- Title
-
Morphogenesis underlying the development of the everted teleost telencephalon
- Authors
- Folgueira, M., Bayley, P., Navratilova, P., Becker, T.S., Wilson, S.W., and Clarke, J.D.
- Source
- Full text @ Neural Dev.
|
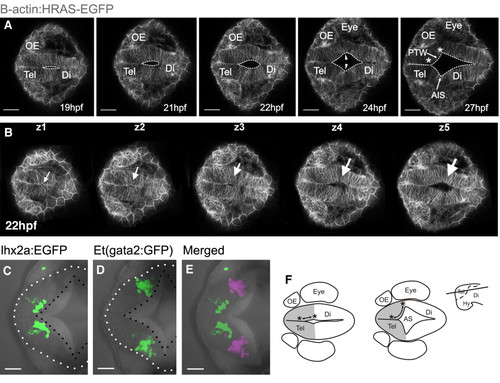
Formation of anterior intraencephalic sulcus (AIS) and posterior wall of the telencephalon. A. Time-lapse sequence of a single z-level of a Tg(β-actin: HRAS-EGFP) vu119 embryo. The midline lumen opens out at the telencephalic-diencephalic boundary to form the AIS and the posterior wall of the telencephalon (ventricular surface between asterisks). Inflation of the ventricular space leads to a lateral protrusion of the telencephalon in its caudal region (arrowheads). B. Five z-levels at a single timepoint showing opening of the AIS (arrowed) is initiated deep (z5) from the dorsal surface (z1). C. Cells of the olfactory bulb, revealed in Tg(10lhx2a:EGFP)zf176 line, lie medially and just in front of the posterior telencephalic wall at 30 hpf. D. Pallial cells in the Et(gata2:GFP)bi105 line lie laterally, just in front of the posterior telencephalic wall at 30 hpf. E. Olfactory bulb [Tg(10lhx2a:EGFP)zf176] and pallial cells [Et(gata2:GFP)bi105] in C and D superimposed to show relative positions (pallial cells pseudocoloured turquoise). F. Diagram to illustrate how generation of AIS folds posterior telencephalon to a more lateral location. Dorsal views, anterior to the left. Scale bars: 100 μm in A and B and 50 μm in B to E. AIS: anterior intraencephalic sulcus; Di: diencephalon; Hy: hypothalamus; OE: olfactory epithelium; PTW: posterior telencephalic wall; Tel: telencephalon. |
|
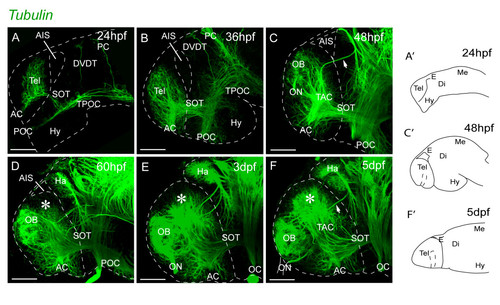
Neuropil organization in the telencephalon between 1 dpf and 5 dpf. A-F. Acetylated α-tubulin inmunostaining. The pallial telencephalic neuropil (indicated by asterisks) expands greatly posterior to the OB between days 2 and 5. The forebrain flexure places the subpallium and hypothalamus more posteriorly from 24 hpf to 36 hpf (A and B). At 2 dpf, the olfactory bulb neuropil is located close to the dorsal rim of the AIS and there is no obvious pallial neuropil. The pallial neuropil (asterisk) expands greatly posterior to the OB between days 2 and 5 (D-F). Lateral views, anterior to the left. A′, C′ and F′ illustrate the orientation of telencephalon in the related photomicrographs. Scale bars, 50 μm. AC: anterior commissure; AIS: anterior intraencephalic sulcus; Di: diencephalon; DVDT: dorsoventral diencephalic tract; E: epithalamus; Ha: habenula; Hy: hypothalamus; Me: mesencephalon; OB: olfactory bulb; OC: optic chiasm; ON: olfactory nerve; PC: posterior commissure; POC: postoptic commissure; SOT: supraoptic tract; TAC: tract of the anterior commissure; Tel: telencephalon; TPC: tract of the posterior commissure; TPOC: tract of the postoptic commissure. |
|
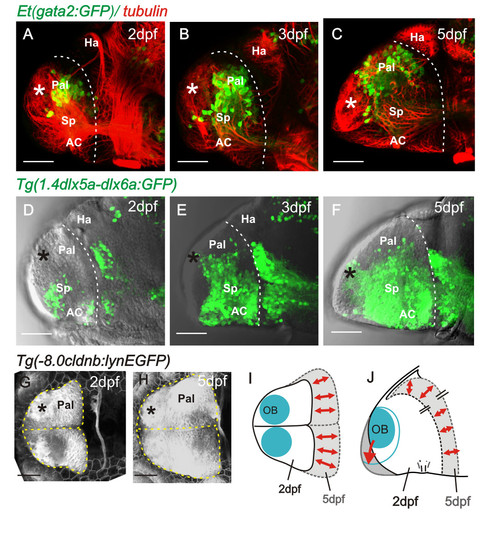
Pallial and subpallial expansion between 2 dpf and 5 dpf. A to C. Lateral views of 2, 3, and 5 day telencephali expressing [Et(gata2:GFP)bi105] in pallial neurons whose numbers expand into the region between the OB (asterisk) and the diencephalic habenulae. D to F. Lateral views of 2, 3, and 5 day telencephali expressing Tg(1.4dlx5a-dlx6a:GFP)ot1 in subpallial cells, whose numbers expand greatly between days 2 and 5. G and H. Dorsal views of telencephalon at 2 and 5 days labelled with the transgene 8.0cldnb:lynEGFP. Positions of olfactory bulbs are superimposed and the outlines of the telencephali are overlaid in I (dorsal view) and J (lateral view), to illustrate that most growth occurs along the anteroposterior axis but that the mediolateral dimensions alter relatively little. AC: anterior commissure; Hab: habenula; OB: olfactory bulb; Pal: pallium; Sp: subpallium. |
|
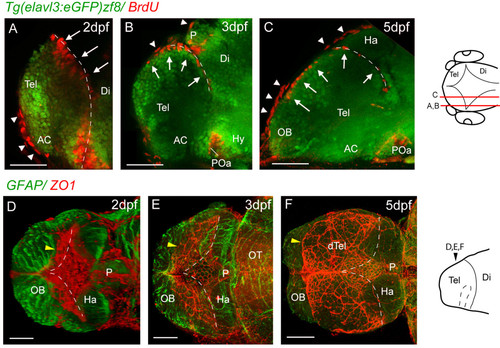
Proliferative cells and tela choroidea expand over the upper telencephalic surface between 2 dpf and 5 dpf. A, B and C. Parasagittal sections of BrdU-labelled (red) telencephali at 2, 3, and 5 days. At 2 days, the BrdU nuclei in the telencephalon (arrows) are seen lining the posterior telencephalic wall. By 3 days, a few nuclei are found on the upper surface of the telencephalon, and by 5 days, a more extensive area of the upper surface is lined with BrdU-positive nuclei (arrows). The more flattened BrdU-positive nuclei (arrowheads) are present in the overlying skin. D, E and F. ZO1 staining (red) reveals that the tela choroidea spreads over the dorsal surface of telencephalon over the same period as the proliferative cells. The diamond-shaped roof of the TDR at 2 dpf expands (yellow arrowhead) to cover the upper telencephalic surface (except for the OBs) by 5 dpf. Each image is a dorsal view created by projecting a z-stack of horizontal confocal sections. Neuroepithelium is counterstained with an anti-GFAP antibody (green). Dotted lines mark the position of the posterior telencephalic wall. Schematics on the right show levels of sections and planes of view. Scale bars 50 μm. AC: anterior commissure; AIS: anterior intraencephalic sulcus; Di: diencephalon; dTel: dorsal telencephalon; Hab: habenula; OB: olfactory bulb; P: pineal; POa: preoptic area; Tel: telencephalon. Dashed lines indicate medial and posterior walls of the telencephalon. |
|
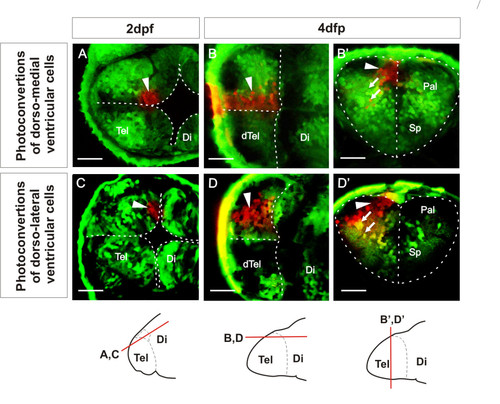
Ventricular zone at dorsal rim of the AIS expands along the AP axis from 2 dpf to 4 dpf. A. Single confocal z-level in the horizontal plane shows ventricular cells photoconverted (arrowhead) in a medial location of the dorsal rim of the AIS at 2 dpf. B. By 4 dpf, a similar horizontal plane close to the upper (now ventricular) surface of the telencephalon shows that these cells have generated an anteroposteriorly expanded column of cells. B′. A transverse plane through these cells shows that most photoconverted cells are ventricular zone cells that remain close to the sagittal plane of the telencephalic lobe. Arrows indicate radial migration of differentiated neurons. C. Single confocal z-level in the horizontal plane shows ventricular cells photoconverted (arrowhead) in a lateral location of the dorsal rim of the AIS at 2 dpf. D. By 4 dpf, a similar horizontal section close to the upper (now ventricular) surface of the telencephalon shows that these cells have generated an anteroposteriorly expanded column of cells. D′. A transverse section through these cells shows that many of these cells are ventricular zone cells contacting the upper ventricular surface of the telencephalic lobe (arrowhead) and projecting radially (arrows) to the lateral pial surface. Schematics show levels of confocal optical sectioning. Scale bars 50 μm. Di: diencephalon; dTel: upper surface of telencephalon; Pal: pallium; Sp: subpallium; Tel: telencephalon. |