at the shield stage. The positions of 28S and 18S ribosomal RNA are indicated. |
|
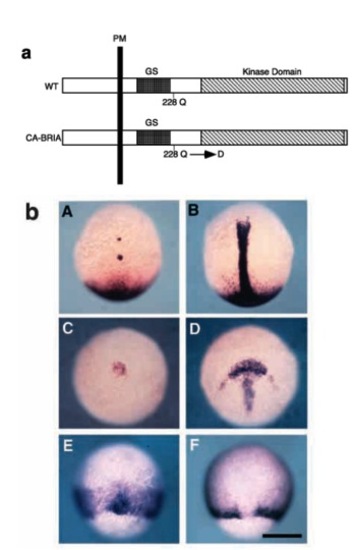
CA-BRIA ventralizes mesoderm like BMP ligand. (a) A schematic drawing of wild-type and constitutively active form of BMPR-IA. The glutamine (Q) residue located at position 228 was replaced with aspartate (D) in the constitutively active variant. (b) Dorsal views (A,B,E,F) and dorsoanimal views (C,D) of experimental (left column) and b-galactosidase mRNA-injected (right column) embryos. All embryos are oriented with their animal pole up. Suppression of ntl (A) and gsc (C) expression in the embryos injected with mRNA encoding CA-BRIA revealed the absence of axial mesoderm. By contrast, expansion of wnt-8 to the dorsal part demonstrated the mesoderm ventralization instead of dorsal mesoderm. Scale bar, 200 μm. |
|
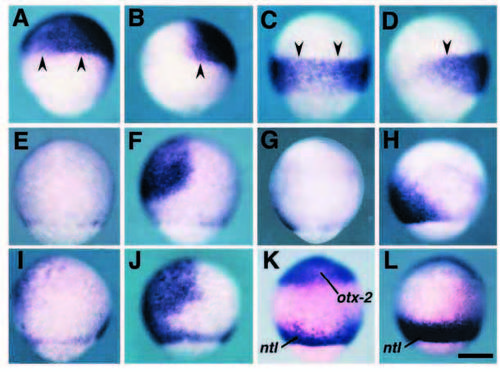
DN-BRIA causes the expansion of the neuroectoderm to the ventral part without any perturbation of the anterior-posterior pattern. At the 80% epiboly stage, embryos injected with mRNA encoding DN-BRIA (A,C,E,G,I,K) and b-galactosidase (B,D,F,H,J,L) were stained with the specific probes for otx-2 (A,B), hoxa-1 (C,D), gata-3 (E,F), eve-1 (G,H) and zbmp-2 (I,J). For the embryos shown in K and L, a mixture of probes for otx-2 and ntl was used. (A-J) Embryos are oriented with their dorsal side to the right and animal pole to the top; (K,L) ventral views with the animal pole at the top. In embryos injected with DN-BRIA mRNA, expression domains of anterior (otx-2, A) and posterior (hoxa-1, C) neuroectoderm marker genes expanded to the ventral part of the embryo, compared with the negative control embryos (B,D, stained with probes for otx-2 and hoxa-1, respectively). The posterior boundary of otx-2 and anterior boundary of hoxa-1 were maintained (arrowheads) in the DN-BRIA-injected embryos. By contrast, ventral nonneural ectodermal marker genes, gata-3 and eve-1, are reduced by the overexpression of DN-BRIA (E and G, respectively). Similarly, zbmp-2 is also reduced (I). This suggests that the neuralization of the ectoderm (A,C) and reduction of non-neural ectoderm (E,G) presented here results from the down-regulation of zbmp-2, caused by interference with the autoactivation process by DN-BRIA. (K,L) DN-BRIA cannot induce involuting dorsal mesoderm as revealed by the axis-like expression pattern of ntl even in the embryo in which neuroectoderm is expanded to the most ventral part. Scale bar, 200 μm. |
|
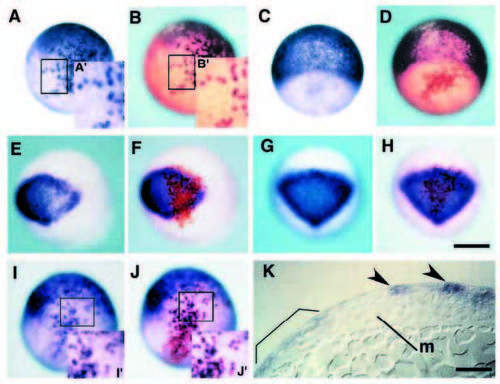
Constitutively active BMPR-IA can simulate BMP signaling in a direct and cell-autonomous manner in ectoderm patterning. (A-J) Chimeras containing cells derived from injected embryos with biotinylated dextran as a lineage tracer and mRNA encoding either constitutively active receptor (A,B, E,F, I,J) or b-galactosidase (C,D, G,H). Embryos after operation are processed for whole-mount in situ hybridization at 80% epiboly with gata-3, epidermal marker gene (A,C), otx-2, neural marker gene (E,G) and zbmp-2 (I). The same embryos are stained with avidin-biotin HRP complex for the purpose of detection of donor cells (B,D), (F,H), (J), respectively). The insets (A′,B′, I′,J′) show a magnification of the boxed area in the same figures. Note that BMP signaling can activate the expression of gata-3 and zbmp-2 only in cells derived from injected embryo (compare Fig. 7A′ with 7B′ and 7I′ with 7J′, respectively). By contrast, otx-2 is downregulated only in donor cells expressing CABRIA (E,F). In chimeric embryos transplanted cells containing b-galactosidase (C,D, G,H), neither ectopic induction nor repression of marker genes were detected. (K) Sagittal section of chimeric embryos containing CA-BRIA in ectoderm. Ectopic gata-3 signals are observed in ectoderm (arrowheads), suggesting that ectoderm ventralization is independent of mesoderm ventralization. Endogenous gata-3 expression is marked by bracket. Abbreviation: m, axial mesoderm. Scale bar, 200 μm (H), 50 μm (K). A-J are the same magnification. |

Unillustrated author statements EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|