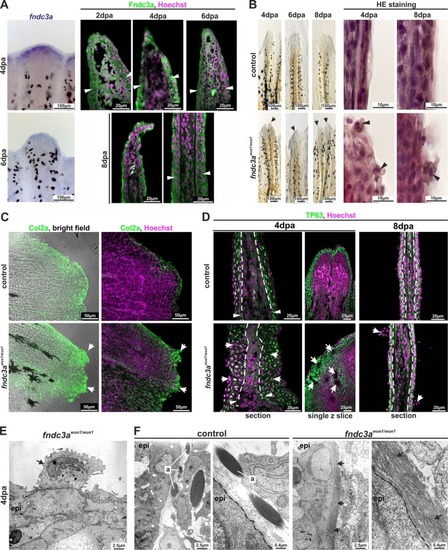
Interference with Fndc3a function during fin regeneration results in epidermal cells defects. (A) Expression of fndc3a and localization of Fndc3a in regenerates could be detected in epidermal cell layers. (B) Phenotypical and histological investigations of fin regeneration in fndc3awue1/wue1 mutants indicated abnormal regeneration by showing unorganized fin borders at the regenerative front and aberrant epidermal cells (arrows; abnormal regenerate phenotypes, control: 3/19; fndc3awue1/wue1: 13/19). (C) Col2a protein localization visualized via immunofluorescence on 8 dpa regenerates showed accumulation of collagen in abnormal cells of fndc3awue1/wue1 mutants (white arrows; n = 6 for each group). (D) TP63 staining in regenerates of fndc3awue1/wue1 mutants 4 and 8 dpa indicated disorganization of epidermal cells (arrows indicate epidermal thickening, cavities within the regenerate and abnormal cells; n = 4 for each group). (E) TEM analysis showed accumulation of electron dense material in the Golgi apparatus of abnormal cells attached to the epidermal layer (arrow). (F) TEM analyses of actinotrichia in fin regenerates 4 dpa revealed loss of these fibers located near the basal membrane of epidermal cells in fndc3a depleted fish (arrows). Arrowheads indicate amputation site. a: actinotrichia; epi: epidermis; dashed lines indicate basal membrane boundary.
|

