- Title
-
Oncogenic mutations in Adenomatous Polyposis Coli (Apc) activate mechanistic Target of Rapamycin Complex 1 (mTORC1)
- Authors
- Valvezan, A.J., Huang, J., Lengner, C.J., Pack, M., and Klein, P.S.
- Source
- Full text @ Dis. Model. Mech.
|
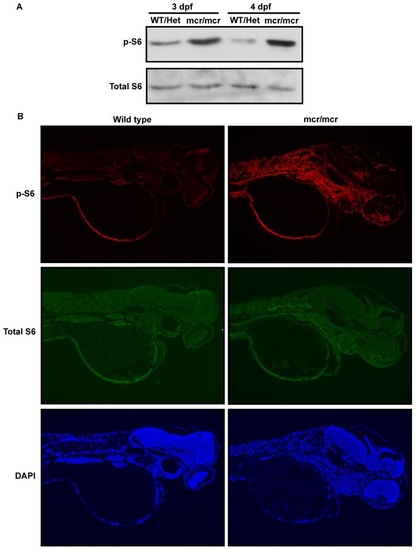
Activation of mTORC1 in apcmcr/mcr zebrafish. Western blot analysis using antibodies to phosphorylated S6 (p-S6), indicating mTORC1 activity, or total S6 on whole embryo lysates from pooled wild-type and heterozygous apcmcr/+ zebrafish or homozygous apcmcr/mcr zebrafish at 3 or 4 dpf. mTORC1 activity was increased in the homozygous apcmcr/mcr zebrafish. (B) Immunohistochemical staining of sagittal sections from wild-type or homozygous apcmcr/mcr zebrafish at 3 dpf using antibodies to phosphorylated or total S6 and counterstaining with DAPI. mTORC1 was aberrantly active in multiple mesodermal and endodermal derivatives in the homozygous apcmcr/mcr zebrafish. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
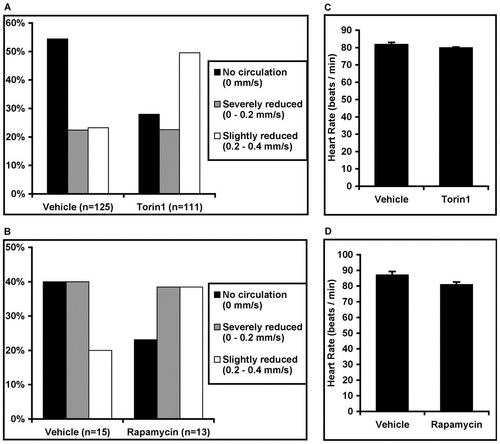
mTORC1 inhibition improves circulation in apcmcr/mcr zebrafish. (A) apcmcr/mcr zebrafish were treated with vehicle or Torin1 (250 nM) and the rate of blood flow through the dorsal aorta was measured using high speed videomicroscopy in unanesthetized larvae at 2-3 dpf. Blood flow phenotypes were categorized according to flow rate as indicated. Representative movies for each scoring category can be found in online supplementary material (supplementary material Movies 1-4). (B) Rapamycin also improved circulation in apcmcr/mcr zebrafish. (C,D) Torin1 and rapamycin treatment did not increase the heart rate of apcmcr/mcr zebrafish. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
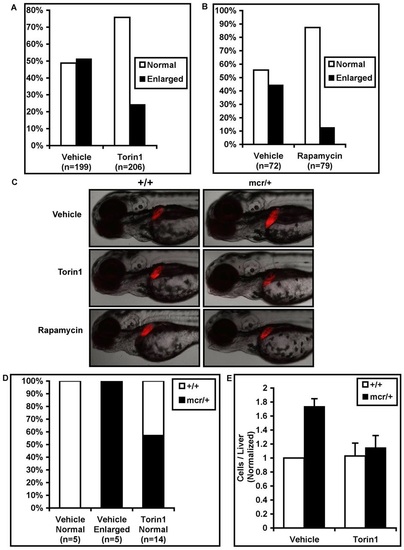
mTORC1 inhibition rescues liver hyperplasia in heterozygous apcmcr/+ zebrafish. Lfabp:rfp zebrafish, which express liver-specific RFP, were mated with apcmcr/+ zebrafish. (A) Resulting progeny (expected 50% apc+/+, 50% apcmcr/+) were treated with vehicle or Torin1 and the percentage of fish with normal or enlarged livers at 3-4 dpf was recorded. Approximately 50% of vehicle-treated fish had enlarged livers, as described previously (Goessling et al., 2008). Torin1 reduced the percentage of fish with enlarged livers. (B) Rapamycin similarly rescued liver enlargement. (C) Representative pictures showing liver enlargement in vehicle-treated heterozygous apcmcr/+ zebrafish but not in Torin1- or rapamycin-treated heterozygotes. (D) Liver size correlated closely with genotype in vehicle-treated embryos, as described previously (Goessling et al., 2008), but heterozygous apcmcr/+ embryos accounted for approximately half of Torin1-treated embryos with normal-size livers, confirming that Torin1 reduces liver size in heterozygous apcmcr/+ embryos. (E) The number of RFP-positive cells per embryo was measured by flow cytometry. Vehicle-treated apcmcr/+ zebrafish had ~75% more hepatocytes than vehicle-treated wild-type fish, and this was rescued by Torin1 treatment. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
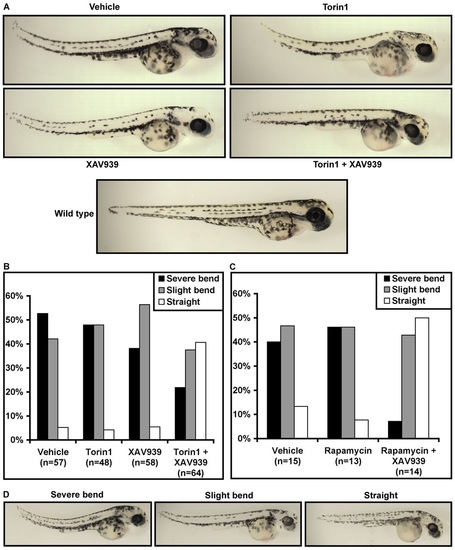
Combined inhibition of mTORC1 and Wnt signaling reduces body curvature in apcmcr/mcr zebrafish. (A) Representative images of apcmcr/mcr zebrafish at 2 dpf treated with vehicle, Torin1 (250 nM), XAV939 (500 nM) or Torin1 plus XAV939. Combined Torin1 and XAV939 treatment rescued body curvature whereas either treatment alone did not. (B) Zebrafish were scored at 2-3 dpf on the basis of severity of body curvature; the percentage of fish in each category is shown. Only combined Torin1 plus XAV939 treatment reduced body curvature. (C) Rapamycin also reduced body curvature in combination with XAV939, but not by itself. (D) Representative pictures of each of the three categories used to score body curvature in B and C. PHENOTYPE:
|