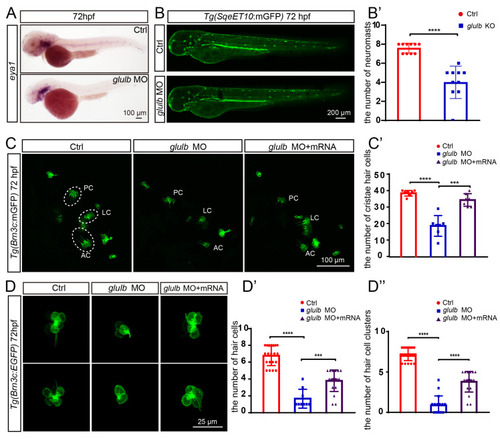
The zebrafish that were injected with glulb-MO exhibited a significant decrease in the number of neuromasts, hair cell clusters, and hair cells, and co-injection of glulb mRNA successfully rescued the observed phenotype following glulb knockdown. (A) In situ hybridization using the eya1 probe revealed a reduced number of neuromasts in the glulb-MO zebrafish group compared to the Ctrl group at 72 hpf. (B) The application of laser confocal microscopy revealed a decrease in the number of neuromasts in glulb-MO zebrafish embryos at 72 hpf compared to the control zebrafish, and (B’) the observed discrepancy exhibited statistical significance. t-test: ****, p < 0.0001. (C) The number of hair cells in the inner ear of glulb-MO zebrafish exhibited a significant decrease compared to the control group. Co-injection of glulb mRNA effectively rescued this phenotype, and (C’) subsequent statistical analysis revealed statistically significant differences. One-way ANOVA: ****, p < 0.0001; ***, p < 0.001. (D) The glulb-MO zebrafish exhibited decreased hair cells within the L3 neuromasts, which can be rescued by co-injection of glulb mRNA. (D’) Statistical analysis revealed a significant difference. (D”) A statistical analysis of hair cell clusters in the control, glulb-MO injected, and glulb-MO co-injection with glulb mRNA embryos was conducted. One-way ANOVA: ****, p < 0.0001; ***, p < 0.001.
|

