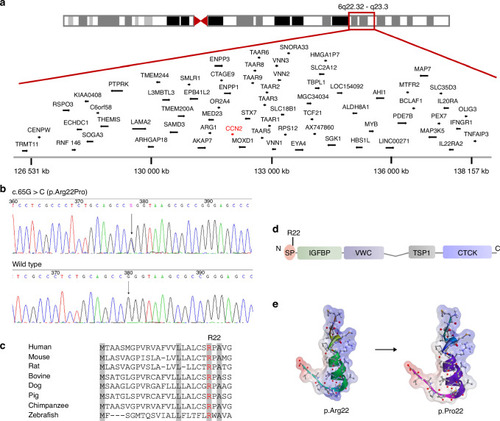
Identification of a pathogenic variant in CCN2 in the family with spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia (SEMD). a Schematic representation of chromosome 6 and a single overlapping region on chromosome 6q22.32–q23.3 identified by linkage analysis. b Sequencing chromatogram of a missense variant (c.65 G > C, arrow) in exon 1 in CCN2. The variant shows segregation with SEMD in all available family members. The base change predicts the replacement of the amino acid arginine in codon 22 with proline (p.Arg22Pro). c Alignments of the region of CCN2 from multiple species, showing the altered residue in red. Highly conserved amino acids are indicated in gray. d Schematic diagrams of protein domain organization of CCN2, along with the position of the identified variant. The molecular structure of CCN2 consists of a signal peptide (SP) and four conserved domains with sequence homologies to Insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP), von Willebrand factor type C domain (VWC), Thrombospondin type 1 repeat (TSP-1), and a carboxy-terminal cystine knot domain (CTCK). The amino acid residue Arg22 is located in the SP. e Structural model of SP of CCN2. Positive and negative charged regions are indicated in blue and red, respectively, and uncharged area is shown in white. The mutant residue Arg22 results in a decrease in positive charge region
|

