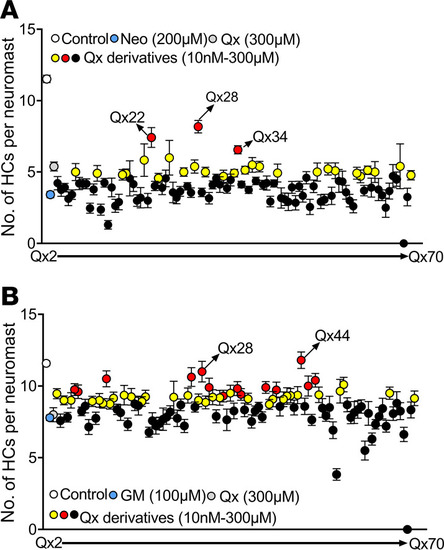
Screening of quinoxaline derivatives. Five dpf Tg(brn3c:GFP) zebrafish were preincubated with quinoxaline (Qx, 300 ?M) or its derivatives (Qx2?Qx70, 10 nM?300 ?M) for 1 hour, followed by coincubation with neomycin (Neo) 200 ?M for 30 minutes (A) or gentamicin (GM) 100 ?M long-term effect (B). Hair cells were quantified employing a Zeiss AxioSkop 2 fluorescence microscope with a 40× oil objective. White dot, vehicle; blue dot, ototoxin alone; gray dot, quinoxaline 300 ?M. Black dots, quinoxaline derivatives that did not show any significant differences compared with ototoxin alone. Yellow dots, quinoxaline derivatives that performed significantly better than ototoxin alone but not significantly different from quinoxaline treatment. Red dots, quinoxaline derivatives that performed significantly better than quinoxaline treatment. Results were expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis: 1-way ANOVA with correction for Dunnett?s multiple comparisons test. Significance was set at P < 0.05 versus ototoxin or quinoxaline. Six fish were used per treatment, and 3 neuromasts were inspected per fish (n = 18).
|

