- Title
-
Zebrafish as a Model System to Study the Physiological Function of Telomeric Protein TPP1
- Authors
- Xie, Y., Yang, D., He, Q., and Songyang, Z.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
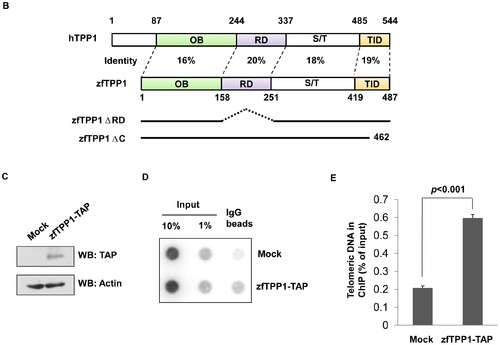
Characterization of zfTPP1. (A) Schematic representation of domain organization of human and zebrafish TPP1. OB, oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide binding fold. RD, POT1 recruitment domain. S/T, Serine-rich region. TID, TIN2-interacting domain. (B) Expression of TAP-tagged zfTPP1 in zebrafish cells. Whole cell extracts from parental and TAP-tagged zfTPP1 expressing zebrafish cell line ZF4 were western blotted with peroxisome-conjugated protein A. Actin was used as a loading control. (C) Telomere association of zfTPP1. Parental and TAP-tagged zfTPP1 expressing ZF4 cells were crosslinked and used for chromatin immunoprecipitation with protein A beads. The precipitated DNA was analyzed by southern blotting. (D) Quantification of data in D. Error bars indicate standard error (n = 3). |
|
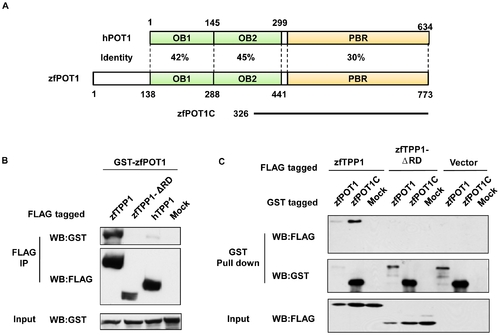
zfTPP1 interacts with zfPOT1. (A) Schematic representation of domain homology between human and zebrafish POT1. PBR, TPP1-binding region. (B) The RD domain is important for zfTPP1-zfPOT1 interaction. Extracts from 293T cells co-expressing GST-tagged zfPOT1 with FLAG-tagged full-length zfTPP1, zfTPP1-ΔRD (RD domain deletion mutant), or hTPP1 were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibodies, and analyzed by western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (C) The C-terminal region of POT1is important for its interaction with zfTPP1. Extracts from 293T cells co-expressing FLAG-tagged zfTPP1 or zfTPP1-ΔRD with GST-tagged full-length zfPOT1 or zfPOT1 C terminal domain (zfPOT1C) were immunoprecipitated with anti-GST antibodies and analyzed by western blotting with the indicated antibodies. |
|
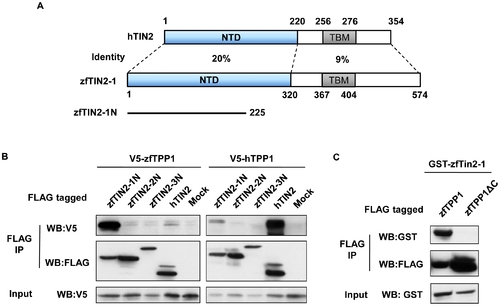
zfTPP1 interacts with zfTIN2-1 through its C-terminus. (A) Schematic representation of domain homology between human and zebrafish TIN2. NTD, N-terminal domain. TBM, TRFH-binding motif. (B) zfTPP1 interacts with zfTIN2-1. Extracts from 293T cells co-expressing V5-tagged zfTPP1 or hTPP1, together with FLAG-tagged N terminal part of zfTIN2-1, zfTIN2-2, or zfTIN2-3, were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibodies and western blotted. FLAG-tagged hTIN2 was also included. (C) The C terminal domain of zfTPP1 mediates its interaction with zfTIN2-1. Extracts from 293T cells co-expressing GST-tagged full-length zfTIN2-1 with FLAG-tagged full-length zfTPP1 or zfTPP1-ΔC were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and western blotting. |
|
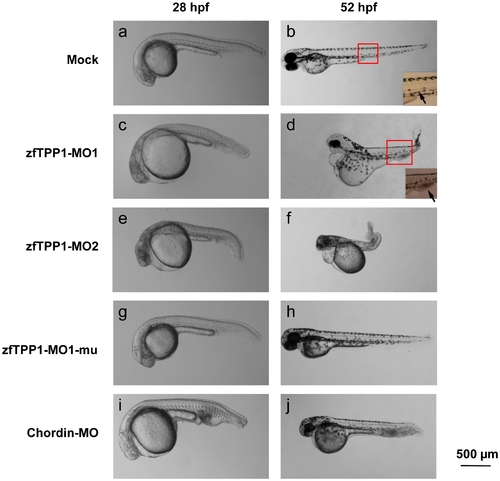
Expression of zfTPP1 morpholinos leads to defects in embryonic development. Mock injected zebrafish embryos (a, b) and those injected with zfTPP1 MO1 (6 ng) (c, d) and MO2 (3 ng) (e, f), zfTPP1 MO1 mutant (6 ng) (g, h), or Chordin MO (6 ng) (i, j), were observed under the microscope at 28 and 52 hour post fertilization (hpf). Magnified images of the trunk region of mock and MO1 injected embryos were also included. Arrows indicate blood in the embryos. Scale bar, 500 μm. |
|
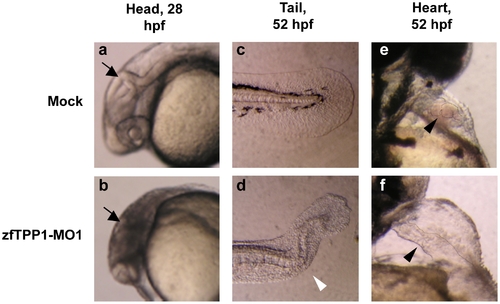
zfTPP1 knockdown results in defects in the brain, tail and heart. Mock (a, c, e) and zfTPP1-MO1 injected embryos (b, d, f) were visualized at the indicated time points. In a and b, arrows point to the brain. In c and d, arrowhead indicates a curly tail. In e and f, arrowheads point to the heart. |
|
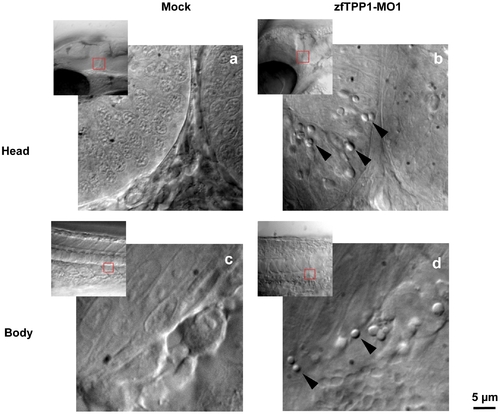
zfTPP1 knockdown leads to accumulation of button-like structures. Nomarski DIC images of regions of the head (a, b) and body (c, d) of mock and zfTPP1 MO1 (6 ng) injected embryos were obtained at 28 hpf. Button-like structures are indicated by arrows. Scale bar, 5 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
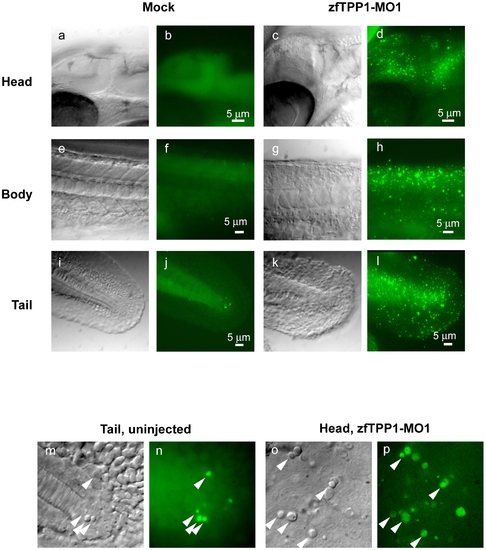
zfTPP1 knockdown induces apoptosis. Embryos injected with zfTPP1 MO1 were stained with acridine orange and visualized (at 28hpf) under Nomarski DIC and fluorescent microscopes (scale bar, 5 μm). Magnified Nomarski DIC and fluorescent images (28 hpf) of the tail (mock injected) (m, n) and head region (zfTPP1 MO1 injected) (o, p) of zebrafish embryos. Arrowheads indicate button-like structures. PHENOTYPE:
|