- Title
-
Forward Genetic Analysis of Visual Behavior in Zebrafish
- Authors
- Muto, A., Orger, M.B., Wehman, A.M., Smear, M.C., Kay, J.N., Page-McCaw, P.S., Gahtan, E., Xiao, T., Nevin, L.M., Gosse, N.J., Staub, W., Finger-Baier, K., Baier, H.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS Genet.
|
Example of a Mutant with Abnormal Morphology of Cone Photoreceptors. Photoreceptors in a retinal section stained with DAPI (A and B) and a marker for double cones, zpr1 (C and D) at 7 dpf in WT larva (A, C, and E) and yois121 mutant retina (B, D, and F). Merged images of DAPI (in green) and zpr1 (in magenta) are also shown (E and F). Both zpr1-positive and zpr1-negative cone photoreceptors in the mutant are "stumpy" when compared to those in the control retina (arrows). B, bipolar cells; C, cone photoreceptor cells; H, horizontal cells; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer. Scale bar is 10 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
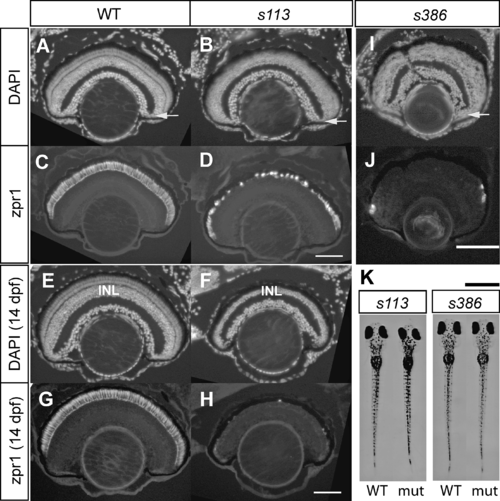
Examples of Mutants with Photoreceptor Degeneration. WT and mutant retinas (A-H, mtis113; I and J, ssds386) were sectioned and stained with DAPI (A, B, E, F, and I) and zpr1 monoclonal antibody (double-cone photoreceptor marker) (C, D, G, H, and J). At 7 dpf, photoreceptors in the central part of the retina have degenerated in both mti (A-D) and ssd (I-J). In the mti retina at 14 dpf, degeneration has spread to the inner nuclear layer (INL). Arrows show the ciliary marginal zone, from which new cells are continually added to the growing retina. Scale bar is 100 μm. (K) Mutants with photoreceptor degeneration may (mtis113) or may not (ssds386) be dark in VBA assay. Scale bar is 1 mm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Example of an OKR Mutant with Normal Morphology. (A) WT sibling and zats125 mutants are indistinguishable in their appearance (shown here at 6 dpf). (B) The mutant showed no OKR, but saccadic eye movements, which were not correlated to the motion stimulus. The zat gene encodes cone-specific Gc3. |
|
Example of a Mutant with a Potential Defect in Light Adaptation. OKR is plotted at several time points before and after dark treatment for 45 min. WT sibling larvae (n = 6) recover quickly from the dark pulse, while nkis136 mutants (n = 6) show reduced responsiveness for several minutes after return to the light. Average number of saccades to a constant motion stimulus is shown for each time point. Error bars indicate standard deviation. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
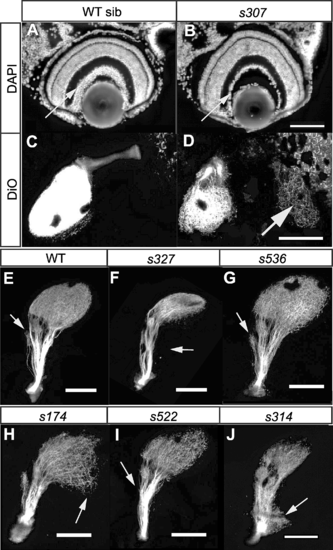
Examples of Retinofugal Projection Mutants. (A and B) Sections of WT and bojs307 retina stained with DAPI. The mutant retina has a thinner RGC layer (arrow). (C and D) Dorsal views of RGC axons from the right eye of a WT and a bojs307 mutant labeled with DiO, showing mutant axons in the ipsilateral tectum (arrow). To show that there is no ipsilateral projection in WT, the image is overexposed. (E-J) Lateral views of RGC axons labeled with DiO after removal of the eye. Anterior is to the left, dorsal to the top. In WT, the tectum and other retinorecipient areas are clearly visible (E). The arrow indicates AF-4. In darls327, the ventral branch of the optic tract is missing (arrow), and only dorsal tectum is innervated (F). In walks536, innervation of AF-4 (arrow) is disorderly (G). In exas174, the posterior tectum (arrow) appears to be incompletely innervated, while AF-4 is larger than in WT (H). In misss522, AF-4 (arrow) is reduced in size (I). In michs314, there is an ectopic arborization (arrow) at the root of the optic tract (J). Scale bars are 100 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
The darl Mutant Shows Retinotectal Mapping Deficits. (A and B) The nasal-dorsal quadrant of the retina was labeled with DiO (green), and the temporal-ventral quadrant was labeled with DiD (magenta). In darls327, the ventral branch of the optic tract is missing (arrow). Scale bar is 100 μm. (C and D) Dorsal view of the tectum in the same larvae as in A and B. The ventral half of the darls327 tectum is not innervated by the dorsal-nasal RGC axons. Anterior is to the left and ventral is to the bottom. Tectal neuropil is demarcated by the dotted line, based on DAPI counterstaining (blue). Scale bar is 50 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Pineal Photoreceptors Are Present in Retinal Photoreceptor Degeneration Mutants Coronal sections of the forebrain at 7 dpf were stained with DAPI (A, C, E, and G) and zpr1, a marker of both retinal and pineal photoreceptors (B, D, F, and H). Pineal photoreceptors (arrow and inset) were consistently present in mutants in which retinal photoreceptors were depleted (D, F, and H). Scale bar is 100 μm for A-J and 25 μm for the insets. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Dorsal RGCs Are Present and Properly Differentiated in darl Mutants Sagittal sections of WT (A and C) and darls327 retina (B and D) were stained with DAPI (A and B) and zn5 (C and D), a marker for differentiated RGCs. RGCs are present in the dorsal part of the retina and sending out axons into the optic nerve head in the mutant. The mutant eyes are reduced in size compared to WT. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
The Tectum of exa Mutants Has an Abnormal Shape RGC axon tracing, following whole-eye DiI fills at 7 dpf, reveals a subtle extension of the tectal neuropil (delineated by DAPI counterstaining) at the ventral-posterior margin (arrow). Scale bar is 50 μm PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Retinal Axon Outgrowth Is Delayed in shir Mutants Lateral views of the retinal ganglion cell axons labeled with DiO. Anterior to the left, dorsal to the top. (A and B) At 7 dpf, the retinofugal projection in shirs362 (B) appears similar to WT (A), although the anterior portion may be less dense (arrow). (C and D) At 5 dpf, RGC axon outgrowth in shirs362 (D) evidently lags behind WT (C). Scale bar is 100 μm. |
|
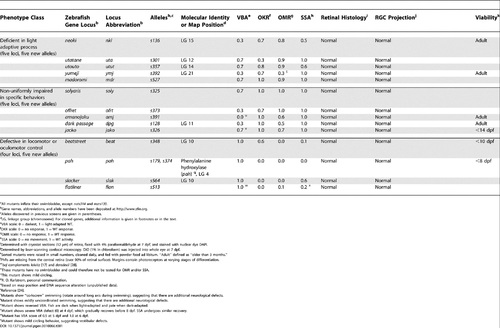
Zebrafish Visual Behavior Mutants. |