- Title
-
Distinct expression patterns of dickkopf genes during late embryonic development of Danio rerio
- Authors
- Untergasser, G., Martowicz, A., Hermann, M., Töchterle, S., and Meyer, D.
- Source
- Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. |
|
Expression pattern of dkk1a and dkk1b during embryonic development Whole mount in situ hybridization analyses with dkk1a (A?E2) and dkk1b (F?K) specific antisense probes in developmental stages ranging from 10 to 76hpf. E2 and K show branchial arches of embryos in higher magnification. Arrowheads in C and D indicate position of individual dkk1a-expressing cells. Note the similar pattern of dkk1a and dkk1b expression in the epidermal edge lining of trunk and tail (arrow) and in the otic vesicles (ov) and lens. Distinct expression patterns of dkk1a were found in lateral line (ll) and of dkk1b in fin buds (fb), prechordal plate (pp), lateral posterior mesoderm (lm), chordaneural hinge (cnh), pituitary (pit), lateral line primordium (llp) and in the late embryonic branchial arches (ba; numbers indicate position the pharyngeal arches 1?5). Embryos are shown in lateral (A?C and F?H) or dorsal view with anterior to the left (D, E, E2, I, J and K). Scale bars in all figures correspond to 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Expression pattern of dkk3a(dkk3l) during embryonic development Expression of dkk3a(dkk3l) was analyzed by whole mount in situ hybridization in embryos ranging from 6 to 72hpf. At 6hpf expression was found throughout the embryo (A). From 24 to 36hpf expression was seen in all formed somites, (B and C). At 36 and 48hpf signals were also found in the neural tube in a ventral to dorsal decreasing gradient (C and E). Strong signals can be detected in the lens (D), in the posterior lateral line ganglion (pl) and in cranial ganglia (cg) (C, E and F). At 72hpf expression was only retained in the anterior dorsal and anterior ventral lateral line ganglion (ad/av), the nucleus of the medial longitudinal fascicle (nucMLF), in reticulospinal neurons of the hindbrain (rsn), and the vagal epibranchial ganglion (v) (G). Embryos are shown in lateral (A?C, E and G) or dorsal view with anterior to the left (D, F and H). Immunohistochemistry with a 3A10- antibody was performed on whole mount in situ hybridizations (I, J and K). Co-labelling of dkk3a(dkk3l) and 3A10-positive neuronal structures by immunohistochemistry (brown staining in I?K) reveal overlapping expression in the nucleus of the medial longitudinal fascicle (nucMLF). Higher magnification of the midbrain in a whole embryo from dorsal (J) and a transversal sections (K) further confirm overlapping expression in the nucMLF. M indicates 3A10 positive Mauthner axons. Scale bars in all figures correspond to 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
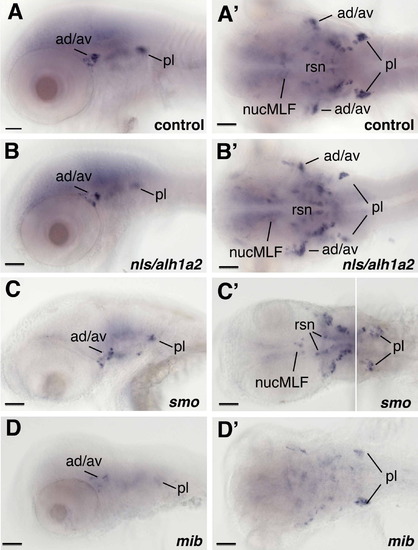
Expression of dkk3a(dkk3l) gene in mutants with defective neural patterning and neurogenesis Neuronal expression at 72hpf in wild type (A and A2), nls/aldh1a2 (B and B2), smo (C and C2) and mib (D and D2) mutant embryos. Expression of dkk3a(dkk3l) in reticulospinal neurons of the hindbrain (rsn) and midbrain (nucMLF: nucleus of the medial longitudinal fascicle) was not significantly altered in nls/alh1a2 mutants. In smo mutants the number of expressing cells is reduced in the central (rsn, nucMLF) but not in the peripheral nervous system (ad/av; anterior dorsal and anterior ventral lateral line ganglion and pl; posterior lateral line ganglia). By contrast, mib mutants show a strong reduction of dkk3a(dkk3l) expressing cells in the central and peripheral nervous system. The same embryos are shown in lateral (A?D) and dorsal view (A2, B2, C2 and D′). Scale bars in all figures correspond to 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
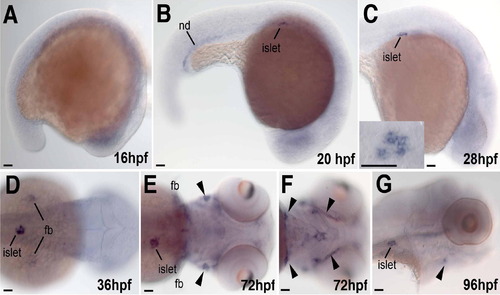
Expression pattern of dkk3b(dkk3) during embryonic development Until 16hpf weak dkk3b(dkk3) signals are found throughout the embryo (A). At 20hpf specific signals are associated with the nephric duct (nd) and the pancreatic islet (B). Strongest signals can be detected in cells of islet within the entire late developmental stages, i.e. 28, 36, 72 and 96hpf (C?E and G). Additionally, 36hpf expression was found in fin buds (fb) and craniofacial arches (arrowheads in E?G). Embryos are shown from dorsal (D and E), ventral (F) or lateral (A?C and G). In order to highlight pancreatic expression on the right side, embryos are shown with the anterior to the right. Scale bar in all figures correspond to 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
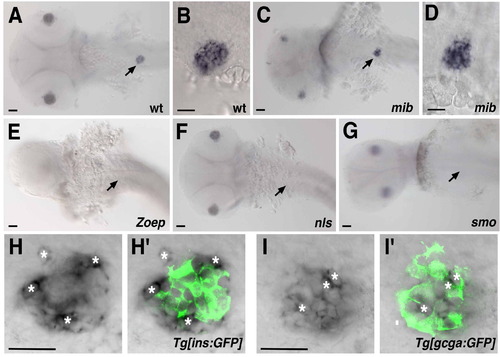
Genetic control and cell specificity of pancreatic dkk3b(dkk3) expression Comparison of dkk3b(dkk3) expression in wild type (A and B) mib (C and D), Zoep (E), nls (F) and smo (G) mutant embryos at 36hpf. Trunk-specific expression is missing in Zoep, nls and smo mutant embryos (arrows indicate corresponding positions). Double labelling of dkk3b(dkk3) mRNA (blue in H and I) and GFP protein (green in H2 and I2) in the beta- and alpha- cell reporter lines Tg[ins:GFP] (H2) and Tg[gcga:GFP] (I2) as determined by confocal microscopy. Dkk3b(dkk3) does not colocalize with transgenic GFP expression in beta or alpha cells. Asterisks indicate cells with a strong dkk3b(dkk3) expression. Scale bars correspond to 50 μm. All embryos are shown from dorsal with anterior to the left (A?G). |
Reprinted from Gene expression patterns : GEP, 11(8), Untergasser, G., Martowicz, A., Hermann, M., Töchterle, S., and Meyer, D., Distinct expression patterns of dickkopf genes during late embryonic development of Danio rerio, 491-500, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns