- Title
-
Balancing cell numbers during organogenesis: Six1a differentially affects neurons and sensory hair cells in the inner ear
- Authors
- Bricaud, O., and Collazo, A.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
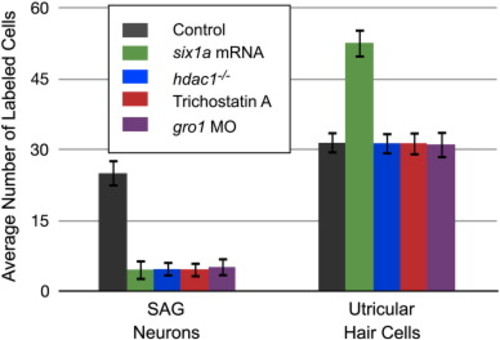
The function of Six1a as a transcriptional repressor in the neuronal lineage of the developing zebrafish inner ear likely involves Hdac1 and Gro1. Loss of function of either hdac1 or gro1 leads to a decrease in number of neurons similar to that observed when six1a is over-expressed. Effects of perturbing these molecules are restricted to the neuronal lineage. Average number of hair cells and neurons in 3 dpf utricular maculae and SAG. Hair cells and neurons were detected by HCS-1 and HuC immunolabeling, respectively, using confocal microscopy. Values represent mean cell counts (± standard deviation) with a sample size of 20 for each experiment. Statistical analyses were performed for both panels with Student′s t test; all comparisons were made to embryos injected with standard MO control (STD) or with six1a mRNA. Comparisons where P < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
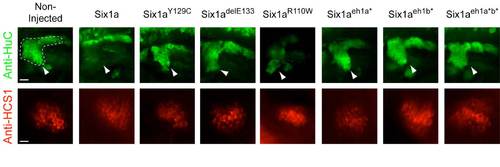
Otic neurons and anterior macula hair cells in a 3 dpf developing zebrafish inner ear. Otic neurons in 3 dpf zebrafish larvae over-expressing mutant forms of Six1a have been detected by anti-HuC immunostaining (upper panels, in green; arrowheads and surrounded by a dotted line in the first panel) whereas hair cells of the anterior macula of 3 dfp zebrafish larvae over-expressing the same mutant forms of Six1a have been detected by anti-HCS-1 immunostaining (lower panels, in red). The upper panels are in a lateral orientation with a scale bar of 30 μm whereas the lower panels are ventral views with a scale car of 20 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
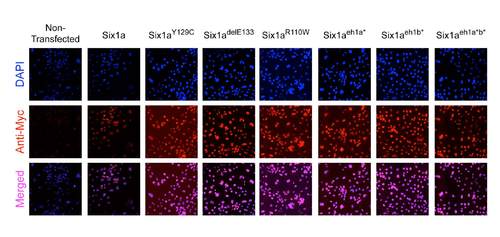
Anti-Myc immunohistochemistry on COS-7 cells transfected with the different mutant forms of Six1a. Co-localization with DAPI staining shows that the generated mutations do not alter either the expression or the nuclear localization of the Six1a proteins. |
|
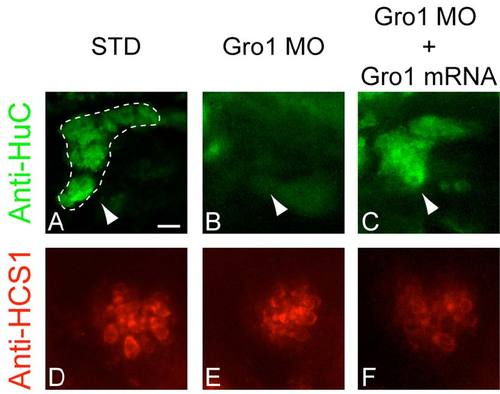
Otic neurons (upper panels, in green; pointed to by arrowheads and surrounded by a dotted line in first panel) and anterior macula hair cells (lower panels, in red) in 3 dpf zebrafish larvae in which Gro1 has been knocked-down by morpholinomodified oligonucleotide injection (B, E), or in which the effect of the Gro1 knock-down has been rescued by injection of Gro1 mRNA (C, F). Otic neurons have been detected by anti-HuC immunostaining whereas hair cells of the anterior macula have been detected by anti-HCS-1 immunostaining. Gro1 mRNA has been generated from a Nterminal HA (Hemagglutinin A)-tagged gro1 cDNA, generated by cloning the zebrafish gro1 cDNA in phase into the pCMV-HA vector (Clontech, Mountain View, CA, USA). Adding the HA tag perturbs the integrity of the MO-binding site on gro1 mRNA, preventing binding of the MO. Upper panels are lateral views with a scale bar of 30 μm, lower panels are ventral views with a scale car of 20 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 357(1), Bricaud, O., and Collazo, A., Balancing cell numbers during organogenesis: Six1a differentially affects neurons and sensory hair cells in the inner ear, 191-201, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.