Fig. 4
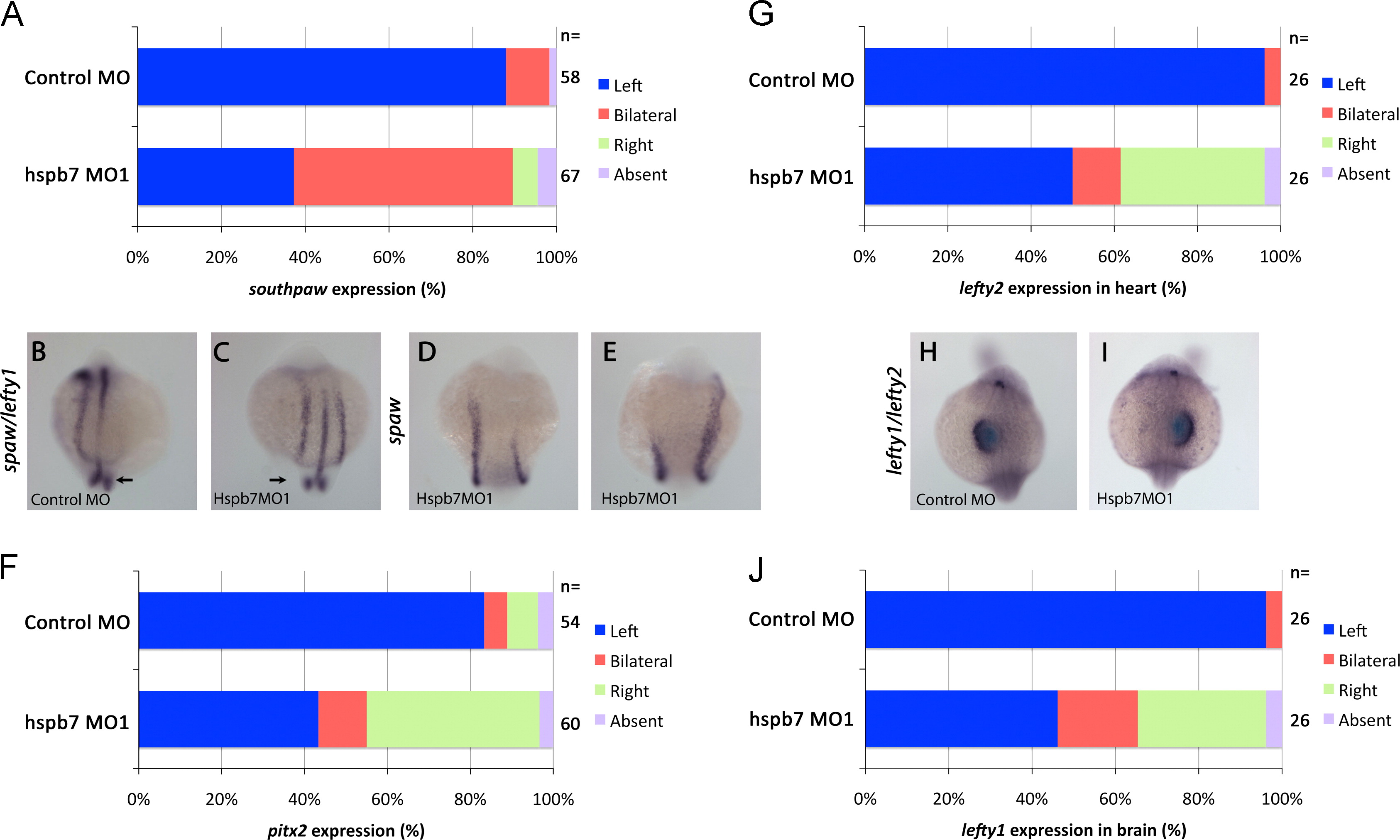
hspb7 was necessary for the expression of laterality genes in the left lateral plate mesoderm (LPM). (A) Embryos injected with 0.5 pmol control MO had primarily left-sided expression of spaw in the lateral plate mesoderm. In contrast, hspb7MO1 induced bilateral spaw expression (Χ2 test; p<0.001). (B-E) 14-18 somite stage embryos. (B) Embryos injected with control MO had normal spaw and lefty1 expression in left LPM and notochord, respectively. In the tail, bilateral peri-KV spaw domains were present (arrow). (C) hspb7MO1-injected embryos expressed spaw bilaterally. lefty1 in the notochord and peri-KV expression of spaw were not disturbed. (D, E) hspb7MO1-injected embryo with bilateral spaw with (D) left side leading leading and (E) right side leading. (F) hspb7MO1 randomized pitx2 expression (Χ2 test; p<0.001), with largely left or right sided expression and a small fraction of bilateral expression. (G) lefty2 expression in the left heart field was randomized or made bilateral by hspb7MO1 injection (Χ2 test; p<0.001). (H) embryos injected with control MO express lefty1 and lefty2 on the left side of the heart and brain at 22?24 somite stages. (I) hspb7MO1 injected embryos expressing lefty1 and lefty2 on the right. (J) lefty1 expression in brain was randomized by hspb7MO1 injection (Χ2 test; p<0.001).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 384(2), Lahvic, J.L., Ji, Y., Marin, P., Zuflacht, J.P., Springel, M.W., Wosen, J.E., Davis, L., Hutson, L.D., Amack, J.D., and Marvin, M.J., Small heat shock proteins are necessary for heart migration and laterality determination in zebrafish, 166-180, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.