- Title
-
Targeted resequencing and systematic in vivo functional testing identifies rare variants in MEIS1 as significant contributors to restless legs syndrome
- Authors
- Schulte, E.C., Kousi, M., Tan, P.L., Tilch, E., Knauf, F., Lichtner, P., Trenkwalder, C., Högl, B., Frauscher, B., Berger, K., Fietze, I., Hornyak, M., Oertel, W.H., Bachmann, C.G., Zimprich, A., Peters, A., Gieger, C., Meitinger, T., Müller-Myhsok, B., Katsanis, N., Winkelmann, J.
- Source
- Full text @ Am. J. Hum. Genet.
|
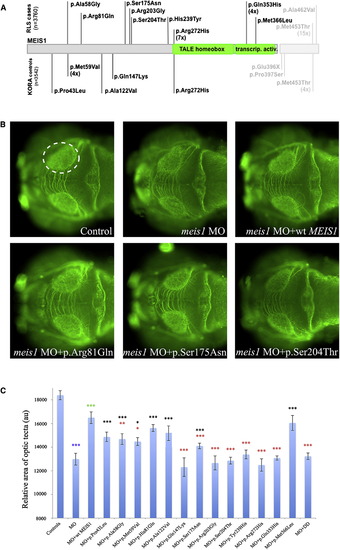
Functional Assessment of Rare Nonsynonymous Variants in MEIS1 by In Vivo Complementation in Zebrafish Embryos (A) Location and frequency of nonsynonymous MEIS1 variants examined in zebrafish. Variants found in case subjects are given above the gene, those found in control subjects below. The short, canonical isoform 1 of MEIS1 is given in dark gray (ENST00000272369); the additional amino acids in the longer isoform 2 in light gray (ENST00000398506). (B) At 72 hpf, zebrafish larvae were stained as whole mounts using an antibody against acetylated tubulin and the size of the optic tecta was measured for phenotypic read out. Control, morpholino injection, and rescue by human WT mRNA are shown in the upper panels. The lower panels illustrate the effects of different alleles tested. (C) Quantification of optic tectum area in zebrafish larvae at 72 hpf (n = at least 51 per genotype). Benign alleles show a significant difference with regard to the MO injection, hypomorphic alleles a significant difference with regard to both the MO injection and the rescue (MO plus WT) injection, and null alleles are significantly different from the rescue only. Asterisks denote significance levels as determined by Student?s t test. Color of asterisks as follows: blue, MO versus control; green, rescue versus MO; black, allele versus MO; red, allele versus WT rescue. Abbreviations are as follows: MO, morpholino; WT, wild-type. Error bars represent standard deviations across all examined embryos. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
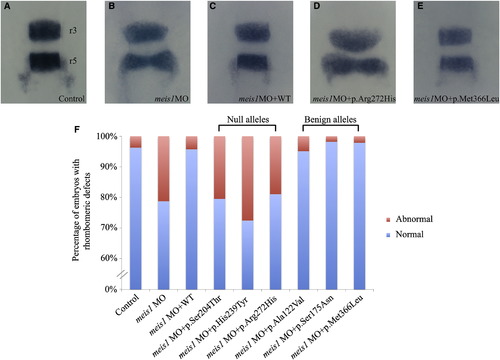
Functional Assessment of Null and Benign MEIS1 Variants by In Vivo Complementation in Zebrafish Embryos and Evaluation of Hindbrain Patterning (A-E) At 14-16 hpf, developing zebrafish embryos were evaluated for the integrity of rhombomeres 3 and 5 (r3 and r5) by in situ hybridization with a riboprobe against krox20. Upon disruption of meis1, we observed rhombomeric defects that involved widening of the evaluated structures (B and D) or shortening of the distance between r3 and r5 (D), as well as thinning or absence of the evaluated structures. (F) Quantification showing that the aberrant phenotypes were especially pronounced in the morphant embryos and embryos coinjected with MO+null mRNA (n ≥ 26 embryos per genotype). Abbreviations are as follows: MO, morpholino; WT, wild-type. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
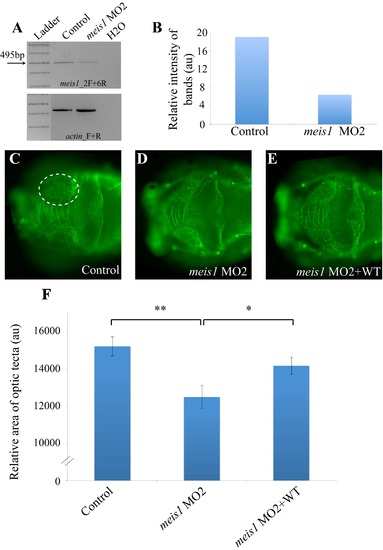
In vivo complementation of MEIS1, using a previously reported MO (meis1_MO2) against the acceptor splice junction of exon 2. (A) The effect of meis1_MO1 targeting the donor site of exon 2 and inducing skipping of exons 2-7 has been evaluated previously5. (B) We here amplified the cDNA sequence between exons 2-6 in control embryos and morphants injected with 9ng meis1_MO2 and detect only ~30% of the wild-type RNA message in the morphant embryos. (C-F) Suppression of meis1 results in a reduction of the size of the optic tectum by 20-30%, similar to the phenotype observed when using meis1_MO1 that can be significantly and reproducibly rescued upon co-injection with wt human MEIS1 mRNA. Asterisks denote significance levels as determined by Student`s t-test (** p-value < 0.005; * p-value < 0.05). MO=morpholino, wt=wildtype PHENOTYPE:
|
|
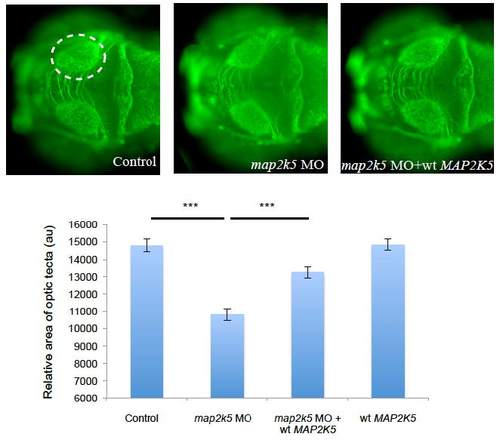
In vivo complementation and overexpression using human mRNA of MAP2K5, another gene harboring RLS risk alleles identified by means of GWAS3; 4. Suppression of map2k5 results in a reduction of the size of the optic tectum in a similar manner to that seen upon in vivo complementation of MEIS1. Asterisks denote significance levels as determined by Student′s t-test (*** p-value < 0.0001). MO=morpholino, wt=wildtype PHENOTYPE:
|