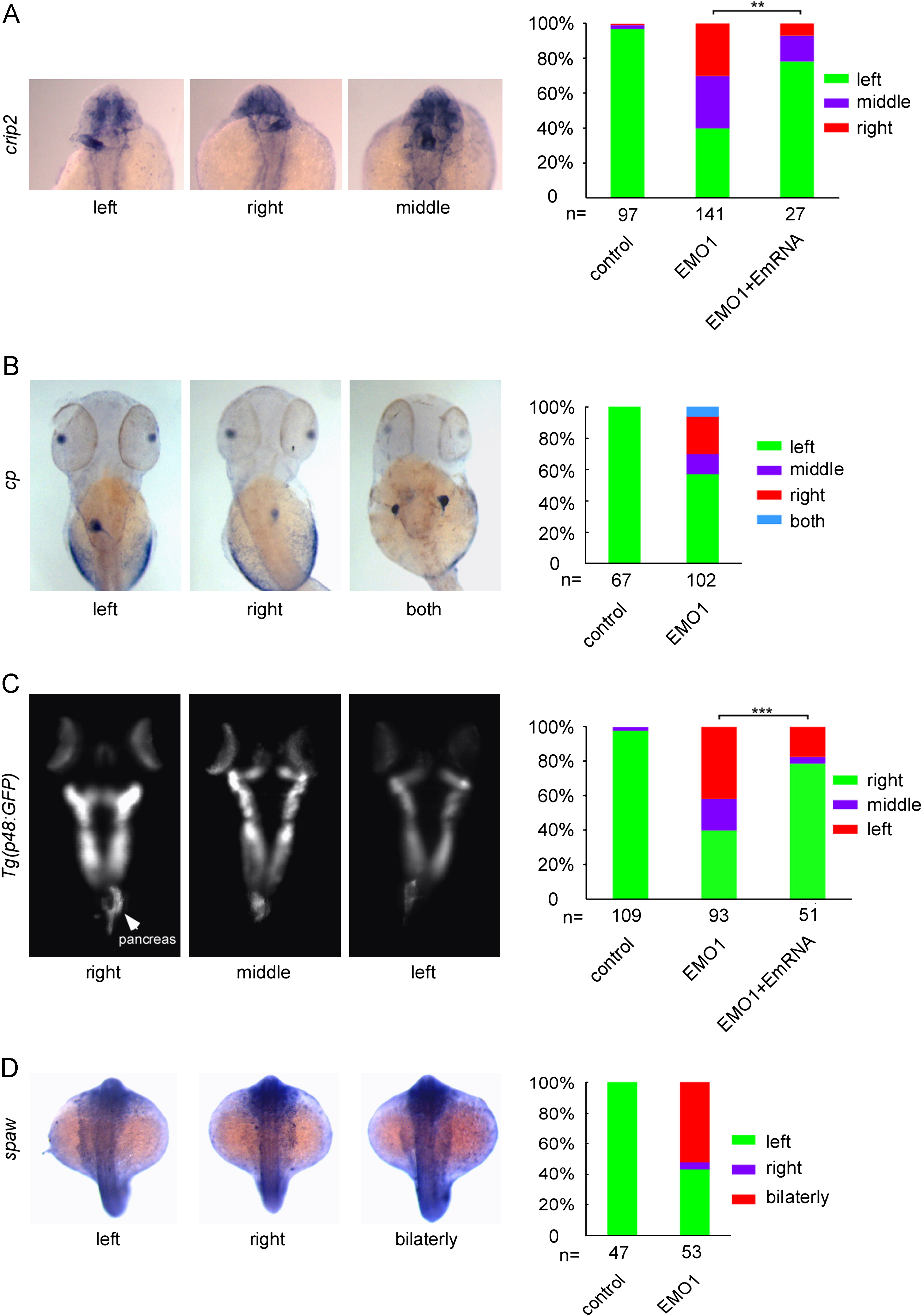
Fig. 2 Enc1l is required for zebrafish left-side gene spaw and organs LR asymmetric formation. (A) Expression of crip2, a marker for heart, as well as the statistical graph indicate that 40%, 30%, and 30% of enc1l-MO1 embryos show that the heart position is on the left-side, middle, and right-side, respectively. The phonotype caused by knockdown of enc1l can be rescued by enc1-mRNA. (B): The liver marker cp and the statistical graph show that disruption of the liver in enc1l morphants cause 57.4%, 13%, 24.1%, and 5.5% of the morphants to have the liver positioned on the left, middle, right, and both positions, respectively. (C): P48:GFP transgenic fish and the statistical graph show that 42.4%, 18.1%, and 39.5% of the morphants have left, middle, and right-side pancreas, respectively. The phonotype caused by knockdown of enc1l can be rescued by enc1-mRNA. (D) WISH and the statistical graph show that approximately 53% of the morphants have bilateral and 4% of the morphants have right-side expression of spaw. **:0.005<p<0.01; ***: p<0.005.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 374(1), Qian, M., Yao, S., Jing, L., He, J., Xiao, C., Zhang, T., Meng, W., Zhu, H., Xu, H., and Mo, X., ENC1-like Integrates the Retinoic Acid/FGF Signaling Pathways to Modulate Ciliogenesis of Kupffer's Vesicle during Zebrafish Embryonic Development, 85-95, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.