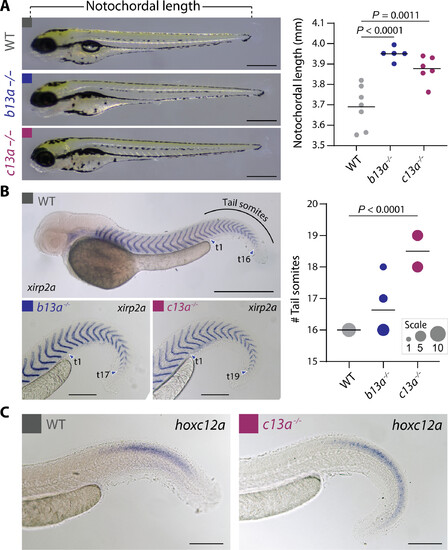
Length and somite number in mutant b13a?/? and c13a?/? larvae. (A) NL of 3-dpf WT, b13a?/?, and c13a?/? mutant larvae. n = WT:7, b13a?/?:5, and c13a?/?:6. ANOVA revealed a significant change in larval length [F2,15 = 18.59, P < 0.0001]. Multiple comparisons indicated significantly longer b13a (P < 0.0001) and c13a (P = 0.0011) larvae compared with WTs. Scale bars, 0.5 mm. (B) Tail somite number in 2-dpf WT, b13a?/?, and c13a?/? mutant larvae, using in situ hybridization with the myotome boundary marker xirp2a. (n = WT:8, b13a?/?:11, and c13a?/?:10). Poisson regression revealed significant increases in somite number for both mutants [?2(2) = 33.19, P < 0.0001]. Post hoc tests were not applied due to the absence of variance in WTs, rendering those tests invalid. Circle size is proportional to fish scored (0.5 mm scale bar for WT, 0.2 mm scale bars for b13a?/? and c13a?/? mutants). (C) In situ hybridization against hoxc12a in 2-dpf WT and c13a?/? mutant embryos. Scale bars, 0.2 mm. For (A) and (B), graph horizontal lines represent the mean.
|

