Fig. S4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-181130-6
- Publication
- Bertuzzi et al., 2018 - Adult spinal motoneurons change their neurotransmitter phenotype to control locomotion
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
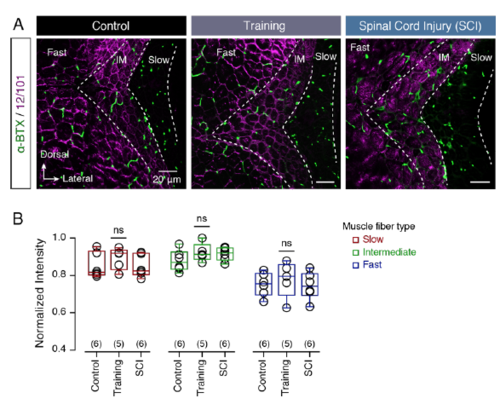
Neuromuscular junctions remain the same after training and spinal cord injury. (A) Representative transverse confocal images from adult zebrafish myotome (purple) showing the location and the number of the neuromuscular junctions (α-BTX; green) in control and after physical exercise and spinal cord injury. (B) Quantification of the normalized intensity of the α-BTX staining in slow, intermediate and fast muscle fibers show no significant changes following training and spinal cord injury. Data are presented as boxplots showing the median, 25th and 75th percentile (box and line), minimal and maximal values (whiskers), mean ± SEM; ns, non-significant; IM, intermediate. For detailed statistics see SI Appendix, Table S1. |