Fig 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-220307-1
- Publication
- Habicher et al., 2022 - Chondroitin/dermatan sulfate glycosyltransferase genes are essential for craniofacial development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
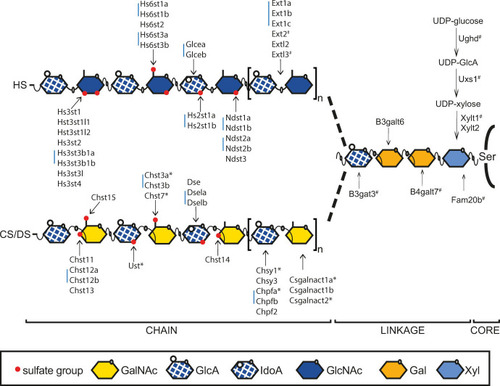
Heparan sulfate (HS) and chondroitin/dermatan sulfate (CS/DS) biosynthesis in zebrafish.
HS and CS/DS chains are attached to serine (Ser) residues of the core protein. The first four monosaccharides form the linkage region of both HS and CS/DS. Extl3 initiates HS polymerization, while Csgalnact1a and Csgalnact2 perform this function in CS/DS polymerization. Elongation of HS is carried out by Ext enzymes, while Chsy and Chpf enzymes polymerize the CS/DS chain. The first modification of HS is carried out by Ndst enzymes, replacing an N-acetyl groups of GlcNAc residues with an N-sulfate group. Glcea and Glceb epimerize GlcA into IdoA in HS, while Dse, Dsela and Dselb are responsible for this modification in DS. Hs2st enzymes add a sulfate groups to the IdoA C-2 position of HS and Hs6st and Hs3st enzymes add sulfate groups to the GlcNAc or GlcNS residues. Ust adds a sulfate group to the hexuronic acid C-2 position of CS/DS while Chst11, Chst12a, Chst12b, Chst13 and Chst14 are GalNAc 4-O-sulfotransferases while Chst3a, Chst3b, Chst7 and Chst15 are GalNAc 6-O-sulfostransferases. Blue bars indicate two or three zebrafish genes orthologous to a single mammalian gene. Ndst3 in zebrafish is a single gene orthologous to two mammalian genes (NDST3 and NDST4). # Indicates previously published mutant zebrafish alleles while * indicates the targeted mutations reported in this study. Xyl: xylose, Gal: galactose, GlcNAc: N-acetylglucosamine, IdoA: iduronic acid, GlcA: glucuronic acid, GalNAc: N-acetylgalactosamine. |