Fig. 1
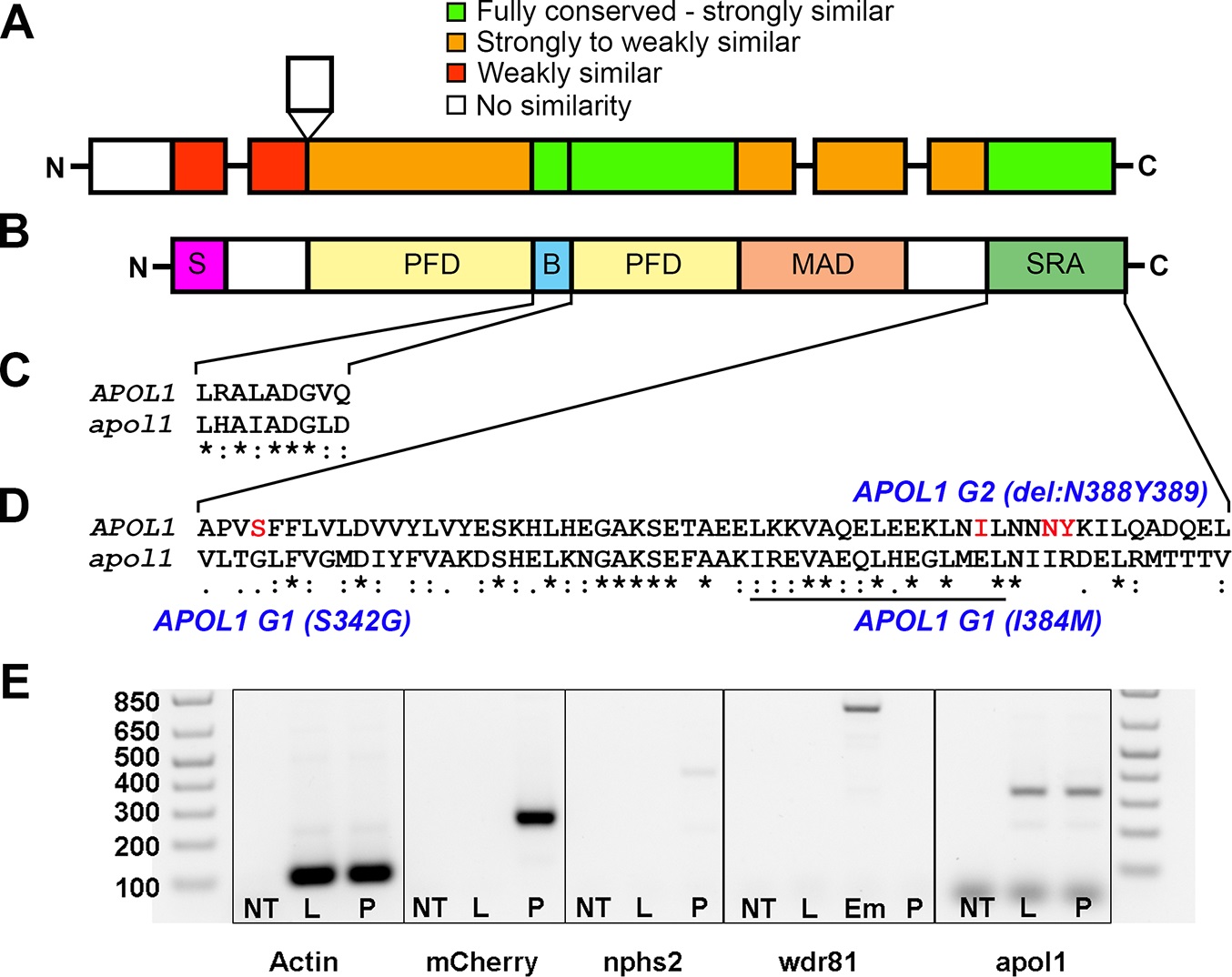
Comparison of APOL1 human and zebrafish protein sequences and relevance to the zebrafish kidney.
Protein domain schematic of (A) zebrafish APOL1 and (B) human APOL1 is shown, with zebrafish domains (NP_001025309) aligned to the human protein (NP_001130012) and coded based on summarized consensus scores (Gonnet PAM 250 matrix, Clustal Omega, Cambridge, UK; S, secretory domain, PFD, pore-forming domain, B, BH3 domain, MAD, membrane-addressing domain, SRA, serum resistance-associated binding domain). Prominent regions of the human and zebrafish alignments are expanded, including the (C) BH3 domain and (D) SRA binding domain, and consensus symbols are displayed (* (asterisk), fully conserved;: (colon), >0.5 in the Gonnet PAM 250 matrix;. (period), = <0.5 in the Gonnet PAM 250 matrix). The leucine zipper domain (codons 365?392 in APOL1, underline), and the location of the G1 and G2 risk alleles in CKD in African Americans (S342G/I384M and ?N388Y389) are highlighted in red. (E) Podocytes from adult glomeruli of pod::NTR-mCherry zebrafish were flow-sorted and evaluated for apol1 RNA expression through RT-PCR. apol1 is expressed in fluorescence-activated cell sorted (FACS) podocytes and the adult liver. FACS podocytes also express zebrafish podocin (nphs2) but a purkinje-cell marker, wdr81[29], was undetectable. NT = non-template reverse transcription control; L = dissected adult liver cells from pod::NTR-mCherry zebrafish; P = fluorescence-activated cell sorted podocytes from dissected glomeruli of pod::NTR-mCherry zebrafish; Em = 5 dpf whole-zebrafish embryo cDNA.