- Title
-
Sodium valproate increases activity of the sirtuin pathway resulting in beneficial effects for spinocerebellar ataxia-3 in vivo
- Authors
- Watchon, M., Luu, L., Robinson, K.J., Yuan, K.C., De Luca, A., Suddull, H.J., Tym, M.C., Guillemin, G.J., Cole, N.J., Nicholson, G.A., Chung, R.S., Lee, A., Laird, A.S.
- Source
- Full text @ Mol. Brain
|
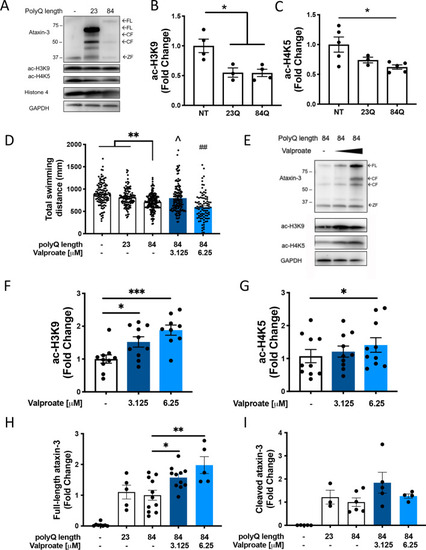
Levels of acetylated histones 3 and 4 are decreased in MJD zebrafish and sodium valproate increases levels of acetylated histones and locomotion in transgenic MJD zebrafish. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
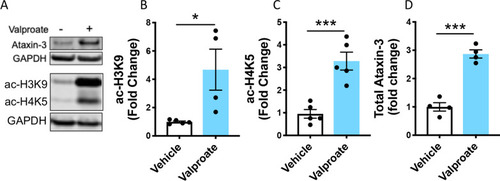
Sodium valproate treatment increased acetylated histones in HEK293 cells expressing human ataxin-3. |
|
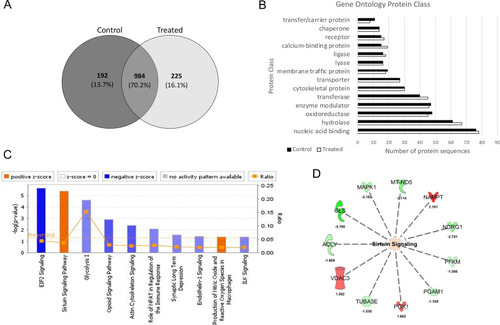
Label-free quantitative proteomics of EGFP-Ataxin-3 84Q transgenic zebrafish treated with vehicle and sodium valproate. |
|
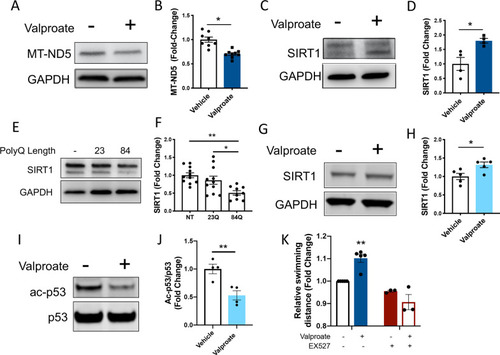
Sodium valproate treatment increases SIRT1 levels and signs of sirtuin activity, validating the increased sirtuin activity predicted by mass spectrometry. |
|
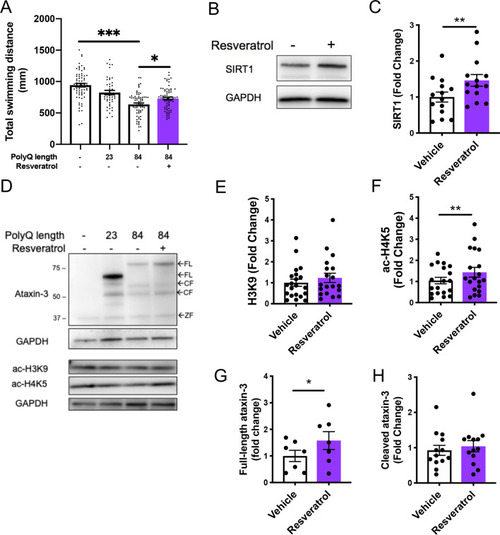
Resveratrol treatment alleviates motor dysfunction whilst simultaneously increasing acetylated histone and SIRT1 levels. |
|
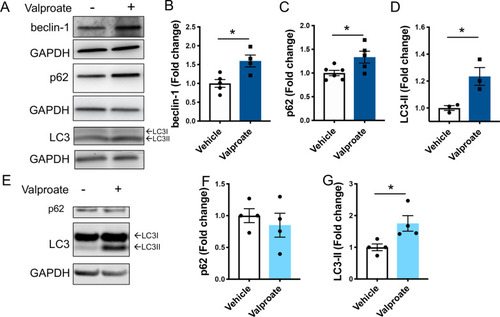
Treatment with sodium valproate (valproate) induces activity of the autophagy pathway in transgenic MJD zebrafish and human ataxin-3 expressing HEK293 cells. |
|
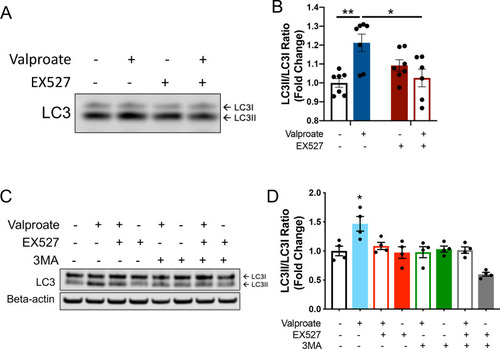
Induction of autophagy following sodium valproate (valproate) treatment of MJD zebrafish and human ataxin-3 expressing HEK293 cells is dependent on sirtuin activity. |
|
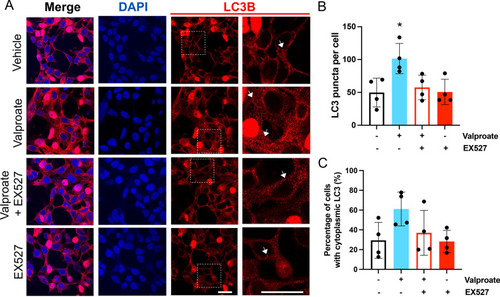
Treatment with sodium valproate (valproate) results in an increase in LC3 within HEK 293 cells expressing ataxin-3 84Q. |