- Title
-
Expression pattern of two zebrafish genes, cxcr4a and cxcr4b
- Authors
- Chong, S.-W., Emelyanov, A., Gong, Z., and Korzh, V.
- Source
- Full text @ Mech. Dev.
|
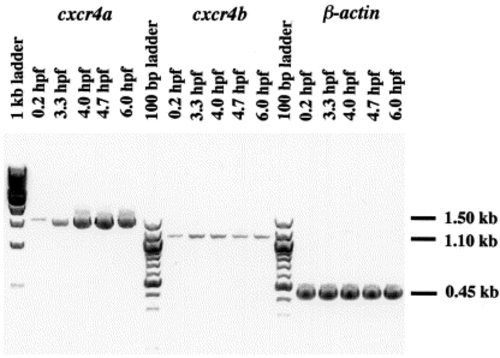
Reverse transcription (RT)-PCR detects the continuous presence of transcripts of the two cxcr4s during early development. cxcr4b mRNA is present at a low level during the first 6 h of development. As shown by whole-mount in situ hybridization, its level starts to increase at the early neurula stage (see Fig. 4). cxcr4a transcripts are present at a low level during blastula stage and zygotic transcription is strongly activated at 3.3 hpf. RT-negative control was carried out at the same time and no band was detected (not shown). |
|
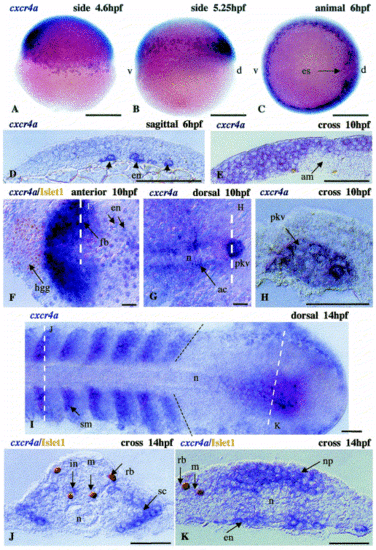
Embryonic expression of cxcr4a. The expression pattern of cxcr4a includes: (A?D), the early endoderm (en); (G,H), the primordium of Kupffer′s vesicle (pkv); and (E,F), the forebrain (fb). (G) The expression appeared relatively late in adaxial cells (ac). (D) is a sagittal section of the embryo shown in (C). In (F), the white broken lines define a section shown in (E). In (G), the white line defines a section shown in (H). During somitogenesis, cxcr4a is expressed in somites (sm) immediately after their separation from the unsegmented lateral mesodermal plate (black dotted line) and in the tail bud (I). In addition, ventral interneurons (in) express this gene (J). In somites, expression of cxcr4a is confined to the sclerotome (sc) (J). In the tail bud (K), cxcr4a expression is found mainly in the neural plate (np) and endoderm (en). am, axial mesoderm; d, dorsal; es, embryonic shield; hgg, hatching gland; n, notochord; rb, Rohon?Beard sensory cells; v, ventral. Black arrowheads in (D) indicate endodermal cells. The broken black line represents the border of segmented and unsegmented lateral mesoderm. Anterior in all figures is oriented to the left unless otherwise indicated. Broken white lines represent the section level. Scale bar in (A?C), 250 μm; remainder, 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
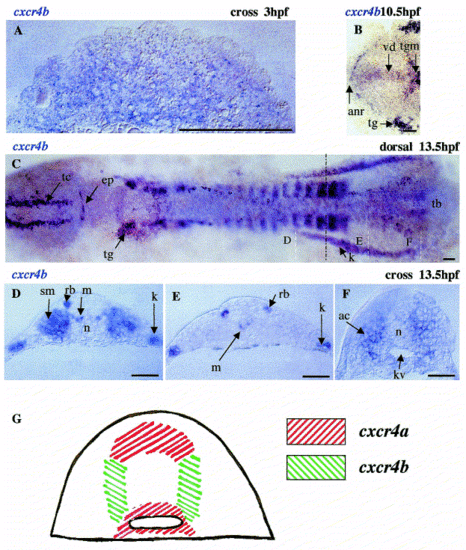
Expression of cxcr4b during early zebrafish development. Expression of cxcr4b has been detected by whole-mount in situ hybridization mainly in deep cells starting from the blastula stage (A). Later on during early neurulation, the level of expression increases in specific regions of the CNS, including the posterior midbrain, the set of sensory neurons (trigeminal ganglia, dorsal sensory cells, epiphysis and telencephalon) (B,C), anterior neural ridge, ventral diencephalon and ventral midbrain (B). In addition, expression is detected in the posterior lateral mesoderm (C,F), where the level of expression increases just before formation of somites. White dashed lines in (C) indicate the level of cross-sections in reference to (D?F). The broken black line shows the border of segmented and unsegmented lateral mesoderm. The complementary mode of expression of the two genes is most obvious in the tail bud. Here, cxcr4a transcripts are in the neural plate and endodermal precursors, while cxcr4b transcripts are in mesodermal cells lateral to the notochord bud (modified from Fig. 3 and Fig. 4). This results in the bulb of the notochord being surrounded by cells specifically expressing one of the two genes (see schematic in (G)). ac, adaxial cells; anr, anterior neural ridge; ep, epiphysis; kv, Kupffer′s vesicle; k, kidney; m, motoneuron; n, notochord; rb, Rohon?Beard cells; sm, somite; tb, tail bud; tg, trigeminal ganglion; tgm, tegmentum; tc, telencephalon; vd, ventral diencephalon. Bar, 50 μm ((A), 250 μm). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
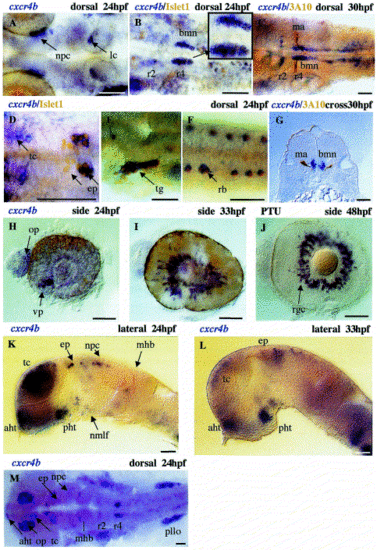
Expression of cxcr4b during late zebrafish development. To confirm the identity of cxcr4b-positive cells in various areas of the CNS, we performed double staining using whole-mount in situ hybridization with the cxcr4b probe in combination with other neuronal markers as indicated on the figure. cxcr4b is expressed in the nucleus of the posterior commissure and locus coeruleus (A), as well as brachiomotor neurons of the hindbrain (B,C). The small box inserted in (B) shows an enlarged view of brachiomotor neurons. A cross-section level through r4 is shown in (G). Note the co-expression of cxcr4b and Islet-1 in the posterior part of the epiphysis (D). The lack of expression of cxcr4b in the anterior epiphysis (arrow), where only Islet-1 is expressed, implies that cells in the epiphysis undergo differentiation according to the same antero-posterior (A?P) time course as the rest of the CNS. (E,F) cxcr4b co-localizes with Islet-1 in trigeminal ganglion (tg) and Rohon?Beard cells (rb). In the eye (H?J), expression starts in the ventral patch and later continues in retinal ganglial cells. (K,L) The expression of cxcr4b is detected in the anterior (aht) and posterior hypothalamus (pht). (M) In the telencephalon (tc), the most intense expression was detected in the olfactory placode (op). In the dorsal diencephalon, expression occurs in the epiphysis (ep) and nuclei of posterior commissure (npc). bmn, brachiomotor neurons; ep, epiphysis; lc, locus coeroleus; ma, Mauthner neuron; op, olfactory placode; mhb, midbrain?hindbrain boundary; nmlf, nucleus of medial longitudinal fascicle; npc, nuclei of posterior commissure; pllo, primordium lateral line organ; r, rhombomeres; rgc, retinal ganglial cells; tc, telencephalon; vp, ventral patch; PTU, embryos treated with 1-phenyl-2-thiourea. Bar, 50 μm. |
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 109(2), Chong, S.-W., Emelyanov, A., Gong, Z., and Korzh, V., Expression pattern of two zebrafish genes, cxcr4a and cxcr4b, 347-354, Copyright (2001) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.