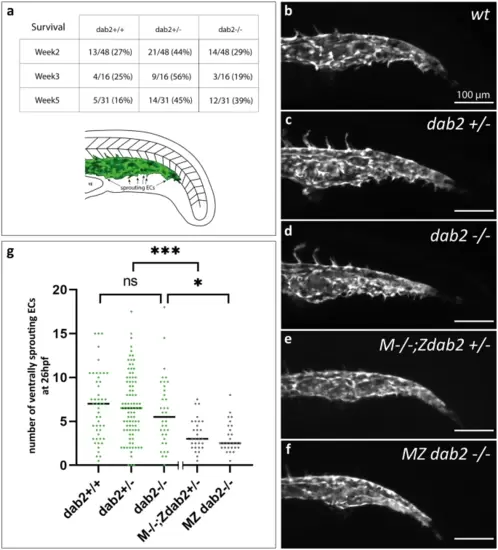
Formation of the caudal vein plexus is severely reduced in embryos that lack maternally provided dab2 mRNA. (a) Number of wild type, heterozygous and homozygous mutant fish after genotyping the progeny from a dab2+/- incross at week 2, 3 or 5 of development. At all time points, there is a high percentage of homozygous mutants. Schematic representation of the caudal vein area in the zebrafish trunk at 26hpf. In green, the caudal vein with ventrally sprouting ECs is represented. (b-f) Maximum projection of flt4:mCitrine positive zebrafish embryos at 26hpf, lateral view. Wild type embryos (b), dab2+/- (c), and dab2-/- (d) embryos develop sprouting ECs that bud off ventrally from the caudal vein. In comparison, M-/-;Zdab2+/- (e) and MZ dab2-/- (f) embryos develop fewer sprouts. (g) Quantification of the number of ventrally sprouting ECs reveals that the number is significantly lower in maternal mutant embryos (Kruskal Wallis, Mann Whitney U-test; M-/-;Zdab2+/- vs. dab2 +/-p = 0.000195 and MZ dab2-/- vs. dab2 -/-p = 0.014). The graph shows the median and all the embryos quantified (dots). hpf, hours post fertilization; MZ maternal-zygotic; YE, yolk extension.
|

