FIGURE
Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-220905-17
- Publication
- Waldmann et al., 2021 - The role of Gdf5 in the development of the zebrafish fin endoskeleton
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
Fig. 1
|
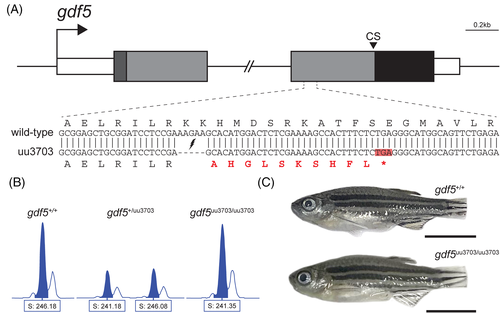
Zebrafish gdf5 knockout generated with CRISPR/Cas9. (A) To-scale schematic of the two-exon gdf5 gene locus on chromosome 6, with the 4267 bp intron truncated. White boxes represent the 5′ and 3′ UTRs, the dark grey box represents the sequence coding for the 22 aa signal peptide, the light grey boxes represent the sequences coding for the rest of the prodomain (334 aa), and the black box represents the sequence coding for the 118 aa mature domain. “CS” indicates the position of the 5 aa cleavage site. The sequence of the zoomed in section of exon 2 shows the alignment between the wild-type and mutant (uu3703) alleles. The mutant allele has a 5-base deletion that results in a frameshift and a premature stop codon highlighted in red. (B) Wild-type, heterozygous gdf5+/uu3703, and homozygous gdf5uu3703/uu3703 fish were identified by fragment length analysis. The wild-type displayed one peak (246.18), gdf5+/uu3703 displayed one wild-type peak (246.08) and one mutant peak (241.18), and gdf5uu3703/uu3703 displayed one mutant peak (241.35). (C) At 60 dpf there is no outward phenotypic difference between gdf5uu3703/uu3703 and wild-type (caudal fins were clipped for genotyping). Scale bars: 5 mm
|
Expression Data
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Days 45-89 |
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Dev. Dyn.