- Title
-
Reduction in N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase-I Activity Decreases Survivability and Delays Development of Zebrafish
- Authors
- Hall, M.K., Hatchett, C.J., Shalygin, S., Azadi, P., Schwalbe, R.A.
- Source
- Full text @ Curr. Iss. Mol. Biol.
|
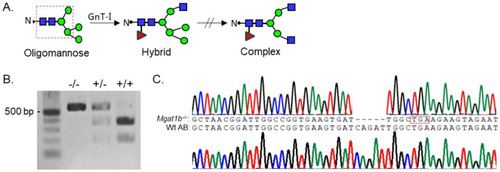
Generation and classification of the |
|
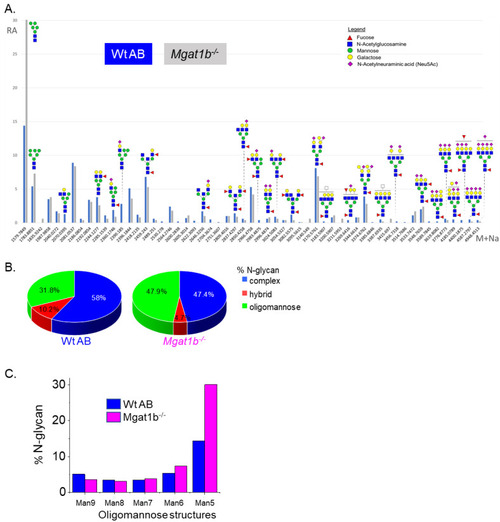
Comparison of LC-ESI-MS relative intensities of the permethylated N-glycans derived from Wt AB and the PHENOTYPE:
|
|
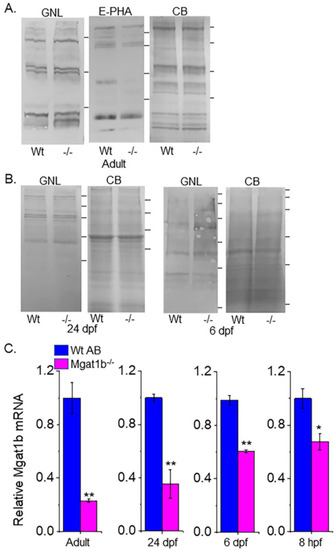
Confirmation of decreased Mgat1b expression, and an increase in oligomannose N-glycans in mutant strain of adult and larvae fish. Lectin blots of whole cell lysates of adult brain ( EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
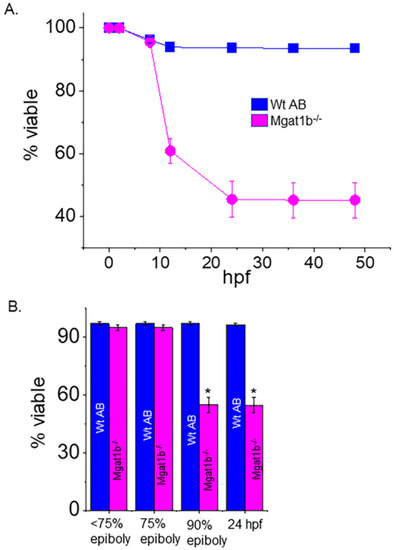
Decline in survivability of Mgat1b−/− mutants post 75% epiboly relative to Wt AB. Survivability of Wt AB and PHENOTYPE:
|
|
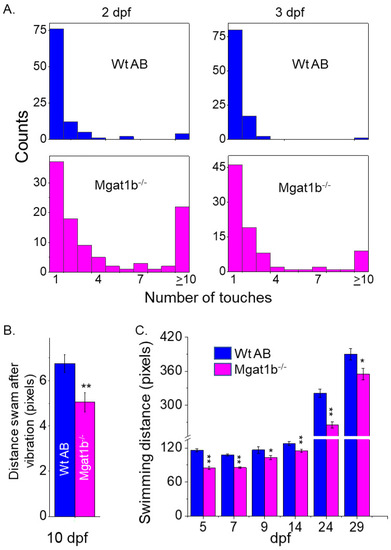
Inhibition of motor and sensory functions in PHENOTYPE:
|
|
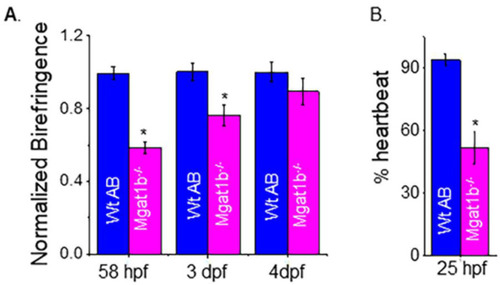
Maldevelopment of skeletal and cardiac muscle in |