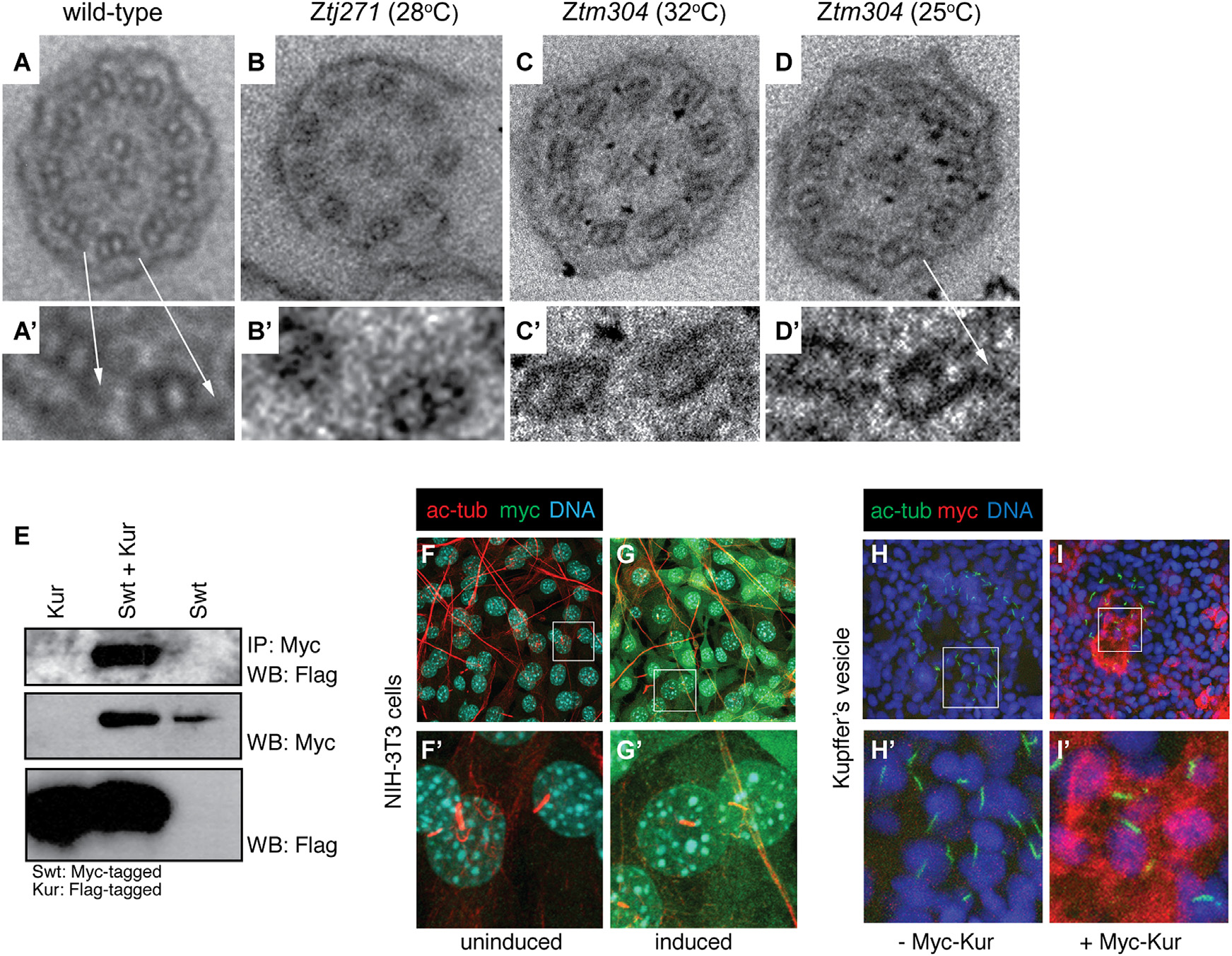
Fig. 2
Kur Is a Cytoplasmic Factor Required for the Localization of ODAs to the Cilium
(A-D′) Transmission electron micrographs (TEMs) showing the ultrastructure of pronephric cilia in cross-section. The arrows in (A) and (A′) indicate ODAs that are missing in mutants (B-C′), but are restored in kurtm304/tm304 mutants raised at permissive temperature (D and D′).
(E) IP of Myc-tagged Swt and subsequent Myc-Swt and FLAG-Kur western blot (WB) reveals physical association between Swt and Kur.
(F-G′) NIH 3T3 cells transfected with inducible Myc-tagged Kur were immunostained for the ciliary axoneme (acetylated alpha tubulin [ac-tub]; red), DNA (Hoechst; blue), and myc (Myc-Kur; green). The Kur is not localized to the cilium, but instead localizes to the cytoplasm.
(H-I′) Immunostaining of KV in control embryos or embryos injected with Myc-Kur. The cilia were marked by ac-tub (green) staining, DNA with Hoechst (blue), and Myc-Kur was localized with an anti-Myc antibody (red). The Myc-Kur, which rescues kur mutants, was present in cells of the KV, but appeared absent from cilia themselves.