- Title
-
Characterization of neural stem cells and their progeny in the adult zebrafish optic tectum
- Authors
- Ito, Y., Tanaka, H., Okamoto, H., and Ohshima, T.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
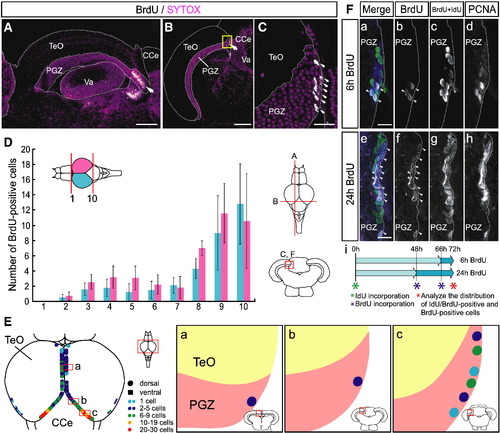
Proliferating cells are distributed through the dorsomedial area of the caudal region of the PGZ in the adult zebrafish optic tectum. (A?C) Proliferating cells in the adult zebrafish optic tectum. Proliferating cells are labeled by 72-hour BrdU administration (white). Cell Nuclei are stained by SYTOX orange (red). (A) Sagittal section of adult zebrafish optic tectum (single plane, anterior left). A large cluster of BrdU-positive proliferating cells are distributed in the caudal region of the PGZ (arrow). (B) Transverse section of the caudal region of the adult zebrafish optic tectum (single plane, dorsal top). BrdU-positive proliferating cells are distributed through the dorsomedial area of the PGZ (arrow). (C) A high magnification view of the dorsomedial area of the PGZ, indicated by the yellow box in B (single plane, dorsal top). BrdU-positive proliferating cells are located on the dorsomedial margin (arrows). (D) Quantitative data of the distribution of BrdU-positive proliferating cells in the PGZ of the adult zebrafish optic tectum. The whole tectal region is divided into 10 parts along the rostrocaudal axis. Large numbers of proliferating cells are distributed through the caudal region of the optic tectum PGZ. Data are expressed as means ± SEM; n = 3. (E) Schematic drawing of the distribution of proliferating cells in the adult zebrafish optic tectum (dorsal view, anterior top, (a?c) transverse view, dorsal top). Proliferating cells are located along the dorsomedial and ventrolateral margins of the PGZ. The majority of BrdU-positive proliferating cells reside in the dorsomedial area of the PGZ caudal region (c). (F) Dorsomedial distribution of proliferating cells after 6 h (a?d) and 24 h of (e?h) BrdU labeling. One-third and one-half of the proliferating cells are labeled by 6 h and 24 h of BrdU administration, respectively (a, b, e, f, arrowheads). Most of the PCNA-positive cells are labeled by 72 h of continuous administration of IdU or BrdU, and visualized by BrdU antibody which detects both BrdU and IdU (c, g). Whole population of proliferating cells as visualized by immunohistochemistry with anti-PCNA antibody (d, h). IdU and BrdU double-labeling scheme is illustrated in panel i. CCe, corpus cerebelli; PGZ, periventricular gray zone; Tel, telencephalon; TeO, tectum opticum; Va, valvula cerebelli. Scale bars: 200 μm in A, B; 20 μm in C; 10 μm in F. |
|
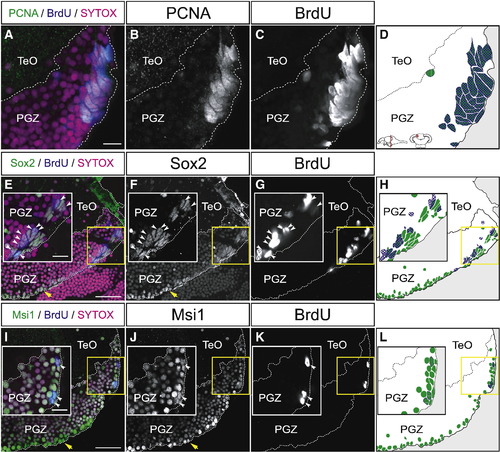
Proliferating cells in the dorsomedial area of the PGZ express neural stem/progenitor cell markers. (A?L) Expression of PCNA (A?D), Sox2 (E?H), and Msi1 (I?L) in the dorsomedial area of the PGZ of the adult zebrafish optic tectum (60 μm transverse sections, single planes, dorsal top). Proliferating cells are labeled with BrdU after 72 h of incubation. Insets in E?L show magnified views of the yellow-boxed areas. (A?D) Most PCNA-positive cells incorporate BrdU after 72 h of BrdU administration. (E?F) The majority of BrdU-positive proliferating cells (insets, arrowheads), and the cells that reside in the ventral edge of the PGZ (yellow arrows) express Sox2. (I?L) A subset of BrdU-positive cells (insets, arrowheads), and the cells that reside in the ventral edge of the PGZ (yellow arrows) express Msi1. CCe, corpus cerebelli; PGZ, periventricular gray zone; TeO, tectum opticum. Scale bars: 10 μm in A, insets of E, I; 30 μm in E, I. |
|
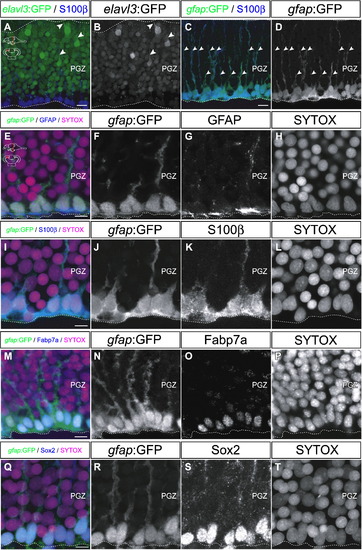
Cells constitute the deep layer of the PGZ are radial glia. (A?D) Distribution of elavl3:GFP-positive cells (A, B) and gfap:GFP-positive cells (C, D) in the PGZ of the adult zebrafish optic tectum (60 μm transverse sections, dorsal top). (A, B) The elavl3:GFP-positive cells are distributed through a broad area of the PGZ, except for the S100β-positive ventral edge. Only a few cells express strong GFP signal and extend dendrite-like processes toward the surface layers of the optic tectum (arrowheads). (C, D) The gfap:GFP-positive cells are distributed along the ventral edge of the PGZ, and extend radial fibers (arrowheads). (E?T) Magnified views of the gfap:GFP-positive cells along the ventral edge of the PGZ (60 μm transverse section, dorsal top). The gfap:GFP-positive cells constitute the deep layer of the PGZ. These cells show immunoreactivities with glial markers, such as GFAP, S100β and Fabp7a (E?P), and the neural stem/progenitor marker Sox2 (Q?T). Scale bars: 10 μm in A, C; 5 μm in E, I, M, Q. |
|
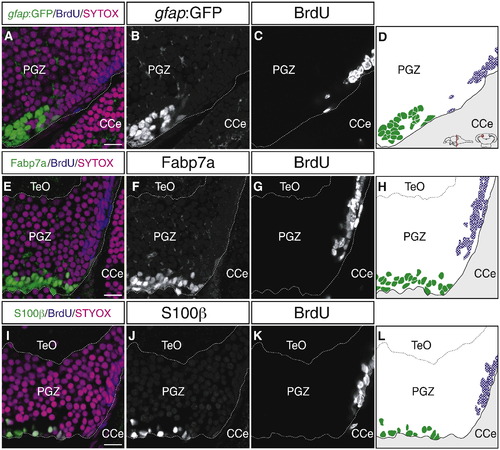
Proliferating cells in the PGZ do not express glial markers. (A?L) Expression of gfap:GFP (A?D), Fabp7a (E?H), and S100β (I?L) in the PGZ of the adult zebrafish optic tectum (60 μm transverse sections, single planes, dorsal top). Proliferating cells are labeled after 72 h of BrdU administration. In the medial region of the PGZ, BrdU-positive proliferating cells (blue) do not express the glial markers, gfap:GFP, Fabp7a and S100β (green); these glial markers are expressed in the deep layer cells. CCe, corpus cerebelli; PGZ, periventricular gray zone; TeO, tectum opticum. Scale bars: 10 μm. |
|
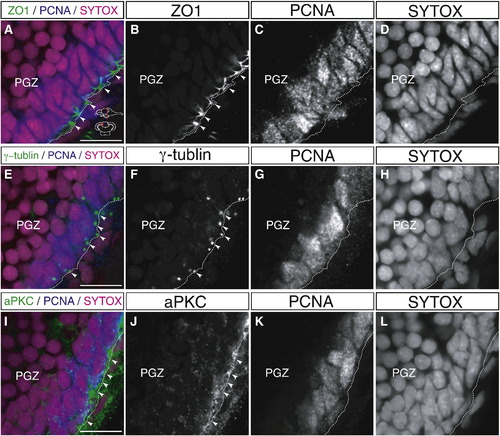
Proliferating cells which face the ventricle maintain apical?basal polarity. (A?L) Localization of apical markers, ZO1 (A?D), γ-tubulin (E?H), and aPKC (I?L) in the proliferating cells of the PGZ of the adult zebrafish optic tectum (60 μm transverse sections, single planes, dorsal top). The proliferating cells are visualized by immunohistochemistry with anti-PCNA antibody. The proliferating cells which localize near the ventricle show highly polarized expression of apical markers such as ZO1 (A, B, arrowheads), γ-tubulin (E, F, arrowheads), and aPKC (I, J, arrowheads). Scale bars: 10 μm. |
|
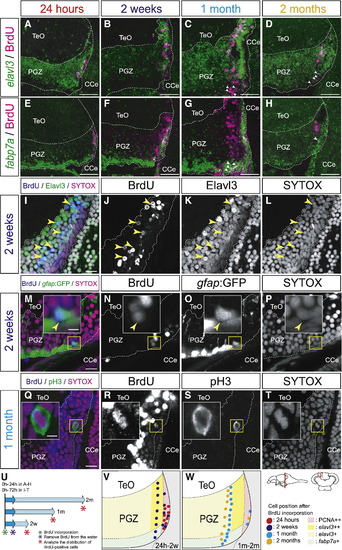
Neural stem/progenitor cells in the mitotic region of the PGZ generate both neuronal and glial cell lineages. (A?H) Distributions of BrdU-positive cells in the elavl3-positive superficial layer (A?D), and the fabp7a-positive deep layer (E?H) of the PGZ in the adult zebrafish optic tectum at 24 h (A, E), 2 weeks (B, F), 1 month (C, G), and 2 months (D, H) post-BrdU administration (14 μm transverse sections, stacked images, dorsal top). After 2 weeks post-BrdU administration, most of the BrdU-positive cells express elavl3 (B?D), however, some BrdU-positive cells express fabp7a but not elavl3 (C, D, G, H, arrowheads). (I?P) Expression of Elavl3 (I?L) and gfap:GFP (M?P) in the BrdU-positive cells at 2 weeks post-BrdU administration (60 μm transverse sections, single planes, dorsal top). Insets in M?P show magnified views of the yellow-boxed areas. The majority of BrdU-positive cells expressed the neuronal marker Elavl3 (I?L), and some BrdU-positive cells expressed the glial maker gfap:GFP (M?P, insets, arrowheads). (Q?T) Distribution of pH3-positive cells in the PGZ at 1 month post-BrdU administration (60 μm transverse sections, single planes, dorsal top). Insets in Q?T show magnified views of the yellow-boxed areas. At 1 month post-BrdU administration, majority of BrdU-positive cells leave the dorsomedial margin (Q, R), while BrdU-positive cells facing the ventricle still undergo cell division and expresses the M-phase marker, pH3 (Q?T, insets). (U) BrdU pulse labeling scheme. (V, W) Summaries of the distribution of BrdU-positive cells at 24 h to 2 weeks (V), and at 1 month to 2 months (W) post-BrdU administration. CCe, corpus cerebelli; PGZ, periventricular gray zone; TeO, tectum opticum. Scale bars: 50 μm in A?H; 10 μm in I, M, Q; 3 μm in inset of M, Q. |
|
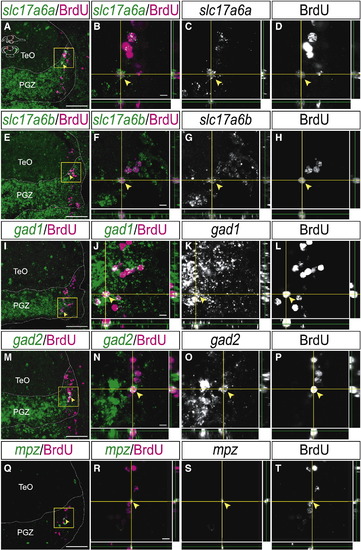
Neural stem/progenitor cells in the mitotic region of the PGZ differentiate into the glutamatergic or GABAergic neurons and oligodendrocytes. (A?P) Expression of glutamatergic and GABAergic neuronal markers in the BrdU-positive cells in the PGZ of the adult zebrafish optic tectum at 1 month post-BrdU administration (14 μm transverse sections, stacked images, dorsal top). (A?H) Some of the BrdU-positive cells express glutamatergic neuronal markers, slc17a6a (A?D, arrowheads) and slc17a6b (E?H, arrowheads) (B?D: high magnification of yellow-boxed area in A, F?H: high magnification of yellow-boxed area in E). (I?P) Some of the BrdU-positive cells express GABAergic neuronal markers, gad1 (I?L, arrowheads) and gad2 (M?P, arrowheads) (J?L: high magnification of yellow-boxed area in I, N?P: high magnification of yellow-boxed area in M). (Q?T) Expression of oligodendrocyte marker, mpz in the BrdU-positive cells in the PGZ of the adult zebrafish optic tectum at 1 month post-BrdU administration (arrowheads) (14 μm transverse sections, stacked images, dorsal top) (R?T: high magnification of the yellow-boxed area in Q). CCe, corpus cerebelli; PGZ, periventricular gray zone; TeO, tectum opticum. Scale bars: 50 μm in A, E, I, M, Q; 5 μm in B, F, J, N, R. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 342(1), Ito, Y., Tanaka, H., Okamoto, H., and Ohshima, T., Characterization of neural stem cells and their progeny in the adult zebrafish optic tectum, 26-38, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.