Fig. 5
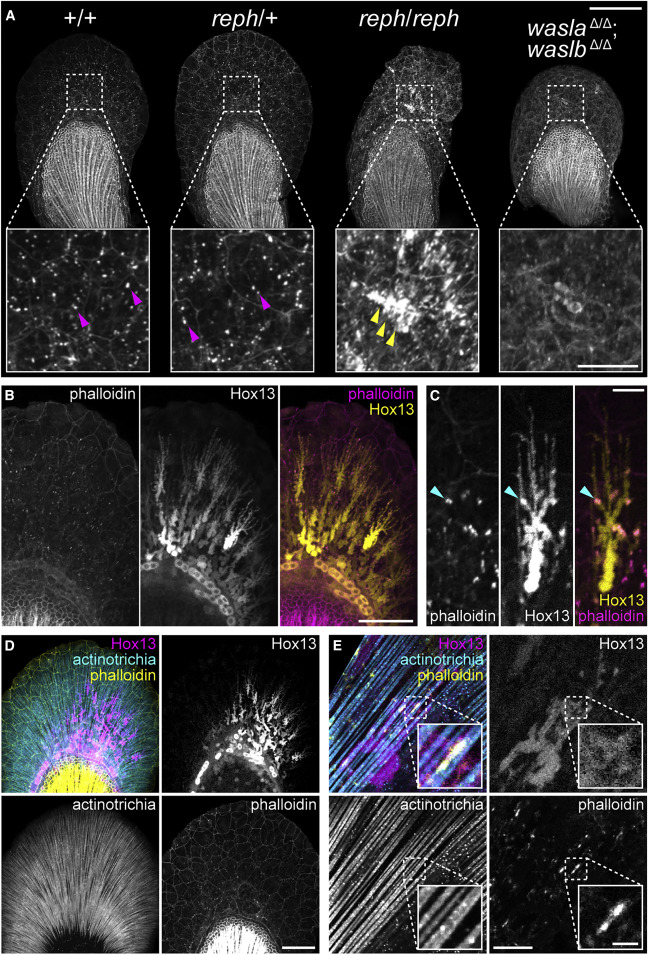
Figure 5. F-actin formation in the early fin fold is affected in wasl mutants and is associated with Hox13-positive cells and the actinotrichia (A) 3 dpf phalloidin-labeled pectoral fins showing modified F-actin in reph homozygous mutants and wasla; waslb double mutants. reph homozygotes develop large F-actin aggregates and dysmorphic fin folds, and wasla; waslb double mutants display a more dispersed F-actin network. (B) F-actin foci colocalize with the extensions of Hox13-positive cells in the fin fold marked with the Tg(2P?epi:eGFP) reporter transgene. (C) A single Tg(2P?epi:eGFP) Hox13-positive cell showing F-actin colocalization. (D) Triple labeling demonstrates colocalization of F-actin foci, Hox13-positive cells expressing the Tg(mInta-11:mCherry) transgene, and actinotrichia in the fin fold. (E) A single Tg(mInta-11:mCherry) Hox13-positive cell showing colocalization with actinotrichia fibrils and F-actin. Anterior to left, distal to top in all panels; scale bars (A) 100 ?m (25 ?m inset), (B, D) 50 ?m, (C, E) 10 ?m (2 ?m inset in E).
Reprinted from Cell, 184(4), Hawkins, M.B., Henke, K., Harris, M.P., Latent developmental potential to form limb-like skeletal structures in zebrafish, 899-911.e13, Copyright (2021) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Cell