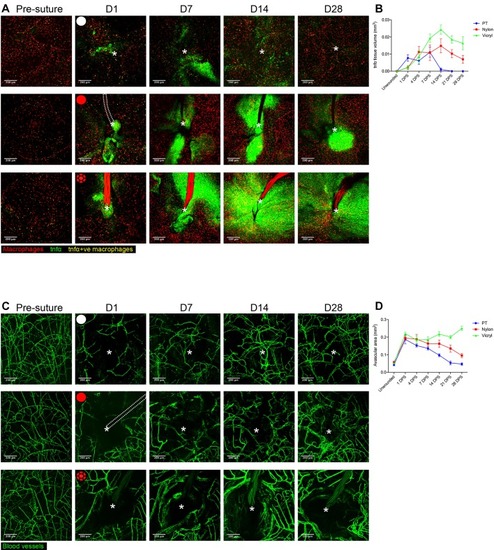
Extent of tnfα expression and size of avascular zone are dependent on suture type. (A) Representative images of Tg(tnfα:GFP); Tg(mpeg:mCherry) double transgenic zebrafish immediately prior to and following suture pull through (PT; top row, white circle), or implantation of nylon (middle row, red circle) or vicryl suture (bottom row, red braided circle), at indicated time points, showing macrophages (red), pro-inflammatory macrophages (yellow) and stromal cells expressing tnfα in the vicinity of the wound/suture zone (green). The area of wounding or implantation is marked by a white asterisk; dotted lines indicate nylon suture. n=8 independent fish per condition. (B) Quantification of the mean±s.d. total inflammatory area surrounding the wound/suture, measured from images in A. (C) Representative images of Tg(fli:GFP) transgenic zebrafish immediately prior to and following suture pull through (top row, white circle), or implantation of nylon (middle row, red circle) or vicryl suture (bottom row, red braided circle), to reveal angiogenic response at the indicated timepoints. The area of wounding or implantation is marked by a white asterisk; the dotted lines indicate nylon suture. n=8 independent fish per condition. (D) Quantification of the mean±s.d.extent of avascular zone immediately adjacent to wound/suture, measured from images in C. Scale bars: 200 μm.
|