- Title
-
A functionally conserved homolog of the Drosophila segment polarity gene hh is expressed in tissues with polarizing activity in zebrafish embryos
- Authors
- Krauss, S., Concordet, J.P., and Ingham, P.W.
- Source
- Full text @ Cell
|
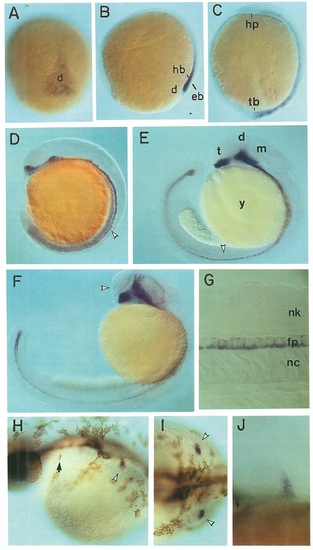
Localization of shh Transcripts in Wild-Type Zebrafish Embryos |
|
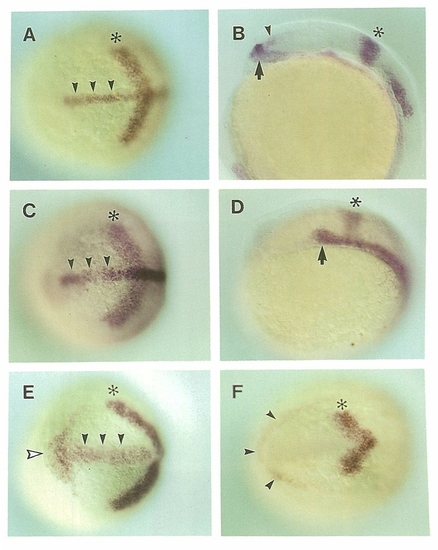
Comparison of shh Expression with Expression of axial, gsc, and pax-2 in the Head Process of Wild-Type Embryos during Early Embryogenesis EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
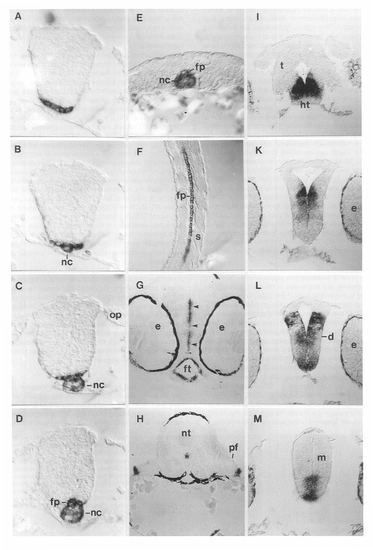
Tissue Sections of Hybridized Embryos Showing shh Expression at Different Developmental Stages EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
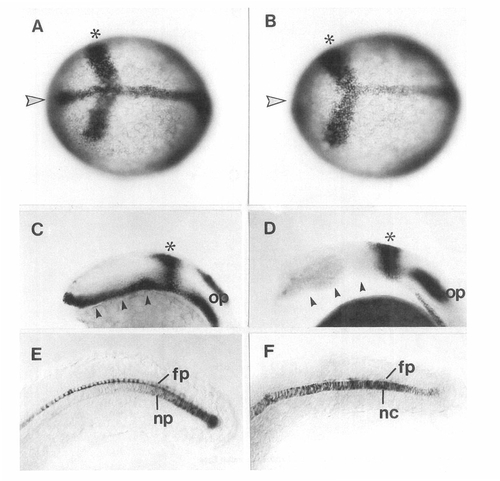
Comparison of shh Expression in ntl Mutant Embryos and Wild-Type Embryos at the Tail Bud Stage EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Comparison of shh Expression in cyc Mutant Embryos and Wild-Type Embryos |
|
Ectopic Expression of axial after Injection of shh RNA into Fertilized Zebrafish Eggs EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|

Unillustrated author statements |
Reprinted from Cell, 75(7), Krauss, S., Concordet, J.P., and Ingham, P.W., A functionally conserved homolog of the Drosophila segment polarity gene hh is expressed in tissues with polarizing activity in zebrafish embryos, 1431-1444, Copyright (1993) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Cell