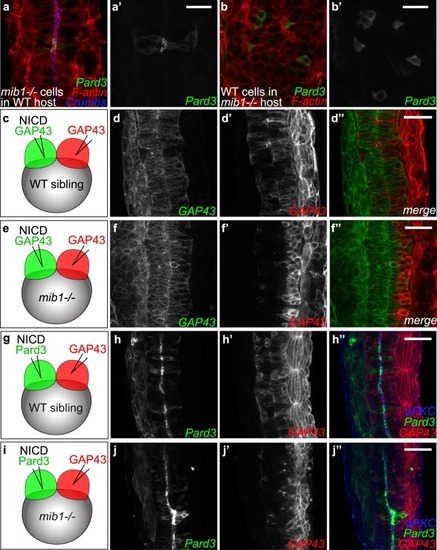
Dissection of the spatial requirement for Notch signaling in neural tube morphogenesis. (a,a’) Pard3-GFP expressing mib1 mutant cells undergo correct polarization when transplanted into WT hosts (n = 30 cells in 6 embryos). (b,b’) In contrast, Pard3-GFP expressing WT cells fail to polarize when transplanted into mib1 mutant hosts (n = 96 cells in 13 embryos). (a,b) are single confocal sections, (a’,b’) maximum projections of 5 slices separated by 2 µm intervals to visualize GFP-positive clones. (c-f) The two halves of the neural tube were labelled by injecting RNAs encoding red or green fluorescent membrane labels (GAP43) into the 2 blastomeres of 2-cell stage embryos (see Methods). (c,d) In WT sibling embryos half-injected with RNA encoding constitutively activated Notch (NICD), cells originating from both sides of the neural tube cross the neural tube midline to integrate the contra-lateral organ half (n = 7/7). (e,f) If NICD is half-injected into mib1 mutants, NICD-containing cells display extensive midline crossing (f,f”), while the crossing of NICD-negative cells is reduced in 6/8 embryos (f’,f”). (g–j) One half of the embryo was injected with RNA encoding NICD Pard3-GFP, the other half with GAP43-RFP. (g,h) 6/6 WT sibling embryos display apical Pard3 accumulation (h) and bilateral midline crossing (h,h’). (i,j) In mib1 mutants, NICD causes apico-basal polarization and midline crossing of Pard3-GFP positive cells in 6/6 embryos (j). NICD-negative GAP43-RFP positive cells fail however to cross the neural tube midline in 5/6 embryos (j’). Pictures represent dorsal views of the spinal cord (anterior up) at 30 somites (a,b), 18 somites (d,f) and 21 somites (h,j) stages. Scalebars: a,b 20 µm, (d,f,h,j) 40 µm.
|

