- Title
-
Notch signaling controls the differentiation of transporting epithelia and multiciliated cells in the zebrafish pronephros
- Authors
- Liu, Y., Pathak, N., Kramer-Zucker, A., and Drummond, I.A.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
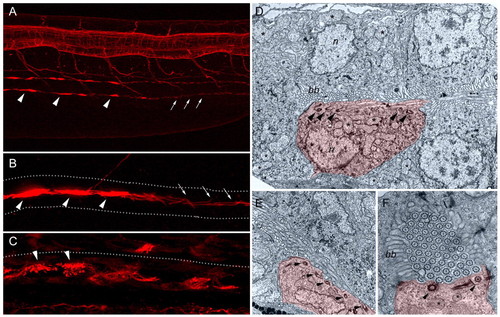
Distribution of multiciliated cells and transporting epithelia containing single cilia in the pronephros. (A) Whole-mount immunofluorescence of the trunk region of a 48 hpf embryo stained with anti-acetylated tubulin reveals bright cilia bundles (arrowheads) in the pronephric lumens, as well as single ciliated cells (arrows) in a more caudal nephron segment. (B) At higher magnification, compressed bundles of cilia (arrowheads) and single cilia (arrows) can be observed in the pronephric lumen. (C) Bundles of cilia emanating from individual cells project into a distended lumen of a mechanically obstructed pronephros. Dotted lines in B and C outline the pronephric tubules. (D-F) Electron micrographs of the pronephros show isolated multiciliated cells (MCC; false-colored in red) interspersed among transporting epithelial cells (false-colored in light blue). Arrowheads show apical basal bodies. (D) MCCs are distinguished by multiple apical basal bodies, by the lack of a brush border (bb), by a small basal cell surface and by multiple apical cilia (asterisks). n, nucleus. (E) Example of an MCC with multiple apical cilia basal bodies, and bundles of cilia in the lumen. (F) Cross section of a pronephric tubule in a 7 dpf larva, showing a single MCC with multiple basal bodies, apical mitochondria (asterisks) and bundles of cilia fitting tightly into the pronephric lumen. |
|
MCCs and transporting epithelia co-exist as separate cell types in the early distal segment of the pronephric nephron. (A) Expression of the axonemal-sheath gene shippo1 in the pronephros of a 34 hpf embryo. (B) Expression of the transcription factor rfx2 in individual pronephric cells. (C) Expression of the cation transporter trpM7 in the early distal segment of the pronephric nephron. (D) Expression of the sodium-sulfate co-transporter slc13a1 in the early distal segment. (E) Double in situ hybridization of the MCC marker shippo1 (red) and slc13a1 (purple) in distinct but adjacent cells of the early distal segment in a 34 hpf embryo. (F) Double in situ hybridization of shippo1 and trpM7 in early distal segment cells. (G) Expression of GFP from the Na,K-ATPase alpha a1A4 subunit promoter is uniform in the most caudal nephron segment (arrowhead) and heterogeneous in the distal nephron. (H,I) Double staining for GFP and acetylated tubulin (red) in confocal z-series projections (H) and in histological sections (I) shows that the Na,K-ATPase alpha a1A4 promoter is not active in MCCs (arrows, arrowhead; cell bodies are outlined with dashed line). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Confocal fluorescent in situ hybridization analysis of ion transporter and ciliogenic gene expression in the pronephros. (A,B) Double staining for shippo1 mRNA (in situ hybridization; green) and acetylated tubulin (immunofluorescence; red) in confocal projections reveals several examples of cilia bundles emanating from shippo1-positive cells (arrowheads) into the lumen; single cilia emanate from shippo1-negative cells (small arrows). Dotted lines outline the pronephros; posterior is to the right. (C-E) Co-expression of shippo1 (C; green) and fleer (D; red) in single cells of the pronephric tubules. (E) Merged image. (F-H) Co-expression of shippo1 (F; green) and rfx2 (G; red) in single cells of the pronephric tubules. (H) Merged image. (I-K) Expression of shippo1 (I; green) and slc13a1 (J; red) in distinct but adjacent cells of the pronephric tubules. (K) Merged image. (L-N) Expression of shippo1 (L; green) and trpM7 (M; red) in distinct but adjacent cells of the pronephros. (N) Merged image. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
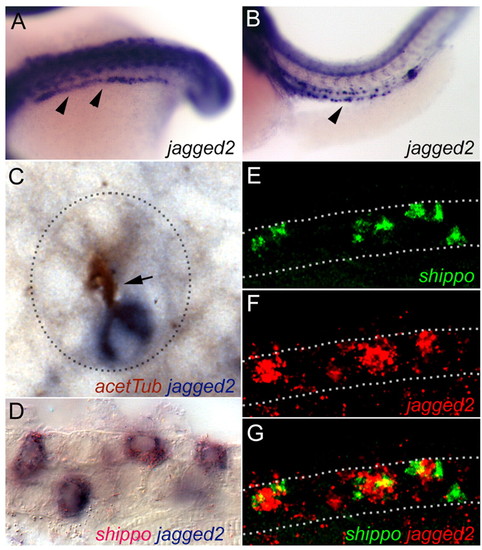
jagged 2 expression in multiciliated cells. (A,B) Whole-mount in situ hybridization showing expression of jagged 2 (arrowheads) at the 18-somite stage in cells of the intermediate mesoderm (A) and in individual cells of the pronephros at 42 hpf (B). (C) Cross section of the pronephros double stained for acetylated tubulin (HRP:DAB immunohistochemistry) and jagged 2 (in situ hybridization) shows that isolated jagged 2-positive cells possess apical cilia bundles (arrow). Dashed line outlines the cross section of the pronephric tubule. (D) Double in situ hybridization with the MCC marker shippo1 (red) and jagged 2 (blue) demonstrates jagged 2/shippo1 co-expression in isolated single cells. (E-G) Confocal optical section of the pronephros in situ hybridized for shippo1 mRNA (E; green) and jagged 2 (F; red) confirm jagged 2 expression in shippo1-positive MCCs. (G) Merged image. Dotted lines outline the pronephros. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
jagged 2 loss of function transfates pronephric cells to MCCs. Three markers of MCCs - shippo1 (A-C), flr (D-F) and rfx2 (G-I) - show expanded expression in the pronephros of jagged 2 morphants at 34 hpf. Control invert morpholino (A,D,G) had no effect on MCC-marker expression, whereas ATG blocking (J2atgMO; B,E,H) and exon 20 mis-splicing morpholinos (J2ex20MO; C,F,I) resulted in uniform expression of MCC markers. (J) MCCs exist as single cells (arrowheads; flr-expressing cells) in the wild-type pronephros in cross section. (K,L) Expressions of shippo1 (K) and flr (L) expand to include all cells in tubule cross sections in J2exon20 morphant embryos. (M-O) slc13a1 expression seen in the control (M) is lost in J2atg (N) and J2exon20 (O) morphants. Similarly, the observed expression of trpM7 in control morpholino-injected embryos (P) is lost in J2exon20 morphants (Q). Control jagged 2 morpholino does not alter the single-cell jagged 2 mRNA expression pattern (R), whereas combined injection of both jagged 2 atg and exon 20 antisense morpholinos (U) result in expanded jagged 2 mRNA expression. (S) Na,K-ATPase:GFP transgenic zebrafish express GFP in the pronephros distal segments (arrowheads). (T) GFP expression is lost specifically in the distal segment of jagged 2 exon 20 morphant embryos (arrowheads). |
|
Notch3 mediates Jagged 2 signaling in the pronephros. (A) Expression of notch3 in the pronephros (arrowheads). (B) Expression of notch3 in the proximal pronephric tubules (arrowhead). (C,D) shippo1 expression in single cells of control embryos at 34 hpf (C) is expanded by notch3 exon 27-morpholino injection (D). (E,F) Similarly, expression of flr that is observed in control embryos (E) is expanded in notch3 exon 27 morphants (F). (G,I) Transporting-cell markers slc13a1 (G) and trpM7 (I) are greatly reduced in notch3 exon 27 morphants (H and J, respectively). |
|
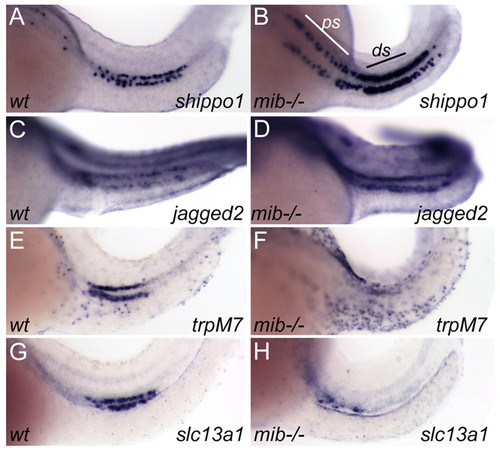
Transfating of pronephric cells in the mind bomb mutant. (A,B) shippo1 expression in control wild-type embryos is restricted to single cells (A), whereas, in mind bomb homozygotes (B), pronephric distal segment cells (ds) are uniformly positive and there is an increase in shippo1-positive cells in the proximal segment (ps). (C,D) Wild-type jagged 2 expression (C) is also expanded in mind bomb homozygotes (D). (E,G) trpM7 (E) and slc13a1 (G) expression is almost completely lost in mind bomb homozygotes (F and H, respectively). |
|
Inhibition of gamma-secretase and the timing of Notch signaling in pronephric development. All whole-mount in situ hybridization was performed at 34 hpf. (A-C) The wild-type pattern of shippo1 expression (A) is dramatically expanded when gamma-secretase is inhibited with 100 μM DAPT starting at 9.5 hpf (B) but not when DAPT is added later, at 24 hpf (C). (D-F) Conversely, the number of shippo1-positive cells seen in control embryos (D) is dramatically reduced in the pronephros of embryos induced to ectopically express the Notch1a intracellular domain under the control of HS-GAL4 induction (nicd hs) at either 8 hpf (E) or 9 hpf (F). (G-I) trpM7 expression is lost when DAPT is added at 9.5 hpf (H), but not when it is added later, at 24 hpf (I). (J-L) slc13a1 expression is lost when DAPT is added at 9.5 hpf (K), and also when DAPT is added later, at 24 hpf (L). |
|
Enhanced ciliogenesis and double bubble-mutant rescue by inhibition of Jagged/Notch signaling. (A) Wild-type double bubble (dbb) heterozygotes viewed in confocal projections show alternating thick acetylated tubulin-positive bundles of cilia (arrowheads) in pronephric lumens (individual tubules are marked with asterisks in A-D).(B) jagged 2 exon 20-morpholino injection results in enhanced ciliogenesis, seen here in a single pronephric tubule with a slightly expanded lumen. (C) A single dbb-mutant pronephric lumen showing lossor shortening of cilia bundles (arrowheads), and a grossly dilated lumen(*). (D) dbb-mutant homozygotes injected with jagged 2 exon 20 morpholino recover normal tubule morphology (paired tubules marked with asterisks) and show a dramatic recovery of ciliogenesis.(E) dbb-mutant homozygote at 2.5 dpf showing bilateral cyst formation in the proximal pronephros (arrow). (F) dbb-mutant homozygote injected with jagged 2 exon 20 morpholino at the one-cellstage, showing the absence of cyst formation (arrow; mutant rescue).(G) Histological section of dbb-homozygote pronephros showing a cystic pronephric tubule (*), dilated pronephric tubules (arrow)and edema (#). (H) Histological section of a dbb homozygote injected with jagged 2 exon 20 morpholino at the one-cell stage,showing complete absence of cystic pathology and edema (arrow,wild-type-appearing pronephric tubules; *, normal glomerular structure). (I) Control DMSO-treated dbb-mutant embryo showing cystic proximal pronephros (*). (J) DAPT treatment (100ÁM started at 9.5 hpf) of dbb homozygotes eliminates cystic distension of the pronephros (*, glomerulus; arrow, pronephric tubule). In these experiments, dbb homozygotes were identified independently of cyst formation by the characteristic mutant ventral axis curvature in 25% of embryos from heterozygote pair matings.
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Splicing defects induced by jagged2 and notch3 morpholinos. (A) Injection of jagged2 exon20 splice donor morpholino results in the deletion of the highly conserved exon 20, the out of frame fusion of exons 19 and 21, and the introduction of a stop codon immediately following the exon 19 sequence. (B) Injection of notch3 exon27 splice donor morpholino results in the deletion of exon 27, the out of frame fusion of exons 26 and 28, and the introduction of a stop codon after a string of missense codons following exon 26 sequence. |
|
her9 expression in the pronephros and effect of Jagged2/Notch3 knockdown. (A) Expression of her9 in wild-type embryos. her9 is expressed in the neural tube, somites and bilaterally in the pronephros (arrowheads) at 34 hpf. (B) DAPT treatment (100 μM) starting at 9.5 hpf results in a reduction in her9 expression. (C) her9 expression in mind bomb homozygotes is reduced in general and absent from the pronephros. (D) jagged2 exon 20 morpholino injection, (E) notch3 exon 27 morpholino, or (F) a combination of jagged2 exon 20 and jagged2 atg morpholino injection results in loss of her9 expression in the pronephros (arrowheads in F). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|