FIGURE 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-211118-4
- Publication
- Xu et al., 2021 - Overexpression of Lifeact-GFP Disrupts F-Actin Organization in Cardiomyocytes and Impairs Cardiac Function
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
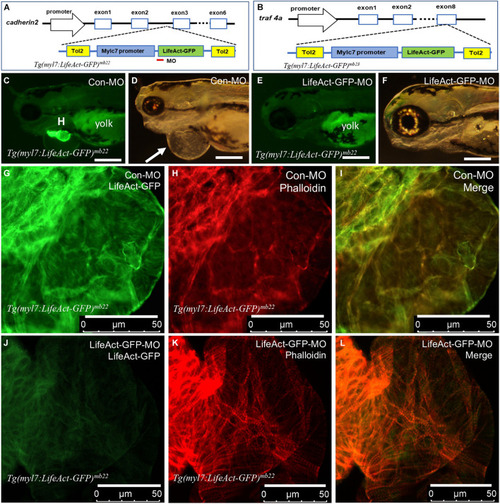
Identification of transgene integration sites in Tg(myl7:Lifeact-GFP)mb22 and Tg(myl7:Lifeact-GFP)mb23 transgenic embryos and the rescue of heart defect by knockdown of Lifeact-GFP expression. (A,B) Mapping the transgene integration sites in Tg(myl7:Lifeact-GFP)mb22 and Tg(myl7:Lifeact-GFP)mb23 transgenic embryos at cadherin2 and traf4a genes, respectively. The Lifeact-GFP-MO is indicated by the red line. (C?F) Morphology of heart region of Tg(myl7:Lifeact-GFP)mb22 transgenic embryos at 72 hpf injected with control-MO (C,D) and Lifeact-GFP-MO (E,F), respectively. Pericardial edema is indicated by the arrow in control-MO injected Tg(myl7:Lifeact-GFP)mb22 (D) transgenic mutant larvae. H, heart; Yolk shows autofluorescence. Scale bars: 250 ?m. (G?L) Lifeact-GFP expression (G,J) and phalloidin staining (H,K) showing actin think filaments in cardiomyocytes of Tg(myl7:Lifeact-GFP)mb22 transgenic embryos injected with control-MO (G?I) or Lifeact-GFP-MO (J?L) at 72 hpf transgenic embryos. (I,L) are merged pictures of (G,H,J,K), respectively. Scale bars: 50 ?m. |