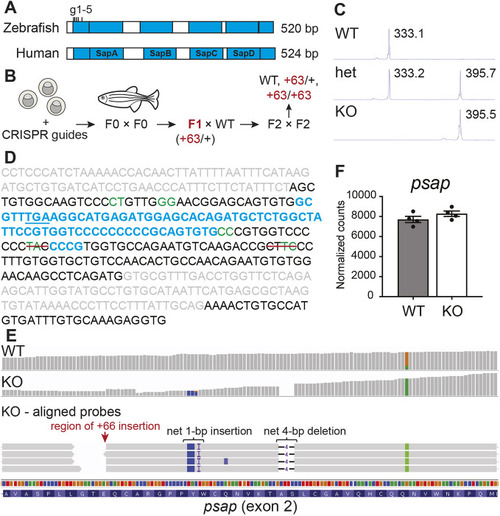
A zebrafish model of combined saposin deficiency. (A) Comparison between human (UniProt: P07602) and zebrafish (UniProt: B8JI17) saposin (blue) domains (detailed amino acid sequence alignment can be found in Fig. S1). CRISPR-Cas9 guide sites (located within exon 2) are indicated. (B) Schematic of combined saposin deficiency model generation in the zebrafish. (C) DNA fragment analyses of psap PCR fragments from WT and mutant zebrafish, demonstrating the presence of a net 63-bp insertion in the mutant sample. (D) Summary of Sanger sequencing results. Exon sequences are in black, intron sequences are in gray, predicted Cas9 cut sites are in green, insertions are in blue, and red lines indicate deletions. The in-frame stop codon (TGA) generated within the largest insertion sequence is underlined. Detailed Sanger sequencing data are in Fig. S1. (E) RNA sequencing probe alignments around the Cas9-targeted region in 4 mpf psap+63/+63 and WT sibling brains, demonstrating preservation of the mutations detected at the genomic DNA level. (F) psap mRNA is not degraded based on RNA sequencing of 4 mpf psap+63/+63 (n=4) and WT (n=4) sibling brains. Data show the mean±s.e.m.
|