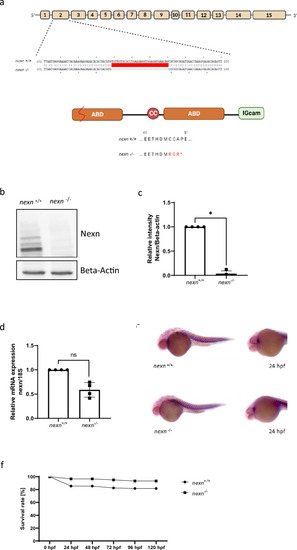
Generation of zebrafish nexn knockout by CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing. (a) Structure of the nexn gene and protein. Nexn consists of a central coiled coil domain (CC) flanked by two actin-binding domains (ABD) and a C-terminal immunoglobulin superfamily class (IGcam). The deletion of 32 nucleotides in exon 2 by CRISPR/Cas9 editing leads to a frameshift and premature stop codon, and thereby to a termination of the Nexn translation after 49 amino acids within the first actin-binding domain. (b,c) Immunoblot and quantification of protein lysates of nexn−/− embryos showing reduced Nexn protein levels compared to nexn+/+ embryos at 72 hpf (N = 4, mean ± SD, p < 0.0286 using Wilcoxon test); original blot shown in Supplementary Fig. S1. (d) Quantitative real-time PCR of nexn−/− embryos showing similar nexn mRNA levels compared to nexn+/+ embryos at 72 hpf (N = 4, mean ± SD, p = 0.149 using Wilcoxon test). (e) in situ hybridization shows nexn expression in heart and skeletal muscle at a similar level in nexn−/− and nexn+/+ embryos at 24 hpf (N = 3, n = 15). (f) nexn+/+ and nexn−/− embryos do not show differences regarding survival rate at any developmental stage (N = 3 with a total number of 87 and 62 embryos, respectively, mean). ns not significant, *p < 0.05.
|

