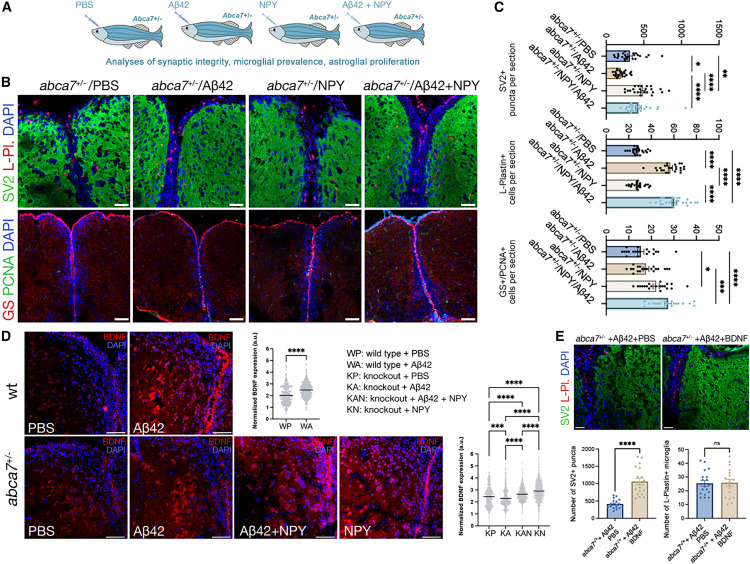
Fig. 6 ABCA7 regulates synaptic integrity and astroglial proliferation through BDNF (A) Experimental setup for investigating the biological relevance of NPY to abca7 function and amyloid-induced alterations in synaptic integrity, microglial activity, and astroglial proliferation. (B) Immunofluorescence for SV2 + L-plastin and GS + PCNA with DAPI counterstains in abca7+/? + PBS, abca7+/? + A?42, abca7+/? + NPY, and abca7+/? + A?42 + NPY brains. (C) Quantification for number of SV2-positive synaptic puncta, L-plastin-positive microglia, and GS/PCNA double-positive proliferating astroglia. n = 4 animals from both sexes and ?20 brain sections per group. One-way ANOVA with Tukey?s multiple comparison test was used for statistical analyses. No comparison bar indicates no significance. (D) BDNF immunoreactivity in wild-type and abca7 knockout zebrafish with and without A?42. A?42 induced BDNF (red) in wild-type animals but not in abca7 knockout. Injection of NPY with or without A?42 restores the induced BDNF expression levels. Non-parametric Kolmogorov-Smirnov test comparing cumulative distributions and one-way ANOVA with Tukey?s multiple comparison test were used for statistical analyses. (E) Immunofluorescence for SV2 and L-plastin with DAPI counterstain in abca7+/? + A?42 + PBS and abca7+/? + A?42 + BDNF zebrafish brains. Quantification for the number of SV2-positive synaptic puncta and the number of L-plastin-positive microglia. Non-parametric Kolmogorov-Smirnov test comparing cumulative distributions was used for statistical analyses. BDNF rescues synaptic integrity changes in abca7+/? knockout similar to NPY. n = 4 animals from both sexes, with 18 brain sections per group. ?p < 0.0332, ??p < 0.0021, ???p < 0.0002, ????p < 0.0001; not significant (ns), p > 0.0332. Scale bars, 50 ?m. See also Figures S1 and S4 , Data S1 and S3 , and Table S1 .
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Cell Genom