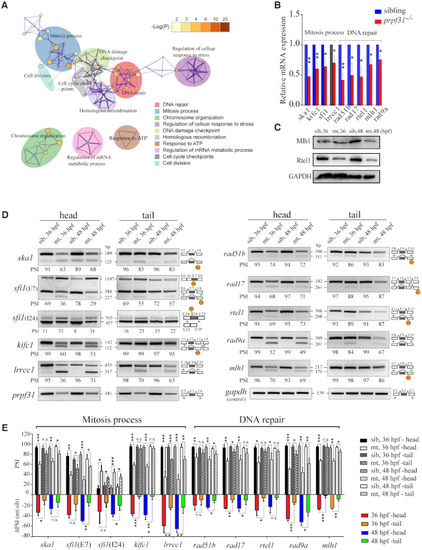
Prpf31 modulates the alternative splicing of a subset of genes involved in DNA repair and spindle assembly. (A) Significantly overrepresented (P < 0.05, enrichment score ≥ 2) DNA repair and mitosis process- associated biological process among upregulated IR and ES DSEs as determined by GO functional enrichment analysis. The top 10 biological process affected by DS events were shown. Node size and color correspond with enrichment score and log(P) value, respectively. (B) The mRNA levels of some genes were significantly down-regulated among DNA repair and mitosis process in RPCs, as detected by RT-PCR. (C) Western blot showed the protein expression of genes with altered splicing efficiency in (B). (D) Increased proportion of transcripts with IR and/or ES among DNA repair and mitosis process in RPCs, as detected by PCR. Sizes (in bp) for major and minor mRNA isoforms (black lines). Head, tail, template cDNA was obtained from the head parts or tail parts of the embryos respectively. PSI values, marked below the DNA band; the black arrows indicate the primers used in this experiment; Hexagon, There was a premature termination codon (PTC) in the corresponding isoforms. (E) Statistical analysis presented as the mean ± SD of PSI values and ΔPSI in two types tissues at 36 and 48 hpf from three biological replicates. PSI, percent splicing in; ΔPSI, the mutant PSI value subtract the wild-type PSI value was used to evaluate the changed extent in pre-mRNAs splicing efficiency after prpf31 knockout.
|

