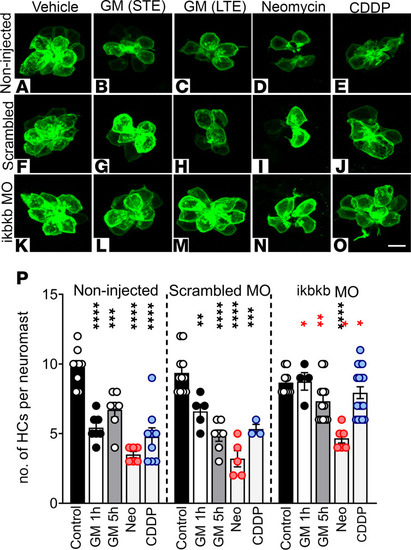
Reduction of I?K? expression protects against aminoglycoside- and CDDP-induced ototoxicity. (A?O) Tg(brn3c:GFP) zebrafish eggs were noninjected (A?E) or injected with a suboptimal dose (2 ng) of scrambled (F?J) or ikbkb morpholinos (MO) (61) (K?O). At 3 dpf animals were incubated with gentamicin (GM) 100 ?M STE (B, G, and L) or LTE (C, H, and M), neomycin (Neo) 200 ?M (D, I, and N), or CDDP 400 ?M (E, J, and O). Animals were fixed and immunostained for GFP. The number of hair cells per neuromast was quantified (P). Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis: 1-way ANOVA with correction for Dunnett?s multiple comparisons test. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001 versus the corresponding control within the group (black asterisks). Two-tailed Student?s t test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 versus identical treatment in scrambled animals (red asterisks). Number of neuromasts inspected: control = 8 (noninjected), 12 (scrambled MO), 10 (I?K? MO); GM-STE = 7 (noninjected), 5 (scrambled), 4 (ikbkb MO); GM-LTE = 7 (noninjected, scrambled), 12 (ikbkb MO); Neo = 6 (noninjected, ikbkb MO), 5 (scrambled); CDDP = 9 (noninjected), 3 (scrambled), 12 (ikbkb MO). Scale bar: 6 ?m.
|

