Fig. S7
|
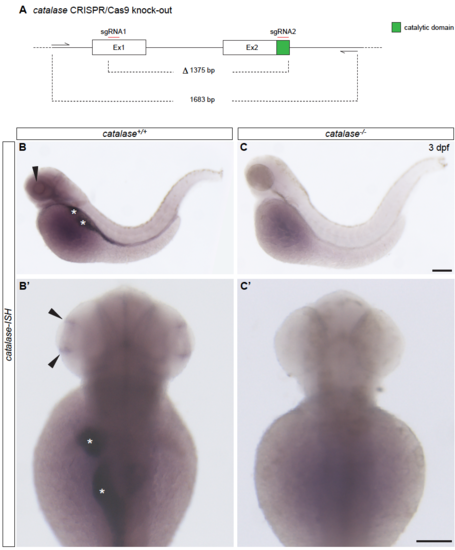
Generation of the zebrafish catalase-/- null-mutant CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing, related to Figure 7. (A) Schematic representation of the first two exons of the catalase gene. Exon 2 contains the catalytic domain of the protein. Each exon was targeted by a sgRNA. In particular, the catalytic site in Exon 2 was targeted by one of the 2 chosen gRNA in order to efficiently disrupt it. The CRISPR/Cas9 induced mutation led to the deletion of a total of 1375 base pairs (bp), causing the removing of the catalytic domain and a frame shift in the following exon that led to the appearance of premature stop codons. (B – C’) The generated mutation caused a non-sense mediated decay of catalase mRNA as shown by in situ hybridization. In contrast to catalase+/+ embryos, no signal could be detected in catalase-/- at 3 dpf in the ciliary marginal zone (black arrows), in the gut and liver (white asterisks). Scale bars, 100 μm. |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 50(1), Albadri, S., Naso, F., Thauvin, M., Gauron, C., Parolin, C., Duroure, K., Vougny, J., Fiori, J., Boga, C., Vriz, S., Calonghi, N., Del Bene, F., Redox Signaling via Lipid Peroxidation Regulates Retinal Progenitor Cell Differentiation, 73-89.e6, Copyright (2019) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell