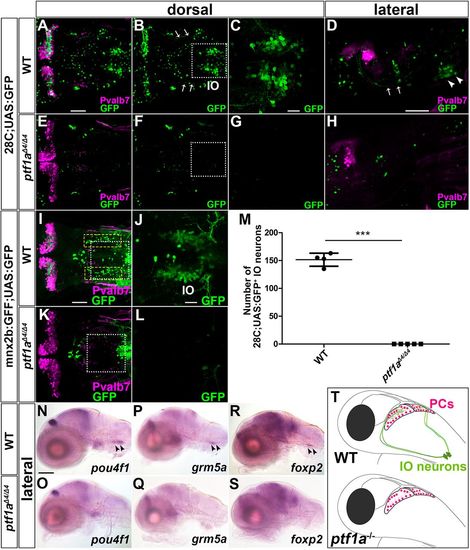
Loss of IO neurons in ptf1a mutants. (A-H) 5 dpf wild-type (A-D, n=5) and ptf1a?4/?4 (E-H, n=5) 28C;UAS:GFP larvae were immunostained using anti-Pvalb7 (magenta) and anti-GFP (green) antibodies. Arrows and arrowheads indicate CFs and IO neurons, respectively. (C,G) Higher magnification of the boxes in B and F. (I-L) 5 dpf wild-type (I-J n=2) and ptf1a?4/?4 (K-L n=4) mnx2b:GFF;UAS:GFP larvae. GFP+ cells in the yellow dotted boxes were fewer or absent in ptf1a?4/?4 larvae. (J,L) Higher magnification of the boxes in I and K. (M) Number of 28C;UAS:GFP+ IO neurons in wild-type and ptf1a?4/?4 larvae. 28C;UAS:GFP+ IO neurons were significantly reduced in ptf1a mutant larvae compared with control larvae. ***P<0.001 (Student's t-test). Data are mean▒ s.e.m. with individual values indicated. (N,O) Expression of pou4f1 in 5 dpf wild-type (n=4) and ptf1a?4/?4 (n=4) larvae. (P,Q) Expression of grm5a in 5 dpf wild-type (n=4) and ptf1a?4/?4 (n=3) larvae. (R,S) Expression of foxp2 in 5 dpf wild-type (n=5) and ptf1a?4/?4 (n=5) larvae. (T) Illustration of Purkinje cells and IO neurons in wild-type and ptf1a mutant larvae. Scale bars: 100?Ám in N (applies to N-S); 50?Ám in A (applies to A,B,E,F), D (applies to D,H) and I (applies to I,K); 20?Ám in C (applies to C,G) and J (applies to J,L).
|

