- Title
-
Zebrafish mab21l2 mutants possess severe defects in optic cup morphogenesis, lens and cornea development
- Authors
- Gath, N., Gross, J.M.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
|
|
EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
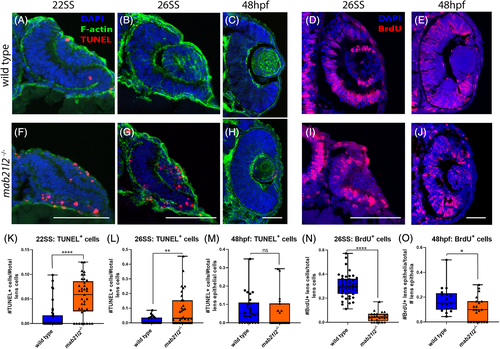
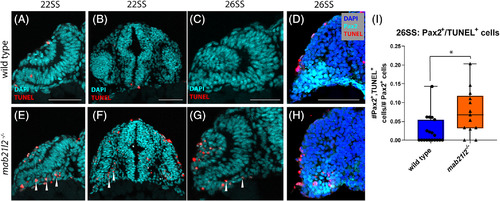
mab21l2 −/− possess elevated cell death in their optic stalk. A?C,E?G: TUNEL stain of wild?type (A?C) and mab21l2 −/− mutant (E?G) embryos. Compared with wild?type, 22SS mutant embryos (E,F) possess an increase in cell death in the optic stalk region of the eye. This difference persists through 26SS (G). D,H: Pax2 and TUNEL co?stain of 26SS wild?type (D) and mab21l2−/−(H) embryos. Compared with wild?type (D), mab21l2 −/−embryos possess increased dying cells in the pax2+optic stalk region. I: Quantification of the proportion of pax2+ and TUNEL+ cells in D and H. Note a significantly higher (P = 0.014) proportion of pax2+ cells are TUNEL+ in mab21l2 −/− mutants when compared with wild?type embryos. Dorsal is up in all panels. Scale bars = 50 μm EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
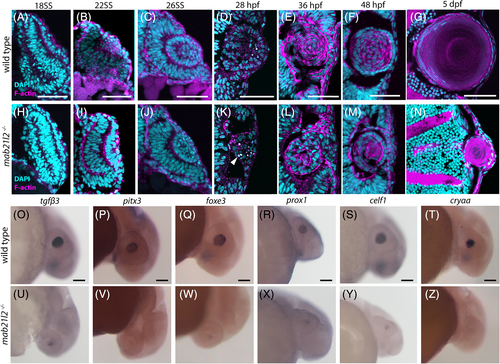
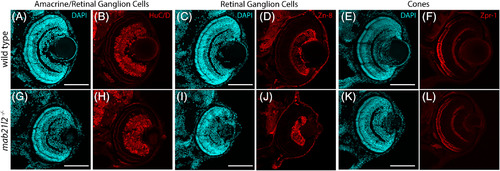
mab21l2 −/− mutants do not possess defects in retinal neuron differentiation. A?L: Wild?type (A?F) and mab21l2 −/− mutant (G?L) 3 dpf sections stained for markers of various retinal cell types. Amacrine cell/retinal ganglion cell marker HuC/D staining is similar in wild?type (B) and mab21l2 −/− mutant (H). Retinal ganglion cell marker zn?8 staining is similar in wild?type (D) and mab21l2 −/− mutant (J). Cone marker zpr?1 staining is similar in wild?type (F) and mab21l2 −/− mutant (L). Dorsal is up in all panels. Scale bars = 100 μm EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
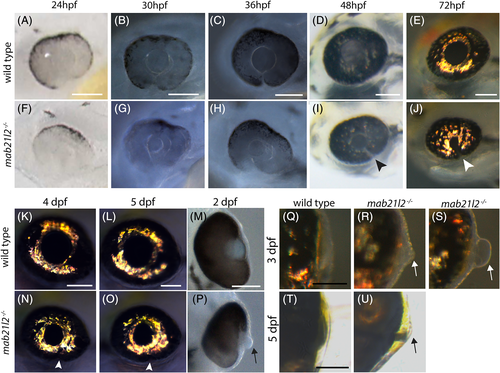
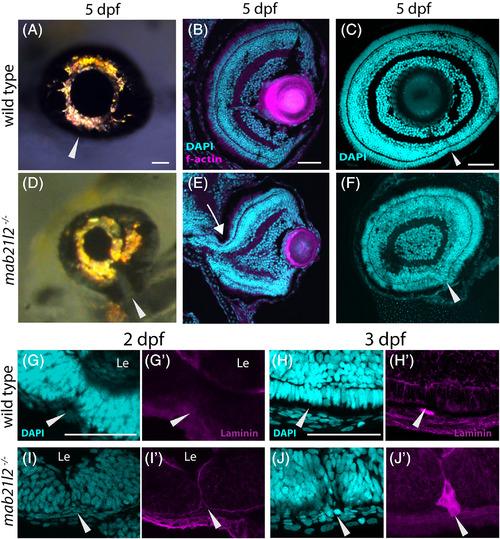
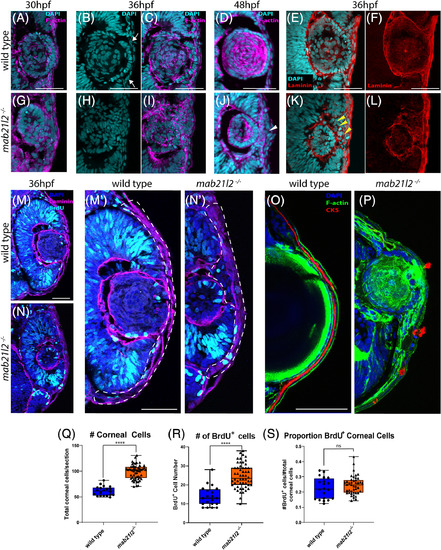
mab21l2 −/− mutants display corneal dysgenesis and failure of stromal patterning. A?D,G?J: Wild?type (A?D) and mab21l2 −/− mutant (G?J) sections demonstrating corneal phenotypes. At 30 and 36 hpf, when compared with wild?type eyes (A?C), mab21l2 −/− lenses (G?I) appear continuous with the overlying surface ectoderm. At 48 hpf, mab21l2 −/− mutants (J) possess a multilayered mass of cells (arrowhead) at the ocular surface when compared with wild?type (D). E,F,K,L: Laminin α1 distribution in 36 hpf wild?type (E,F) and mab21l2 −/− mutant (K,L) embryos demonstrating the presence of ectopic, nonlens, nonretinal cells in mab21l2 −/− mutants (K, arrowheads). M?N′: BrdU incorporation assays of 36 hpf wild?type (M) and mab21l2 −/− mutant (N) embryos. At 36 hpf, mab21l2 −/− mutants (N) possess more corneal cells, but these cells are not ectopically proliferative relative to wild?type (M). Zooms in M′ and N′; dotted lines show area counted for quantification. O?P: Corneal keratan sulfate (CKS) stain of 5 dpf wild?type (O) and mab21l2 −/− mutant (P) embryos. Mutants do not properly express CKS in the stroma. Q?S: Quantification of total and BrdU+ corneal cells in M and N. (P < 0.0001, P < 0.0001, P = 0.27, respectively). Scale bars = 50 μm |