- Title
-
Cadherin-4 plays a role in the development of zebrafish cranial ganglia and lateral line system
- Authors
- Wilson, A.L., Shen, Y.C., Babb-Clendenon, S.G., Rostedt, J., Liu, B., Barald, K.F., Marrs, J.A., and Liu, Q.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
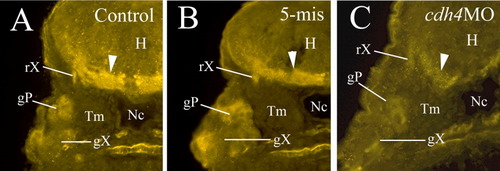
Cdh4 immunostaining showing that Cdh 4 protein expression levels are greatly reduced in a cdh4 morphant injected with RcadMphA (cdh4MO, C) compared to a control embryo (A) or a 5-mis MO-injected embryo (5-mis, B). All panels are cross-sections in the hindbrain region (dorsal is up) at the level of posterior lateral line ganglion and vagal ganglion (55 hpf). The arrowhead points to Cdh4 immunoreactive fiber tracts in the ventral hindbrain. gP, posterior lateral line ganglion; gX, vagal ganglion; H, hindbrain; Nc, notochord; rX, vagal root; Tm, trunk muscles. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
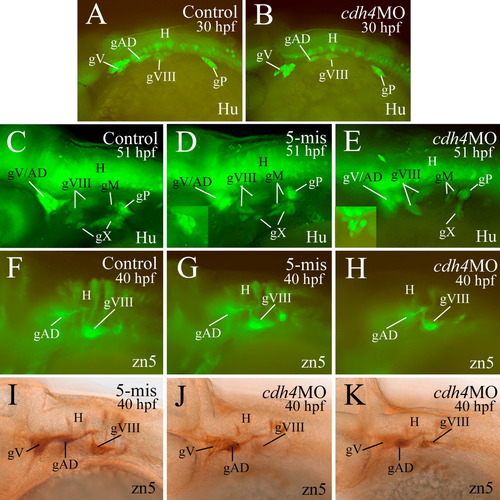
Cranial and lateral line ganglia as revealed by anti-Hu immunostaining (Hu, A-E) and zn5 immunostaining (F-K). All panels are lateral views of whole mount zebrafish embryos with anterior to the left and dorsal up. A-H are from immunofluorescent methods, while panel I-K are from immunoperoxidase methods. The cdh4 morphant in H was from RcadMphB injections, while the remaining morphants were from RcadMphA injections. The trigeminal (gV) and anterodorsal lateral line ganglia (gAD) in D and E were out of focus, and their focused images are shown in their respective insets. J and K are from the same embryo with the former panel focusing on gV and gAD, while the latter one focuses on the statoacoustic ganglion (gVIII). gM, medial lateral line ganglion. Other abbreviations are the same as in Figure 1. |
|
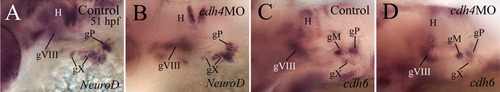
Lateral views of the hindbrain region of whole mount embryos (anterior is to the left and dorsal is up) processed for in situ hybridization using NeuroD (A,B) or cadherin6 (cdh6, C,D) cRNA probes. The cdh4 morphants were from RcadMphA injections. Abbreviations are the same as in Figures 1 and 2. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Cranial and lateral line ganglion nerves in a control embryo (A,B) and an embryo injected with RcadMphA (C,D), as demonstrated by anti-acetylated tubulin immunostaining (an-tub). All panels are lateral views of the hindbrain region with anterior to the left and dorsal up. A and B, C and D are from the same embryos, respectively, with A and C focusing on the gV/AD nerves, and B and D focusing on the gX and gP nerves. nADb, buccal ramus of the anterodorsal lateral line nerve; nADso, superior ophthalmic ramus of the anterodorsal lateral line nerve; nAVm, mandibular ramus of the anteroventral lateral line nerve; nIX, glossopharyngeal nerve; nP, posterior lateral line nerve; nVDl, dorsolateral nerve of the trigeminal ganglion; nX, vagus nerve; rX, vagus root. Other abbreviations are the same as in Figures 1 and 2. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
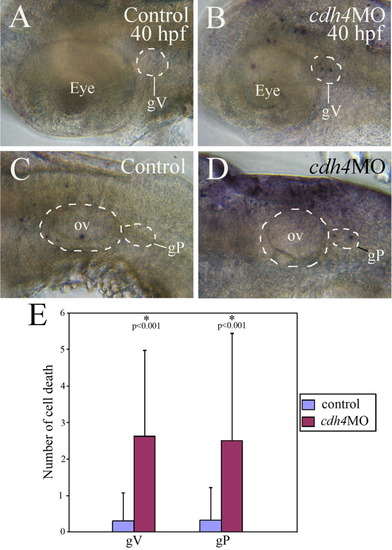
TUNEL staining of whole mount embryos demonstrates increased cell death in cdh4 morphants trigeminal ganglion (gV) and posterior lateral line ganglion (gP). A-D: Lateral views of the embryo head (anterior to the left and dorsal up), with A and B focusing on the eye and gV, and C and D focusing on the otic vesicle (ov) and gP. E: Cell death was significantly greater (P < 0.001) in both the gV and gP of cdh4 morphants (RcadhMphA injected, n = 26) than those of control embryos (n = 37). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
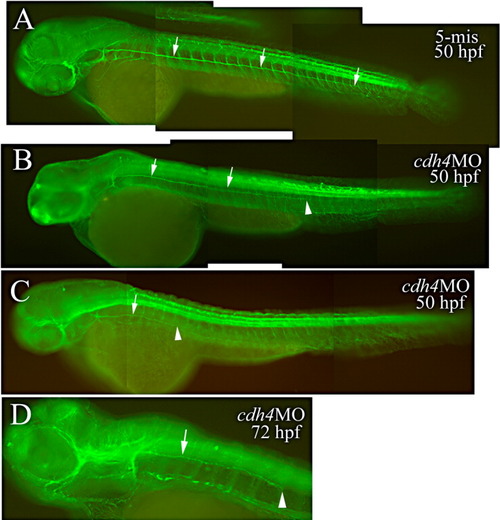
The posterior lateral line system in a 5-mis MO-injected embryo (A) and embryos injected with RcadMphA (B-D) as revealed by anti-acetylated tubulin immunostaining. A-C: Lateral views of whole embryos (50 hpf, anterior to the left and dorsal up) of the same magnification. D: A higher magnification of lateral view of the anterior half of an older cdh4 morphant (72 hpf, anterior to the left and dorsal up). In all panels, arrows point to the lateral line nerve, while the arrowhead indicates the terminus of the lateral line nerve. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
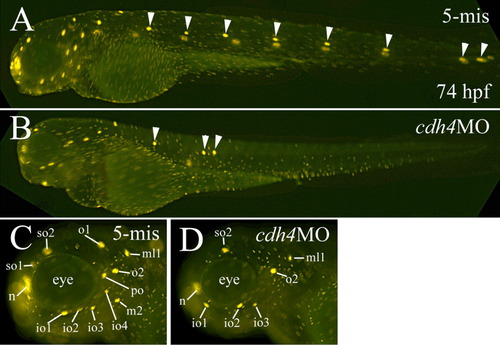
DASPEI labeling of neuromasts in a 5-mis MO-injected embryo (A,C), and embryos injected with RcadMphA (cdh4MO, B,D). A and B are lateral views of whole live embryos (anterior to the left and dorsal up) with the same magnification. The neuromasts in the body and tail on the same side are indicated by arrowheads in these panels. C,D: Higher magnifications of the lateral view of the head region with anterior to the left and dorsal up. io1-4, infraorbital line neuromasts 1-4; n, nasal organ; m2, middle lateral line neuromast 2; ml1, middle line neuromast 1; o1 and o2, otic lateral line neuromasts 1 and 2; po, postorbital neuromast; so1 and so2, supraorbital line neuromasts 1 and 2. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
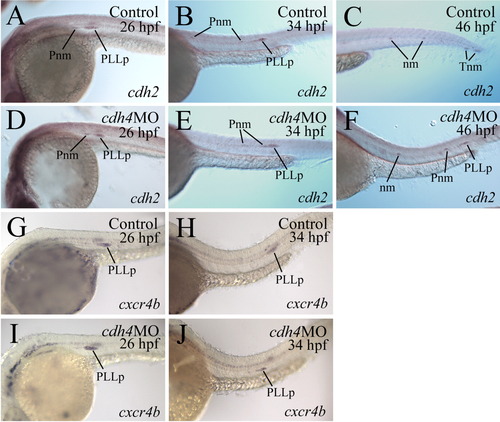
Formation and migration of posterior lateral line primordium (PLLp), and deposition of proneuromasts (Pnm) and neuromasts (nm) in control embryos and embryos injected with RcadMphA as shown by whole mount in situ hybridization using cadherin2 (cdh2, A-F) or cxcr4b (G-J) cRNA probes. C: Lateral view of the mid trunk and tail region of a control embryo, while the remaining panels show lateral views of the mid trunk region of control embryos and cdh4 morphants, with anterior to the left and dorsal up. |

Unillustrated author statements PHENOTYPE:
|