Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240506-57
- Publication
- Jayawardena et al., 2024 - Investigating the role of phenylalanine residues for amyloid formation of the neuropeptide neurokinin B
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
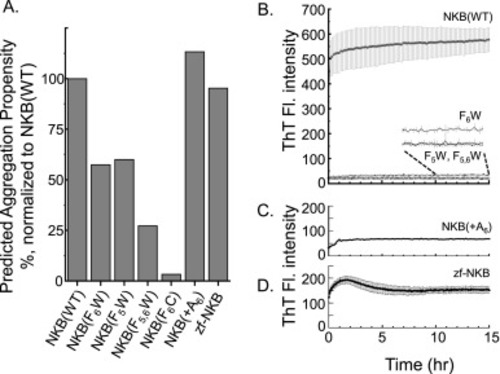
Amyloidogenic properties of NKB. A. Predicted aggregation propensity (using TANGO) of NKB(WT) and the mutants investigated in this study. B. Time-resolved ThT fluorescence of NKB(WT) and mutants NKB(F6W), NKB(F5W) and NKB(F5,6W) shows that mutations in the diphenylalanine motif severely disrupt the ability of the peptide to form fibrils. C. Time-resolved ThT fluorescence of NKB(+A6) which inserts an alanine within the diphenylalanine motif shows limited fibril formation. D. Time-resolved ThT fluorescence of the zebrafish NKB (zf-NKB) shows some fibril formation, but much less compared to mammalian wild-type NKB. All peptides were 200 μM in 10 mM nEM, pH 7.4. |