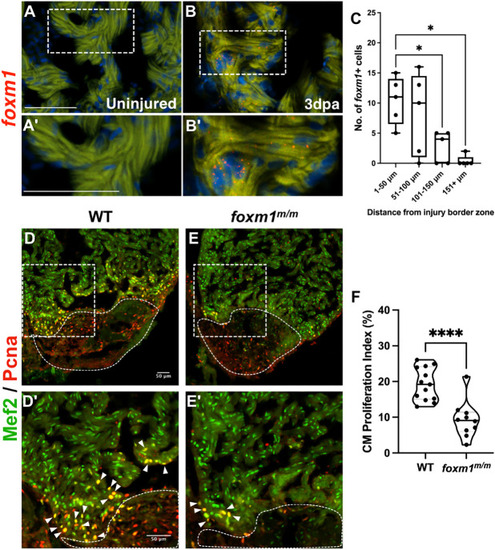
Loss of foxm1 significantly limits cardiomyocyte proliferation after ventricular resection. (A-B?) Fluorescence in situ hybridization revealed foxm1 (red) is not expressed in the uninjured myocardium (A,A?) but is detected in border zone cardiomyocytes after injury (B,B?). The myocardium is marked by 488 nm as background fluorescence. (C) foxm1+ cardiomyocytes were localized within 100 Ám from the injury and expression decreased distal to the wound. Box plots show minimum to maximum. The whiskers show the minimum and up to the maximum value, with the middle line representing the median. Each point represents foxm1+ cardiomyocytes from each heart with respect to distance from the border zone. Each point is representative of an individual heart (n=5). (D-E?) WT (D,D?; n=13) and foxm1m/m (E,E?; n=10) hearts at 7 dpa stained for the cardiomyocyte nuclei marker Mef2 (green) and proliferation marker Pcna (red). White dotted lines represent the injury border. Arrowheads indicate proliferating cardiomyocytes. (F) Cardiomyocyte proliferation index is significantly decreased in foxm1m/m hearts. Each point on the truncated violin plot represents an individual heart and these data represent three biological replicates. The middle line represents the median. Statistical significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA multiple comparison test. *P<0.05, ****P<0.0001. A?,B?,D?,E? show magnified images of boxed areas in A,B,D,E, respectively. Scale bars: 50 ?m.