- Title
-
Wnt signalling mediated by Tbx2b regulates cell migration during formation of the neural plate
- Authors
- Fong, S.H., Emelyanov, A., Teh, C., and Korzh, V.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
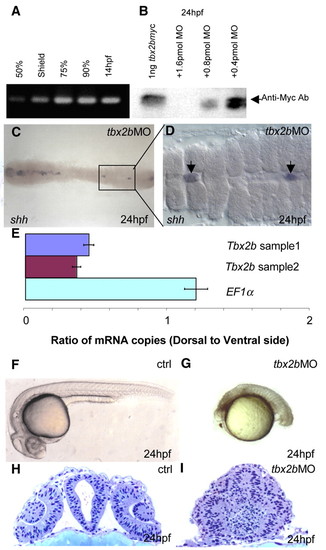
tbx2b MO blocks translation of tbx2b and impairs normal development. (A) RT-PCR using primers specific to the 5'-UTR of tbx2b shows that this transcript was present as early as 50% epiboly. (B) Western blot with anti-Myc antibody shows that translation of recombinant tbx2b-myc was blocked in the presence of tbx2b MO in a dose-dependent manner. (C) Dorsal view of tbx2b morphant shows the almost complete loss of shh in the trunk region of the embryo. The boxed section is enlarged in D, showing the shh-positive cells as remnants of notochord (arrow). (E) Real-time PCR shows that tbx2b transcripts are present at a higher level in the ventral gastrula (5.5 hpf) when compared with EF1α. (F,G) Phenotype of tbx2b morphant (2 pmol) (G) when compared with control (F) (see text for description). (H,I) tbx2b is required for proper development of the eyes and forebrain. (H) Plastic cross-section through the forebrain of a 24 hpf control embryo at the level of the lens. (I) Cross-section of the tbx2b morphant shows severe disorganization of the forebrain and eyes. |
|
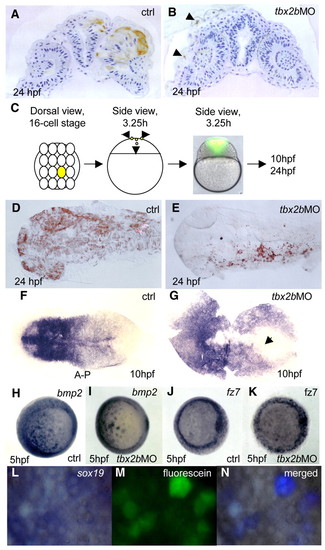
Tbx2b is required for cells to adopt a neural fate. Deep cells from embryos co-injected with fluorescein-dextran (70 kDa) and tbx2b MO at 30% epiboly were transplanted into homochronic wild-type hosts. (A) Cross-section through the neuroretina and brain shows transplanted control labelled cells in the CNS. By contrast (B) transplanted Tbx2b-deficient cells were present only in the epidermis (arrowheads). (C) One central blastomere of 16-cell stage embryos was injected with fluorescein either with or without tbx2b MO, and embryos were allowed to develop to 24 hpf. Both control and tbx2b morphants developed normally and showed a similar distribution of labelled clones in vivo at 3.25 hours. (D) Dorsal view of 24 hpf control embryo shows labelled cells in neural plate and epidermis. (E) tbx2b morphant labelled cells were present only in epidermis. (F,G) Whole-mount in situ hybridization with the pan-neural marker sox19 shows a delay in convergence of the neural plate in tbx2b morphant (arrow in G) compared with control (F). (H-K) Whole-mount in situ hybridization with bmp2 (H,I) and fz7 (J,K) show similar expression patterns in control and Tbx2b morphant at 5 hpf. (L-N) Transplanted fluorescein labelled Tbx2b-deficient cells continue to express sox19 in 5 hpf wild-type host. (N) The merged photographs were enhanced in Adobe Photoshop such that only the simultaneous presence of blue (whole-mount in situ hybridization signal) and green (fluorescence) produced a purple signature. Otherwise, cells remain grey. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
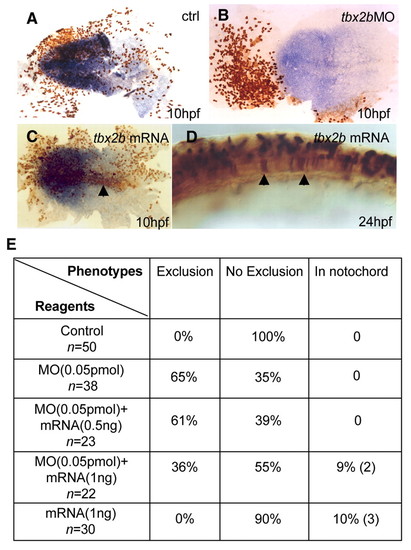
`Exclusion' phenotype can be rescued by tbx2b mRNA. Compared with control (A), a 1/16 injection of tbx2b MO led to `exclusion' phenotype (B) at 10 hpf. Neural plate highlighted with sox19 in blue; fluorescein labelled cells in brown. By contrast, 1/16 injection of tbx2b mRNA (1.0 ng) led to (C) labelled cells with normal morphology in the midline (arrow) at 10 hpf and, (D) the notochord (arrows) at 24 hpf, consistent with the role of Tbx2b in axial mesodermal specification. (E) Exclusion phenotype at 10 hpf from tbx2b MO (0.05 pmol) was rescued with tbx2b mRNA lacking the target site in a dose-dependent manner. In the presence of tbx2b MO, 1.0 ng mRNA led to appearance of labelled cells in the midline similar to C and D, while significantly reducing the number of embryos with `exclusion' phenotype. 0.5 ng mRNA was less effective in reducing the `exclusion' phenotype but did not cause appearance of labelled cells in the midline. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
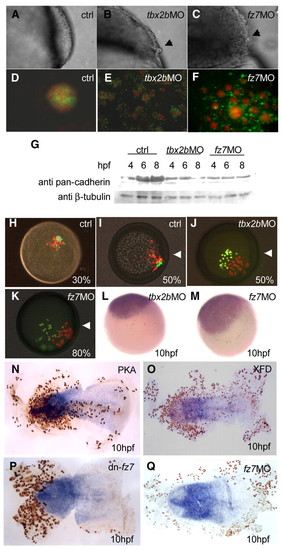
Early function of Tbx2b and Fz7 is required for cell adhesion. The smooth surface of (A) a wild-type gastrulating embryo, is in contrast to the `rough phenotype' (black arrows) in (B) Tbx2b and (C) Fz7 morphants. (D) In control, dissociated 6 hpf cells labelled with fluorescein (green) and Texas Red (red) formed a single aggregate after 24 hours in hanging drop culture. By contrast, cells derived from fluorescein-labelled (E) Tbx2b- and (F) Fz7-morphant cells formed single layer shells around wild-type Texas Red-labelled aggregates. (G) Western blot with a pan-cadherin antibody showed that the level of cadherins in Tbx2b and Fz7 morphants remained the same or declined in contrast to the control. (H-M) Cell movement during gastrulation was affected in Fz7- or Tbx2b-deficient cells. Control cells with fluorescein and Texas Red transplanted into wild-type host at (H) 30% epiboly co-migrated towards the dorsal side by (I) 50% epiboly, but fluorescein labelled (J) Tbx2b and (K) Fz7 morphant cells were unable to migrate (white arrowheads indicate position of the shield). A 10 hpf embryo stained for fluorescein (brown) shows that transplanted (L) Tbx2b and (M) Fz7 morphant cells were excluded from the sox19-positive neural plate. (N-Q) Flat mounts of 10 hpf embryos, double stained for fluorescein (brown) and sox19 (blue), after single cell injection at 16-cell stage with (N) PKA, (O) XFD, (P) dn-Fz7 and (Q) fz7 MO. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
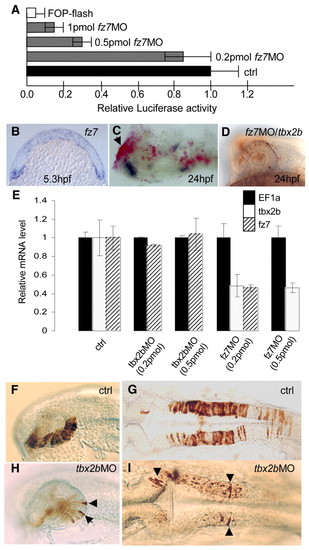
(A-D) Tbx2b is regulated by Fz7. (A) TOP-flash assay shows a reduction of ß-catenin-dependent Tcf activity in fz7 morphants. (B) Expression of fz7 at 5.3 hpf (cross-section). (C) Expression of a dn-fz7-EGFP/BAC (red, see Materials and methods) caused the loss of tbx2b expression (blue) in the eye (arrow). (D) The absence of fz7 MO/fluorescein-injected cells in the eyes and CNS at 24 hpf is rescued by co-injection of tbx2b mRNA. (E) Real-time PCR analysis of Tbx2b and Fz7 morphants showed a decrease in tbx2b and fz7 transcripts in the presence of fz7 MO, but no effect from tbx2b MO at 5 hpf. n=15 for control, n=7 for tbx2b MO and n=4 for fz7 MO. (F-I) Rescue of cell movement defect by transplantation into wild-type host at shield stage. Wild-type donor cells differentiated into morphologically distinct cells in the eye (F) and hindbrain (G) by 24 hpf. By contrast, only a few Tbx2b-deficient cells differentiated into distinct eye (H) and hindbrain (I) cells (arrowheads). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|