|
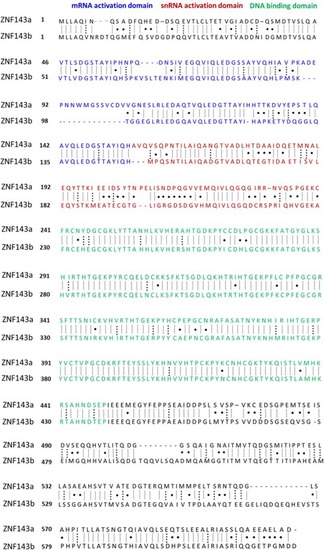
Amino acid sequence alignment of zebrafish ZNF143a vs. ZNF143b. Protein sequences of ZNF143a and ZNF143b were aligned with the |
|
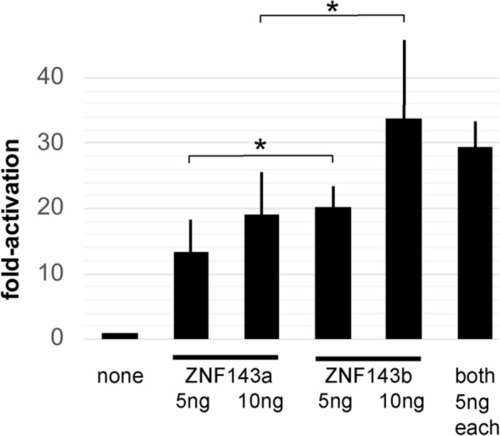
ZNF143a and ZNF143b exhibit similar transcriptional activation potential. Zebrafish ZF4 cells were transfected with pGL3-SPH5 firefly luciferase reporter gene plasmid, plus pRL-SV40 renilla luciferase reporter plasmid, and as noted, pCI-myczznf143a or pCI-myczznf143b expression vector plasmid. Relative luciferase expression was determined by comparing the firefly/renilla luciferase ratio for each sample to that ratio for the sample with addition of expression vector plasmid containing no gene. Bar height shows the mean value from independently transfected wells, and error bars report the standard deviation from the mean. The single asterisk denotes a significant difference ( |
|
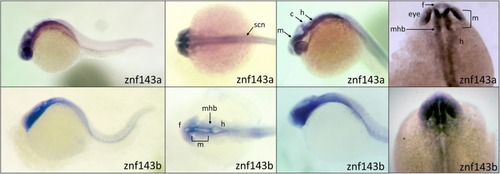
Similar spatial expression of |
|
|
|
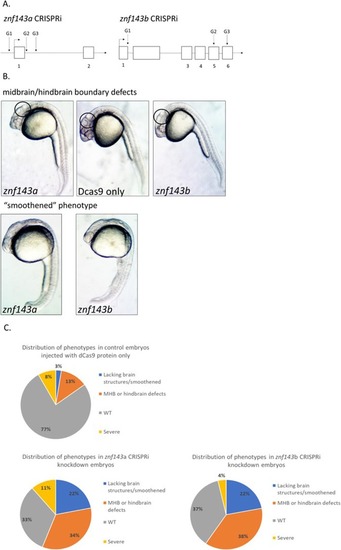
CRISPRi knockdown of either PHENOTYPE:
|
|
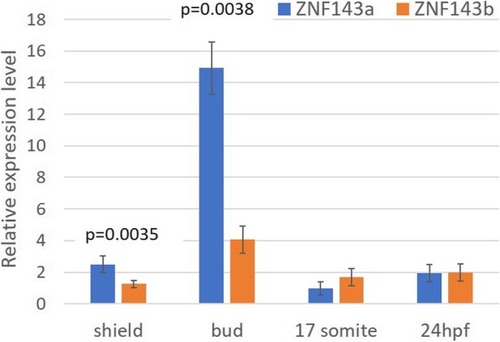
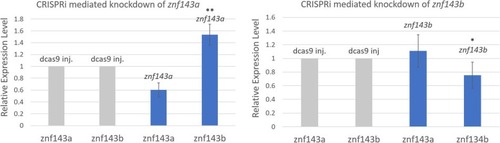
Analysis of specific gene knockdown in CRISPRi experiments. Quantitative RT-PCR was used to analyze relative levels of |