Fig. 7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-220307-21
- Publication
- Gao et al., 2022 - Pluripotency factors determine gene expression repertoire at zygotic genome activation
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
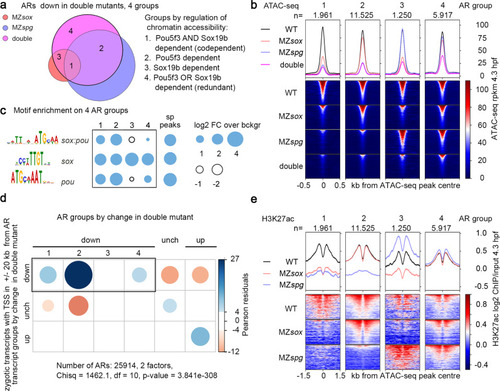
Codependent, Pou5f3-dependent, and redundant cis-regulatory elements regulate the major ZGA wave.
a Venn diagram: 20653 ?down? ARs (regions where chromatin accessibility was reduced in the double mutant) were subdivided to groups 1?4 by reduction of chromatin accessibility in the single mutants. b ATAC-seq signals on AR groups 1?4 in the wild type, single and double mutants. ARs were sorted by descending ATAC-seq peak score. c Enrichment for sox:pou, sox and pou motifs in AR groups 1?4 compared to the regions bound by Pou5f3 and SoxB1 (sp peaks). d Chi-squared test. Codependent(1), Pou5f3-dependent (2), and redundant (4) ARs, but not Sox19b-dependent ARs, are enriched around Transcription Start Sites (TSS) of zygotic genes, downregulated in MZsox19bspg double mutant. P-value is two-tailed. e H3K27ac on 4 AR groups depends on the same TFs as accessibility (compare with ATAC-seq in b). (1) codependent ARs: Pou5f3 and Sox19b are required for H3K27ac, (2) Pou5f3-dependent ARs: Pou5f3 is required for H3K27ac, (3) Sox19b-dependent ARs: Sox19b is required for H3K27ac, (4) redundant ARs: any factor is sufficient for H3K27ac, no reduction in the single mutants. ARs were sorted by descending ATAC-seq peak score. MZsox = MZsox19b, double = MZsox19bspg, n number of regions in each group. Source data for a?c, and e are provided as a Dataset S3. Source data for c are provided as Dataset S4. Source data for d are provided as Dataset S5. |