- Title
-
Gata5 and Gata6 are functionally redundant in zebrafish for specification of cardiomyocytes
- Authors
- Holtzinger, A., and Evans, T.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
The gata5 morpholinos can be used to phenocopy the faust mutant. (A, B) Shown are representative embryos following in situ hybridization using a gata5-specific probe at 24 hpf analyzing (A) wild-type embryos or (B) embryos injected with a gata5 morpholino that targets a splice site (ssG5 MO). Injection of ssG5 MO efficiently blocks accumulation of mature gata5 mRNA. While most embryos lack detectable message, the embryo shown in panel B represents an example of one that demonstrates a low level of remaining transcripts in a bifid pattern. (C?M) Shown are representative embryos following whole mount situ hybridization to detect transcripts for the cardiac marker nkx2.5 at 24 hpf. Samples represent results with (C) wild-type embryos (D, E) embryos injected with a translation-blocker morpholino specific to gata5 (tbG5), (F?I) ssG5 morphants, and (J?M) embryos derived from crossing two adult fish heterozygous for the faus26 allele. The ssG5 morphants display the same variable expressivity phenotype as the faus26 mutants, including embryos with a fused heart tube (F, J), a partially fused tube (G, K), cardia bifida (H, L) or a significant reduction of cardiac progenitors (I, M). The tbG5 morpholino more reproducibly generates cardia bifida. See Table 1 for all statistics. In panels A and B, embryos were flat mounted, views are dorsal, with anterior to the left. All other views are dorsal, with anterior to the top. |
|
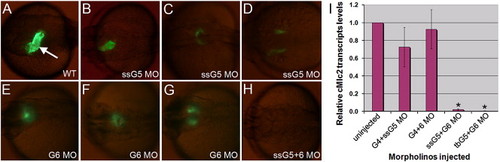
Embryos targeted for gata5 and gata6 fail to express GFP in a cmlc2:gfp reporter line. (A) A typical cmlc2:gfp embryo at 30 hpf shows GFP+ cardiomyocytes forming a heart tube (arrow). (B?G) Examples are shown representing cardiac phenotypes generated by injection of the ssG5 MO (B?D) and G6 MO (E?G). (H) Co-injection of ssG5 MO and G6 MO results in an absence of GFP+ cardiomyocytes. Brightness of GFP appears lower in the reproduced images of panels B?G compared to panel A, because the injected embryos are slightly delayed, but also because the signal is more diffuse in the defective heart tubes. (I) Quantitative real-time PCR for cmlc2 transcripts. Endogenous cmlc2 transcript levels are reduced to approximately 1% the normal level in ssG5+6 and tbG5+6 double morphants (p < 0.01). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
The gata5 and gata6 genes are functionally redundant for atrial cardiomyocyte differentiation. Shown in each panel is a typical representative embryo following processing by whole mount in situ hybridization to detect transcripts for the atrial cardiomyocyte marker amhc at 32 hpf. Samples represent: wild-type embryos (WT), gata4 morphants (G4 MO), gata6 morphants (G6 MO), gata5 morphants (ssG5 MO or tbG5 MO), gata4+5 double morphants (G4+ssG5 MO or G4+tbG5 MO), gata4+6 double morphants (G4+6 MO), and gata5+6 double morphants (ssG5+6 MO and tbG5+6 MO). Despite morphogenetic defects, the atrium is specified in both gata4+6 and gata4+5 double morphants. However, ahmc transcripts are not detectable in gata5+6 double morphants. While these results were reproduced in multiple independent experiments, the number of embryos from the experiment represented in this figure by the phenotype (x) for a given number of embryos (n) is shown in each panel (x/n). Views are either ventral or dorsal, depending on the heart tube position, with anterior to the top. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
The gata5 and gata6 genes are functionally redundant for ventricular cardiomyocyte differentiation. Shown in each panel is a typical representative embryo following processing by whole mount in situ hybridization to detect transcripts for the ventricular cardiomyocyte marker vmhc at 32 hpf. Samples represent: wild-type embryos (WT), gata4 morphants (G4 MO), gata6 morphants (G6 MO), gata5 morphants (ssG5 MO or tbG5 MO), gata4+5 double morphants (G4+ssG5 MO or G4+tbG5 MO), gata4+6 double morphants (G4+6 MO), and gata5+6 double morphants (ssG5+6 MO and tbG5+6 MO). Despite morphogenetic defects, the ventricle is specified in both gata4+6 and gata4+5 double morphants. However, vmhc transcripts are not detectable in gata5+6 double morphants. Note that staining is unperturbed in the somites, showing that the defect is specific to the heart. While these results were reproduced in multiple independent experiments, the number of embryos from the experiment represented in this figure by the phenotype (x) for a given number of embryos (n) is shown in each panel (x/n). Views are ventral, with anterior to the top. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
The gata5 and gata6 genes are functionally redundant for cardiomyocyte specification. Shown in each panel is a typical representative embryo following processing by whole mount in situ hybridization to detect transcripts for the cardiomyocyte progenitor marker nkx2.5 at the 17-somite stage. (A) wild-type embryos, (B) gata4 morphants, (C) gata5 (ssG5) morphants, (D) gata6 morphants, (E) gata4+5 (ssG5) double morphants, (F) Gata4+6 double morphants and (G) Gata5(ssG5)+6 double morphants. The cardiogenic program is initiated and cardiomyocytes are specified in both gata4+6 and gata4+5 double morphants. However, the early cardiac progenitors are missing in gata5+6 morphants. Embryos were flat-mounted; views are dorsal, with anterior to the top. Reproduced in multiple independent experiments, the phenotypes/number of embryos from this experiment represent A: 17/17; B: 20/20; C + D combined: 26/26; E: 29/29; F: 25/25; G: 25/25. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
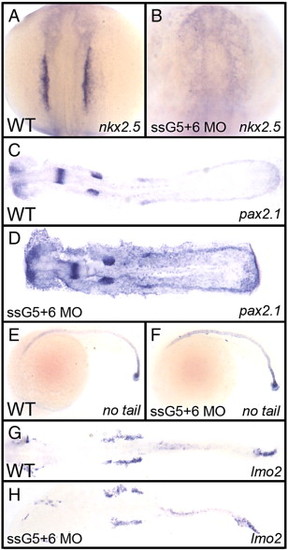
The defect in gata5+6 morphants is specific to cardiac mesoderm. Shown in each panel is a typical representative embryo following processing by whole mount in situ hybridization. Embryos were either wild-type (A, C, E, G) or gata5(ssG5)+6 double morphants (B, D, F, H). (A, B) The cardiomyocyte progenitor marker nkx2.5 at the 12-somite stage shows the lack of cardiac progenitors in gata5+6 morphants. (C, D) The pronephric marker pax2.1 shows that the intermediate mesoderm was not affected in morphants. (E, F) The axial mesoderm marker no tail shows that gata5+6 morphants develop a normal notochord. (G, H) The lateral plate mesoderm, marked by the lmo2 probe, is also not altered in gata5+6 morphants. (A and B) views are dorsal, with anterior to the top. (C, D, G, and H) embryos were flat mounted, views are dorsal, with anterior to the left. (E and F) Views are from the left side, with anterior to the left. These panels represent patterns seen in A: 39/39; B: 38/38; C: 10/10; D: 23/23; E: 26/26; F: 45/45; G: 28/28; H: 42/42. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 312(2), Holtzinger, A., and Evans, T., Gata5 and Gata6 are functionally redundant in zebrafish for specification of cardiomyocytes, 613-622, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.