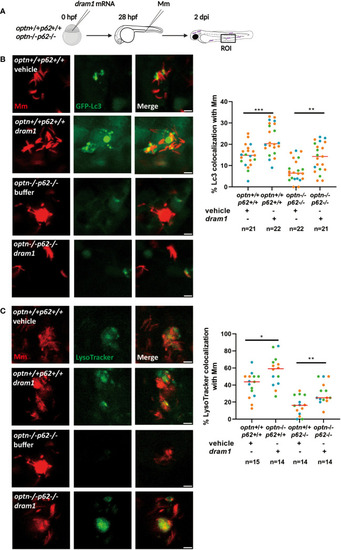
Dram1 increases the colocalization between Lc3 and Mm in optn/p62 double mutant lines. Effect of dram1 overexpression on the colocalization between Mm and GFP-Lc3 in optn/p62 double mutant and wildtype background. In the experimental workflow (A), dram1 mRNA was injected into optn+/+p62+/+ and optn-/-p62-/- embryos at the one cell stage, followed by injection of 200 CFU of Mm into the blood island at 28 hpf and imaging of a region of interest (ROI) in the caudal hematopoietic region at 2 dpi (representative confocal microscopy images shown). (B) Quantification shows that dram1 overexpression increased Mm/GFP-Lc3 colocalization independent of optn and p62. Complete or partial overlap of GFP-Lc3 with Mm was considered as co-localizing events. Data are displayed as percentage of GFP-Lc3-positive Mm clusters relative to the total number of Mm clusters and are accumulated from three independent infection experiments, of which the data points (each representing a single ROI from an individual embryo) are indicated with different colors. (C) Quantification shows that dram1 overexpression increased Mm and LysoTracker colocalization independent of optn and p62. Complete or partial overlap of LysoTracker with Mm was considered as co-localizing events. Data are accumulated from three independent experiments (each data point representing a single ROI from an individual embryo)* p<0.05, ** p<0.01.
|

