- Title
-
The transmembrane protein Crb2a regulates cardiomyocyte apicobasal polarity and adhesion in zebrafish
- Authors
- Jiménez-Amilburu, V., Stainier, D.Y.R.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
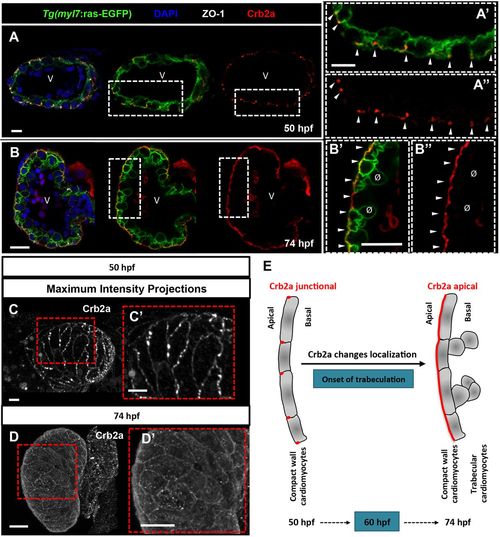
Crb2a localization changes during cardiac trabeculation in zebrafish. (A-B″) Crb2a immunostaining in Tg(myl7:ras-EGFP)hearts at 50 (A-A″, n=12) and 74 (B-B″, n=15) hpf. At 50?hpf, Crb2a mostly localizes to the apical junctions between CMs (A-A″, arrowheads). At 74?hpf, Crb2a localizes to the entire apical membrane of compact layer CMs (B-B″, arrowheads), and is not observed in delaminated CMs (B′,B″, ø). (C-D′) Maximum intensity projections of ventricles showing junctional Crb2a immunostaining at 50 hpf (C,C′) and apical Crb2a immunostaining at 74 hpf (D,D′). (E) Schematic illustration of Crb2a relocalization in CMs from junctional to apical during the onset of trabeculation. V, ventricle. |
|
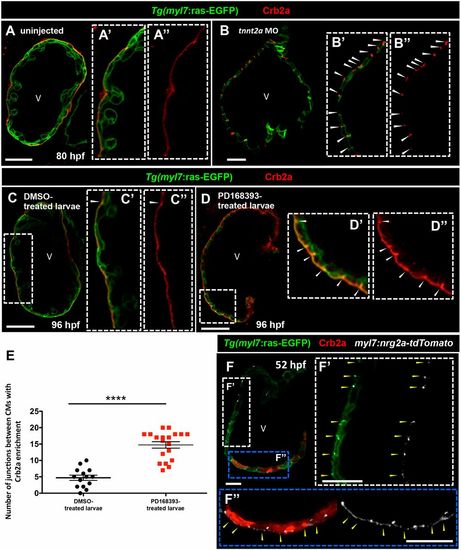
Crb2a localization in developing CMs is modulated by blood flow and Nrg2a/ErbB2 signaling. (A-B″) Crb2a immunostaining in Tg(myl7:ras-EGFP) control (A, n=8) and tnnt2a morphant (B, n=8) hearts at 80?hpf. Higher-magnification images show apical localization of Crb2a in control (A′,A″) and tnnt2a morphant hearts (B′,B″); arrowheads indicate junctional localization of Crb2a between CMs. (C-D″) Crb2a immunostaining in 96?hpf Tg(myl7:ras-EGFP) hearts treated between 54 and 96?hpf with DMSO (C-C″, n=14) or PD168393 (D-D″, n=19); arrowheads indicate Crb2a enrichment at the junctions between CMs. (E) Number of junctions between CMs with Crb2a enrichment. Each dot or square represents data from one heart. Data are mean±s.e.m. ****P<0.0001 by Student's t-test. (F) Crb2a immunostaining in 52?hpf Tg(myl7:ras-EGFP) embryos injected at the one-cell stage with a myocardial-specific nrg2a construct (myl7:nrg2a-p2a-tdTomato) (n=8). (F′,F″) Higher-magnification images show junctional localization of Crb2a in non-nrg2a-expressing CMs (arrowheads in white dashed box, F′) and apical Crb2a localization in nrg2a-expressing CMs (arrowheads in blue dashed box, F″). V, ventricle |
|
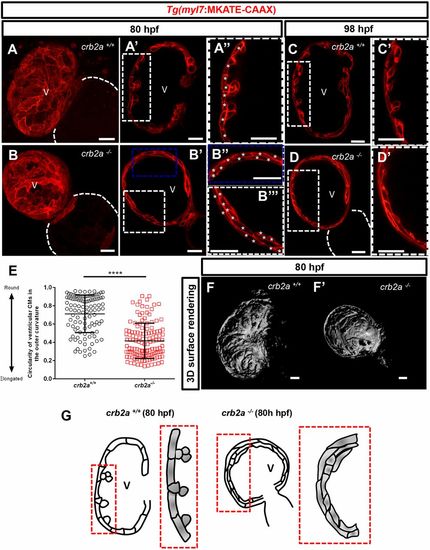
crb2a−/− hearts display disrupted compact wall integrity and fail to form trabeculae. (A-B″) Confocal images (maximum intensity projections) of 80?hpf Tg(myl7:MKATE-CAAX) crb2a+/+ (A-A″) and crb2a−/− (B-B″) hearts. (A-D′) Confocal images (mid-sagittal sections) of Tg(myl7:MKATE-CAAX) hearts of crb2a+/+ (A-A″, n=8; C,C′, n=8) and crb2a−/− (B-B″, n=14; D,D′, n=14) larvae at 80 and 98?hpf. Asterisks in A″,B″ and B? indicate individual CMs in the compact wall. (E) Circularity of ventricular CMs (outer curvature) in 80?hpf crb2a+/+ (n=7 hearts) and crb2a−/− (n=10 hearts) larvae. Each point represents data from an individual CM. Data are mean±s.e.m. ****P<0.0001 by Student's t-test. (F,F′) 3D surface rendering images of 80?hpf crb2a+/+ (F) and crb2a−/− (F′) ventricles. (G) Schematic illustration of the myocardial wall in 80?hpf crb2a+/+ and crb2a−/− ventricles. V, ventricle. |
|
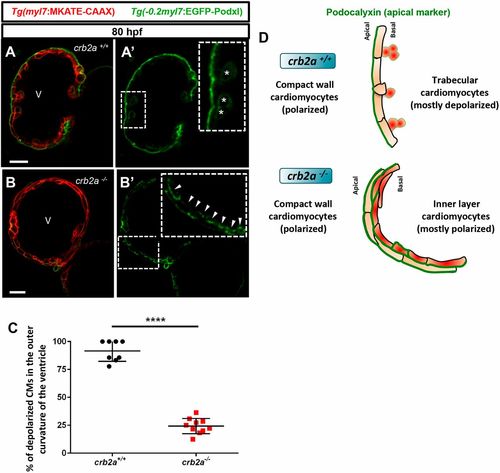
Most inner layer CMs in crb2a−/− remain polarized in the apicobasal axis. (A-B′) Confocal images (mid-sagittal sections) of 80?hpf Tg(−0.2myl7:EGFP-podxl); Tg(myl7:MKATE-CAAX); crb2a+/+ (A) and crb2a−/− (B) hearts. Asterisks in A′ mark delaminated CMs and arrowheads in B′ indicate polarized CMs. (C) Percentage of depolarized CMs in the outer curvature of the ventricle of 80?hpf crb2a+/+ (n=8) and crb2a−/− (n=10) larvae. Data are mean±s.e.m. ****P<0.0001 by Student's t-test. (D) Schematic illustration of A′ and B′ showing depolarized CMs in the trabecular layer of crb2a+/+ hearts and polarized CMs in the inner layers of crb2a−/− hearts. V, ventricle |
|
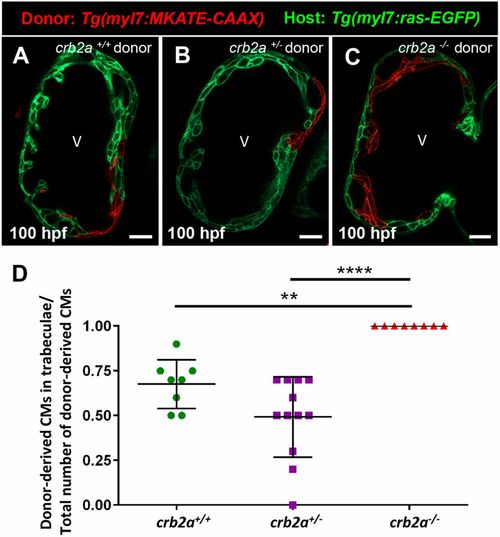
Crb2a regulates CM behavior cell-autonomously. (A-C) Confocal images (mid-sagittal sections) of mosaic 100?hpf crb2a+/+Tg(myl7:ras-EGFP) host hearts transplanted with Tg(myl7:MKATE-CAAX); crb2a+/+, crb2a+/− or crb2a−/− cells. (D) Percentage of donor-derived CMs in trabeculae versus total number of donor-derived CMs. Each point represents data from one heart. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed corrected by Tukey's multiple comparisons test. **P<0.01; ****P<0.0001. V, ventricle |