- Title
-
Semaphorin 3d guides laterality of retinal ganglion cell projections in zebrafish
- Authors
- Sakai, J.A., and Halloran, M.C.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
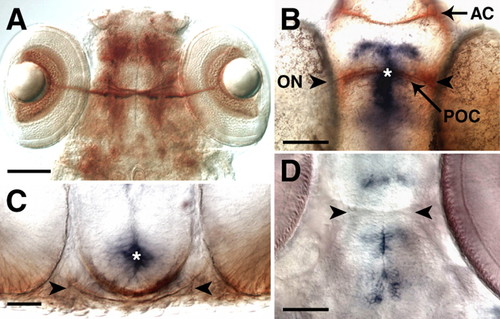
sema3d is expressed at the midline of the ventral diencephalon throughout optic pathway development. A,B,D are ventral views with anterior up; C is a cross-section with dorsal up. (A) RGC axons labeled by Zn-5 immunohistochemistry at 5 dpf form the optic chiasm in the ventral diencephalon. (B,C) sema3d in situ hybridization (blue) and α-tubulin immunohistochemistry (brown) at 36 hpf (B) and 38 hpf (C) show sema3d expression at the midline of the ventral diencephalon, anterior, posterior and dorsal to where RGC axons cross the midline. (D) sema3d expression is maintained in the diencephalon through 5 dpf. Arrowheads show the location of RGC axons, and asterisks indicate the same region of sema3d in B and C. AC, anterior commissure; ON, optic nerve; POC, postoptic commissure. Scale bars: 100 μm in A; 50 μm in B,D; 25 μm in C. |
|
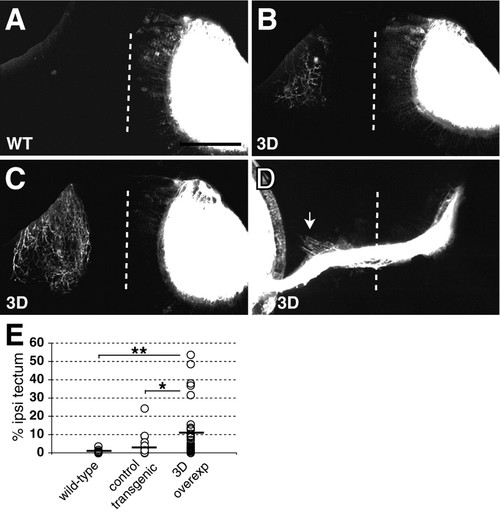
Ubiquitous Sema3d overexpression increases aberrant ipsilateral projections. (A-C) Confocal projections of dorsal views of tecta in 5 dpf wild-type (A) and Sema3d-overexpressing (B,C) embryos show tectal innervation. Left eyes were injected and labeled eyes were digitally removed from images. Wild-type embryos (WT) contained few or no ipsilateral axons (A), whereas Sema3d-overexpressing embryos (3D) contained more extensive ipsilateral arbors (B,C). (D) Confocal projection of a ventral view of the optic chiasm in a 3 dpf Sema3d-overexpressing embryo, injected eye on the left, shows ipsilaterally projecting axons in the region of the optic tract (arrow). Ipsilateral axons are obscured near the midline by the labeled optic nerve in this projection. Dotted lines indicate midlines; anterior is up in all panels. Scale bars: 100 μm in A-C; 63 μm in D. (E) Scatter plot summarizing the extent of ipsilateral tectal innervation in each embryo at 5 dpf; lines indicate means. Sema3d overexpression significantly increased ipsilateral innervation at 5 dpf. WT, n=25; control transgenic embryos, n=20; Sema3d-overexpressing (3D overexp) embryos, n=32. *P<0.05, **P<0.02. |
|
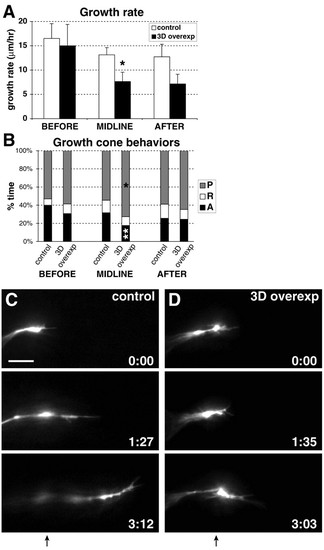
Ubiquitous Sema3d overexpression slows midline growth by increasing growth cone pausing and decreasing growth cone advancing. (A) Overall growth rates in regions before, at and after the midline, reported as mean+s.e.m. Sema3d overexpression significantly decreased RGC growth rate in the midline region. Sema3d-overexpressing embryos, n=14 growth cones in 12 embryos; control embryos, n=2 growth cones in two wild-type embryos, 15 growth cones in 13 heat-shocked wild-type embryos, and two growth cones in two non-heat-shocked Tg(hsp70:sema3dmyc) embryos. (B) Percentage of time growth cones spent advancing, pausing and retracting. Sema3d overexpression significantly increased time spent pausing and significantly decreased time spent advancing in the midline region. P, pausing; R, retracting; A, advancing. Sema3d-overexpressing embryos, n=15 growth cones in 12 embryos; control embryos, n=3 growth cones in two wild-type embryos, 15 growth cones in 12 heat-shocked wild-type embryos, and one growth cone in one non-heat-shocked Tg(hsp70:sema3dmyc) embryo. *P<0.05; **P<0.02. (C,D) Frames taken from timelapse movies of growth cones in representative control (C) and Sema3d-overexpressing (D) embryos. Over a similar time period, the control growth cone extended from the midline into the optic tract, but the growth cone in the Sema3d-overexpressing embryo showed very limited forward growth. Times are indicated in hours:minutes; arrows below frame sequences indicate the midline. Anterior is up in all frames. Scale bar: 10 μm. |
|
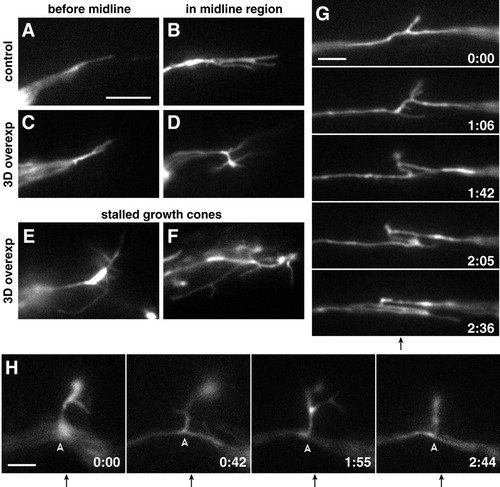
Live imaging reveals increased growth cone complexity and axonal dynamics following ubiquitous Sema3d expression. (A-D) Single frames from timelapse movies show representative RGC growth cone morphology in wild-type (A,B) and Sema3d-overexpressing (C,D) embryos before and at the midline. Sema3d overexpression did not affect morphology before growth cones reached the midline but increased complexity in the midline region. (E,F) Stalled growth cones in Sema3d-overexpressing embryos showed extremely complex morphology. (G,H) Frames taken from timelapse movies of Sema3d-overexpressing embryos show examples of (G) dynamic axonal movements and (H) an interstitial projection (arrowheads) from the midline. Times are reported in hours:minutes; midlines are indicated by arrows below frame sequences. Anterior is up in all frames. Scale bars: 10 μm in A-F; 5 μm in G,H. |
|
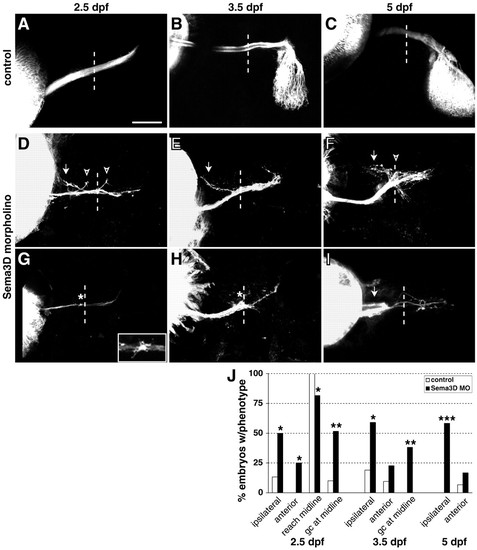
Sema3d knockdown increases ipsilateral guidance errors and reduces midline crossing. (A-I) Confocal projections of DiI-labeled RGC axons in control (A-C) or Sema3d (D-I) morpholino-injected embryos at 2.5 (A,D,G), 3.5 (B,E,H) and 5 (C,F,I) dpf; injected eyes are on the left. A,D-I are ventral views; B and C are dorsal views. Sema3d knockdown caused aberrant projections ipsilaterally (arrows) and anteriorly (arrowheads) from the normal pathway, and increased the occurrence of axons extending to but not beyond the midline (asterisks). Inset in G shows an enlargement of a growth cone near midline. Dotted lines indicate midlines; anterior is up in all panels. Scale bars: 50 μm in A,D-I; 80 μm in B,C. (J) Summary of guidance and extension errors following Sema3d morpholino (Sema3d MO) knockdown. At 2.5 dpf: control morpholino, n=30 for all analyses; Sema3d morpholino, n=38 analyzed for reaching the midline, n=31 analyzed for presence of growth cones, n=28 analyzed for guidance errors. At 3.5 dpf: control morpholino, n=21; Sema3d morpholino, n=22. At 5 dpf: control morpholino, n=30; Sema3d morpholino, n=36. *P<0.01; **P<0.001; ***P<0.000001. |
|
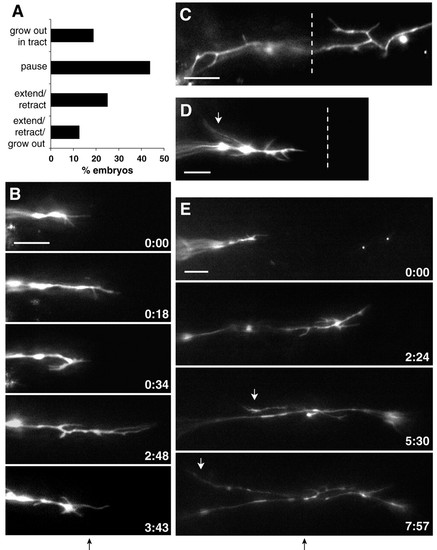
RGC axons show ipsilateral and interstitial projections and reduced growth beyond the midline following Sema3d knockdown. (A) Summary of growth cone behaviors after reaching the chiasm midline in Sema3d morphant embryos. (B) Frames taken from a timelapse movie of a Sema3d morphant embryo show repeated growth cone extensions and retractions at the midline. (C,D) Sema3d knockdown induced interstitial processes, including ipsilateral projections (white arrow). (E) Some processes developed into ipsilateral growth cones (white arrows). Times are indicated in hours:minutes; midlines are indicated by dotted lines or black arrows below frame sequences. Anterior is up in all frames. Scale bars: 10 μm. |